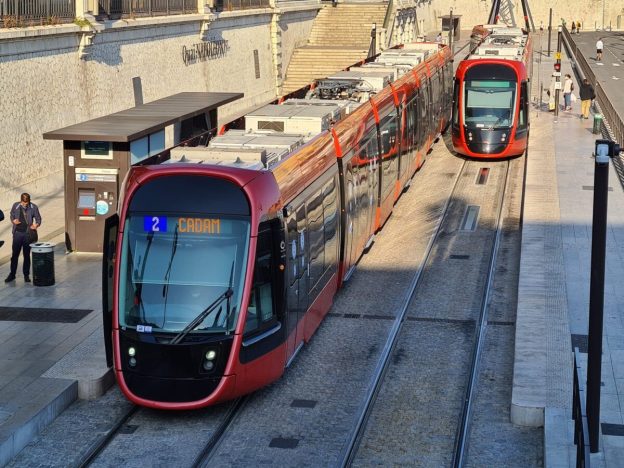
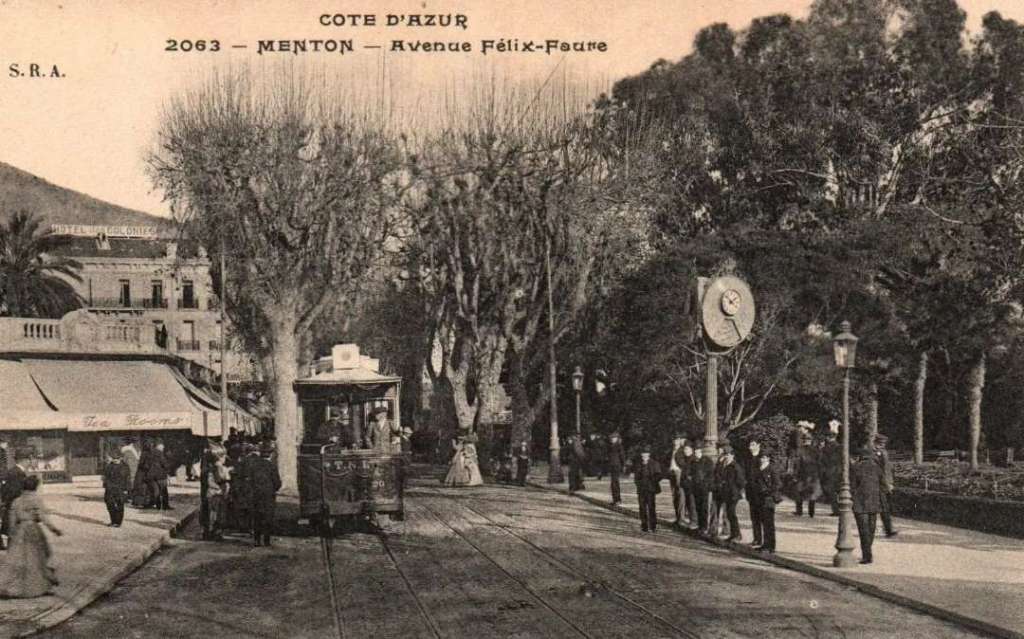
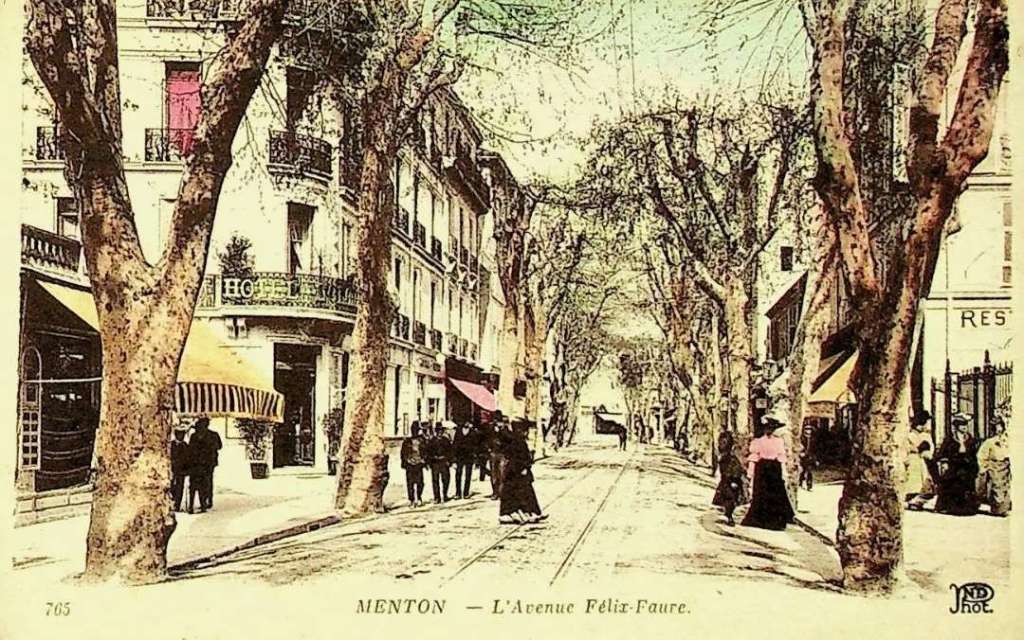
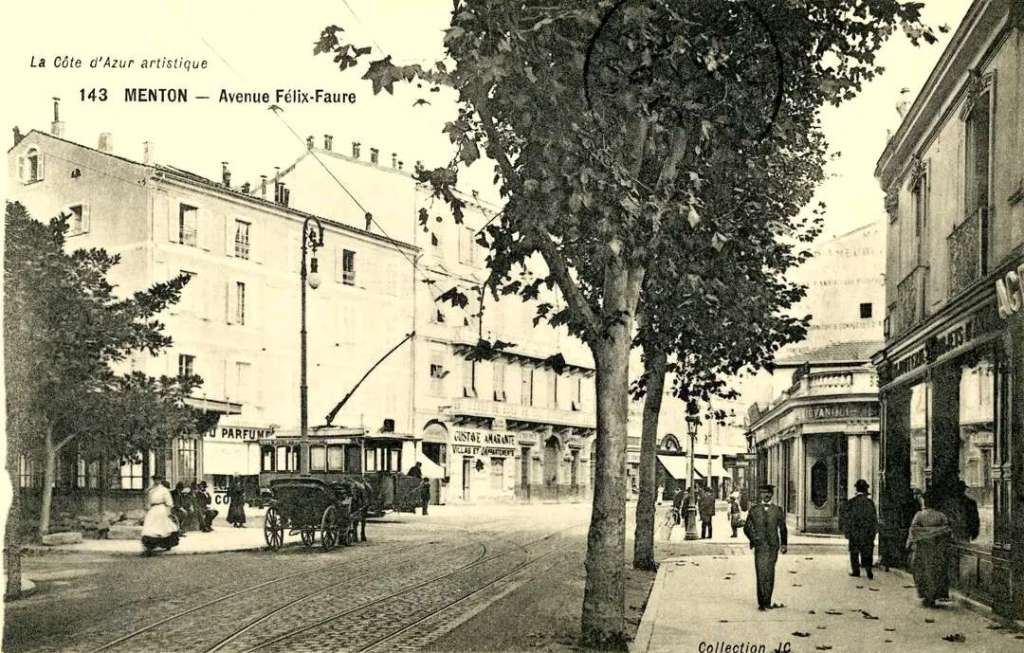
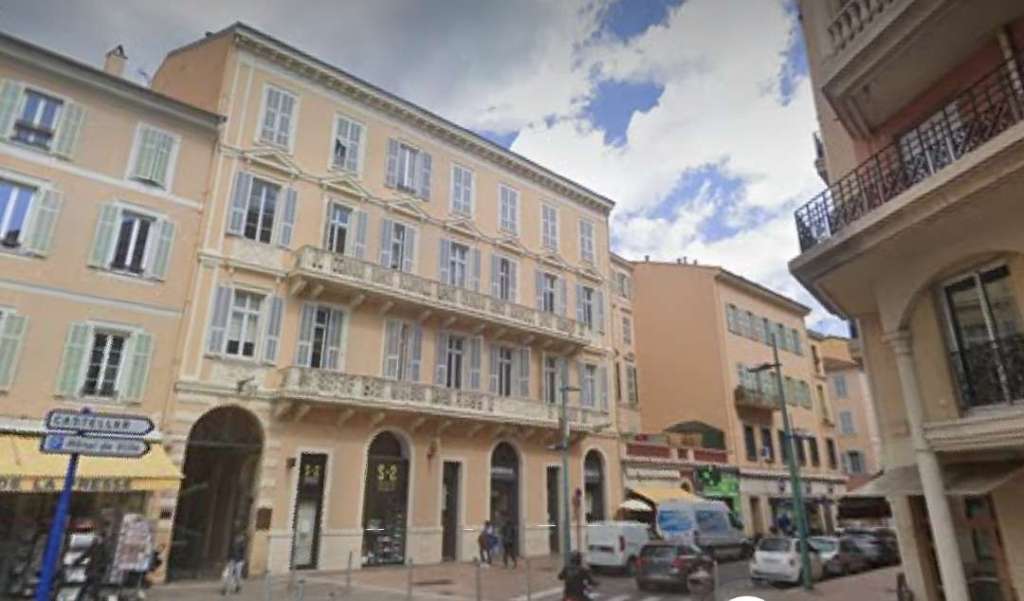
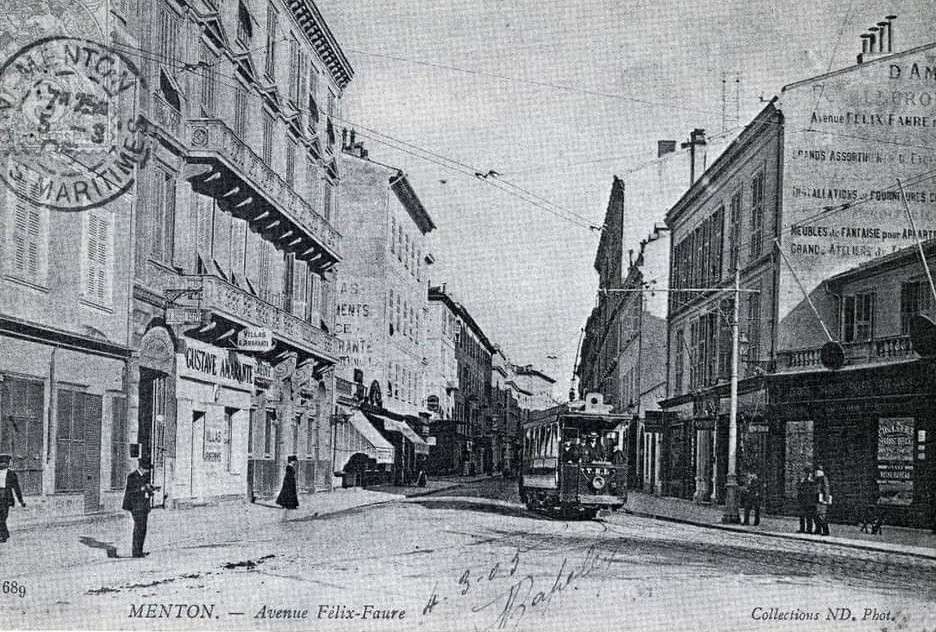
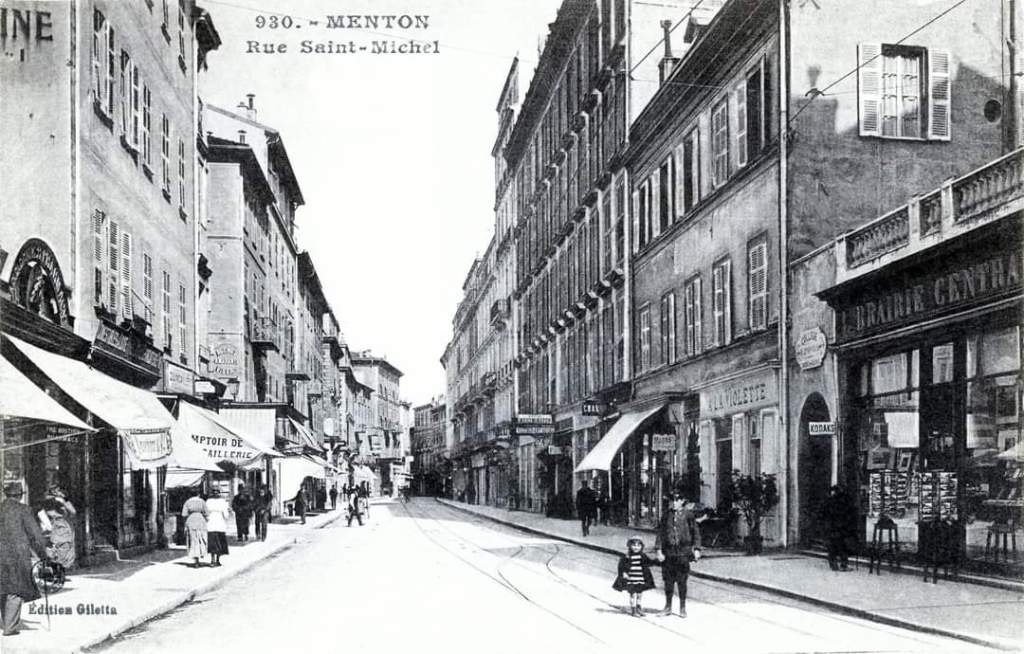
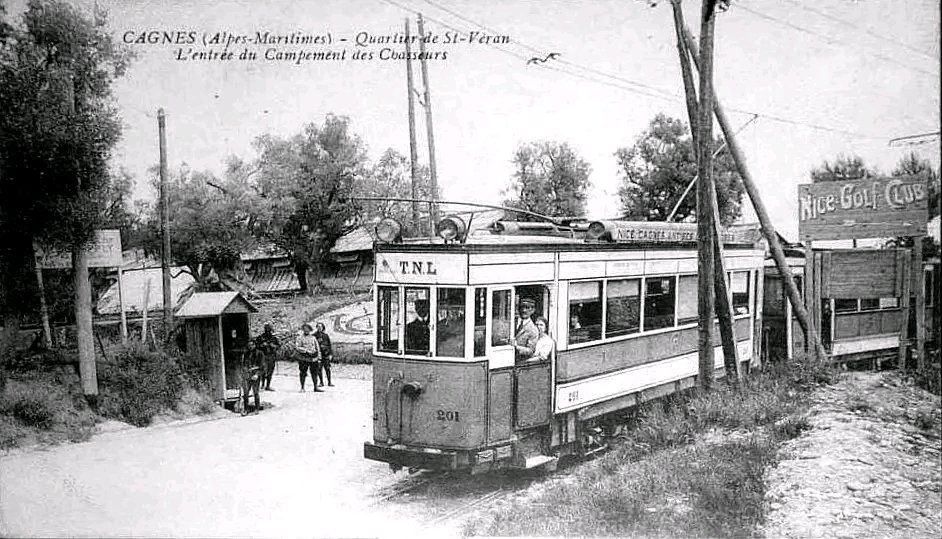
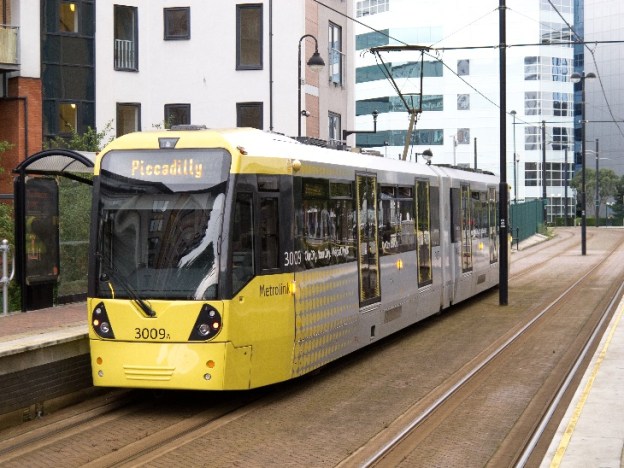
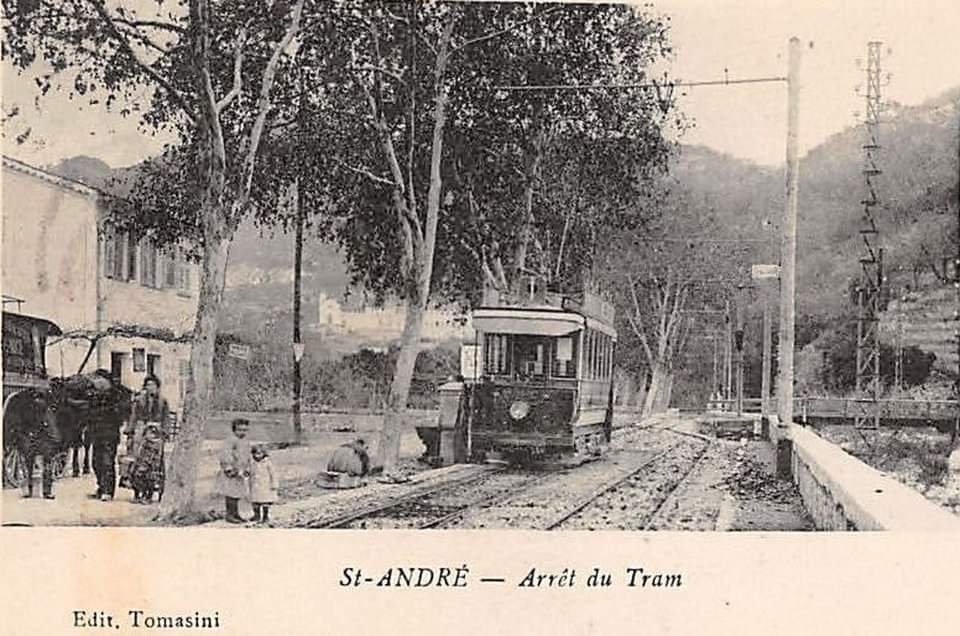
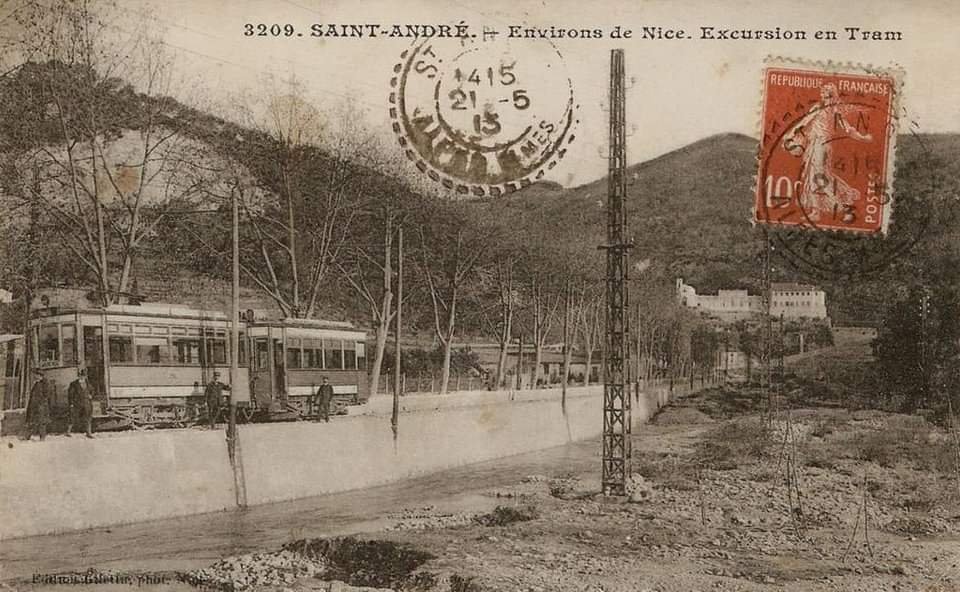
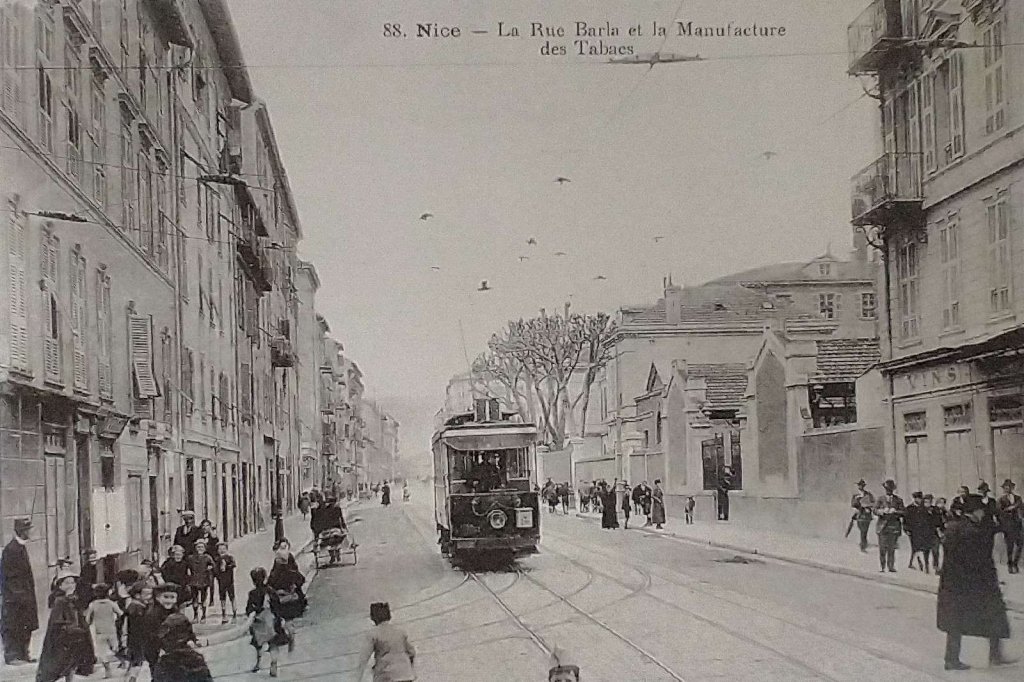
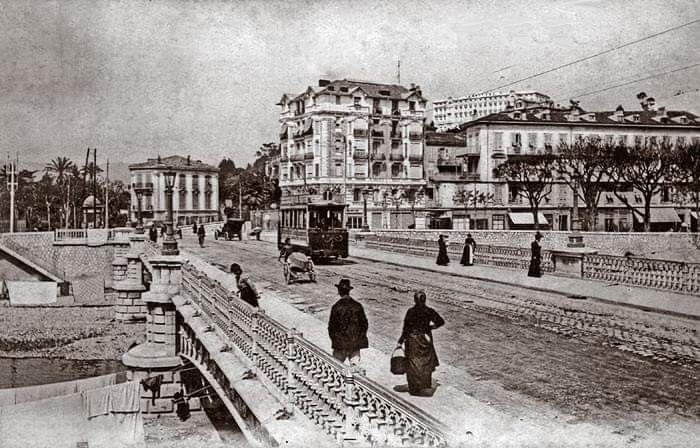
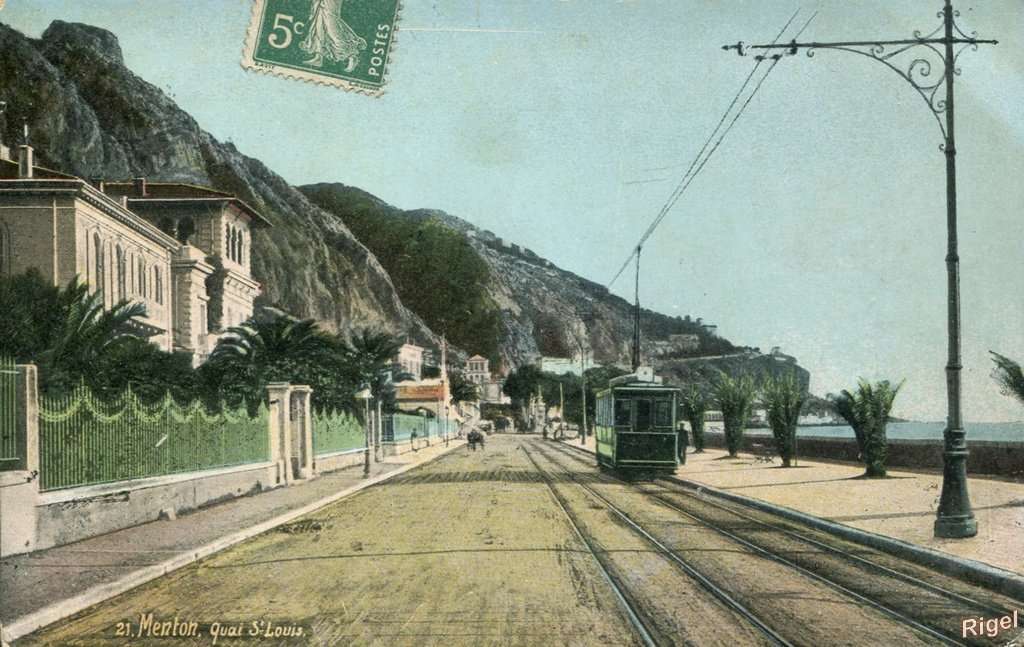
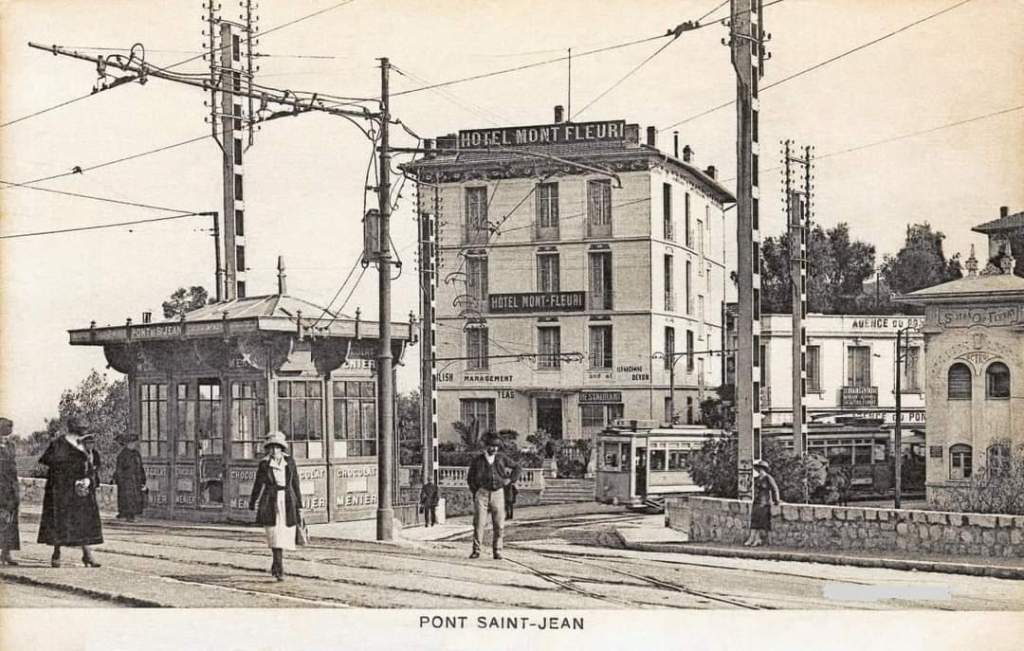
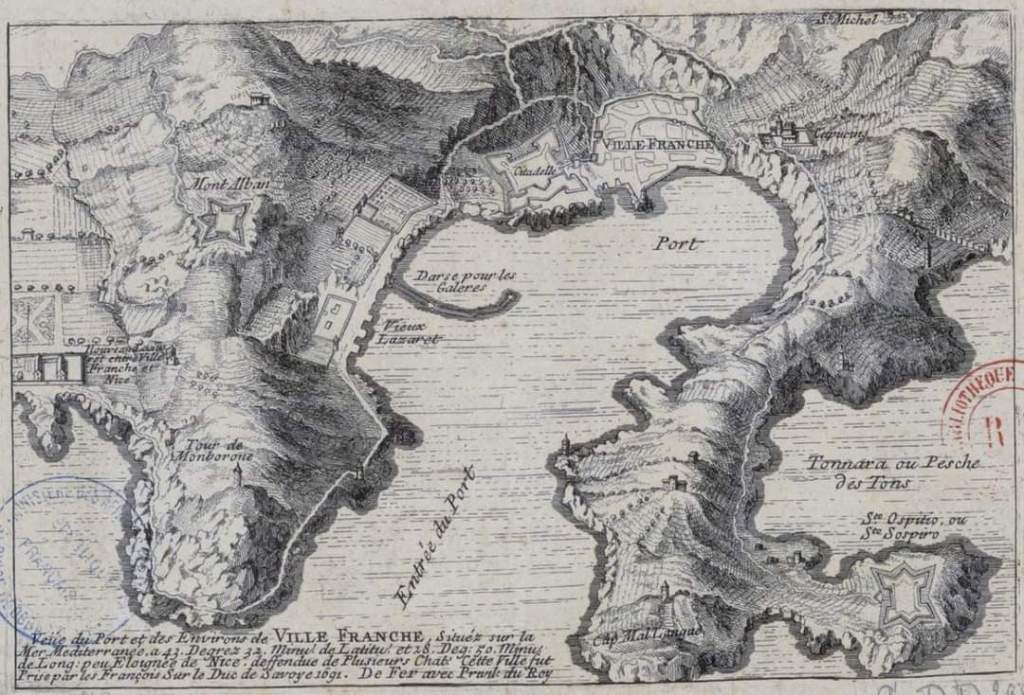
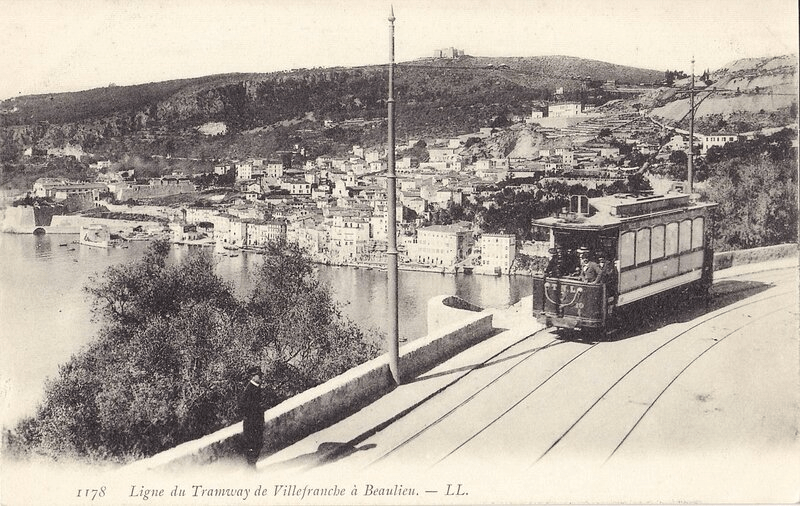
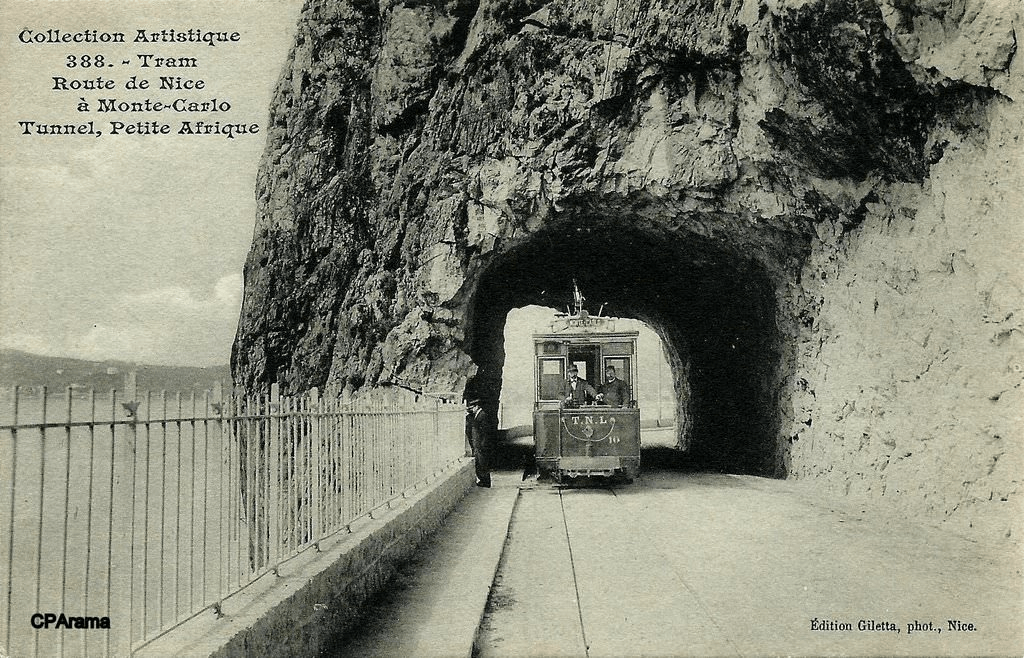
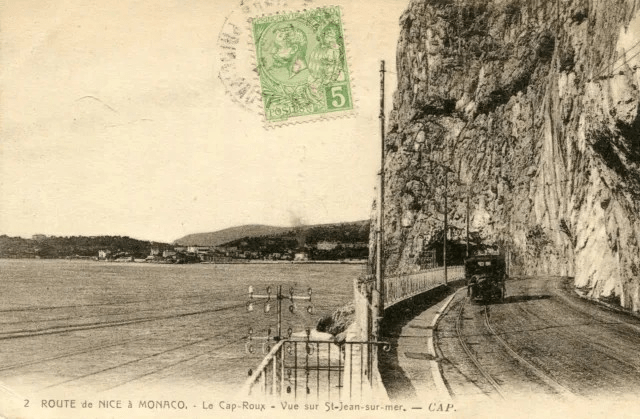
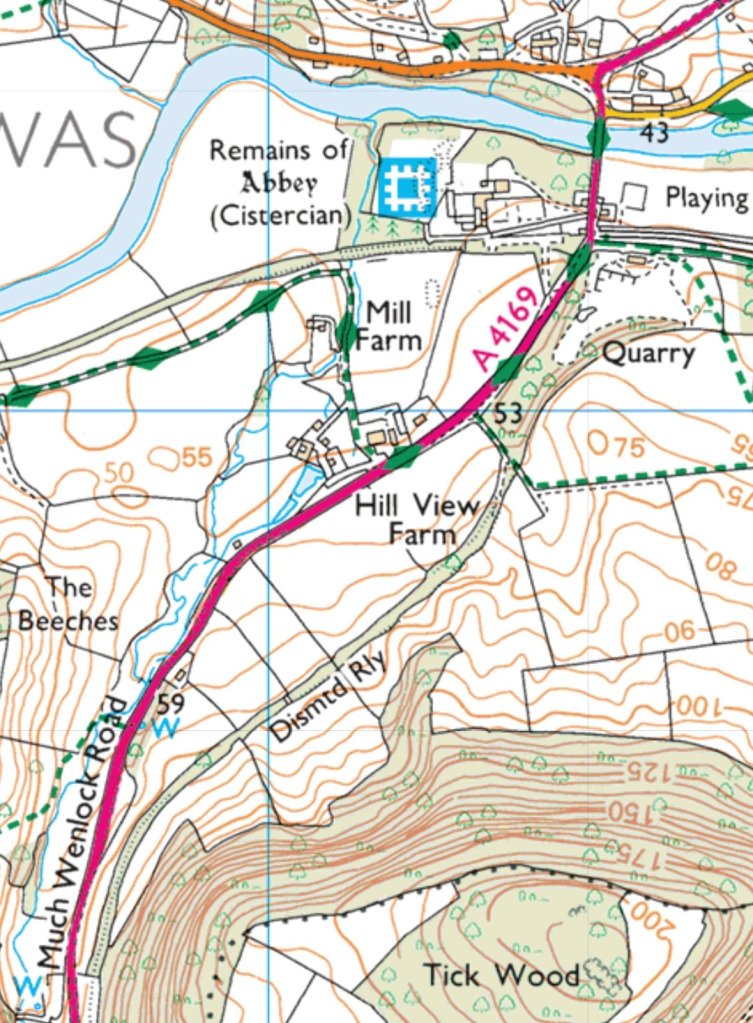
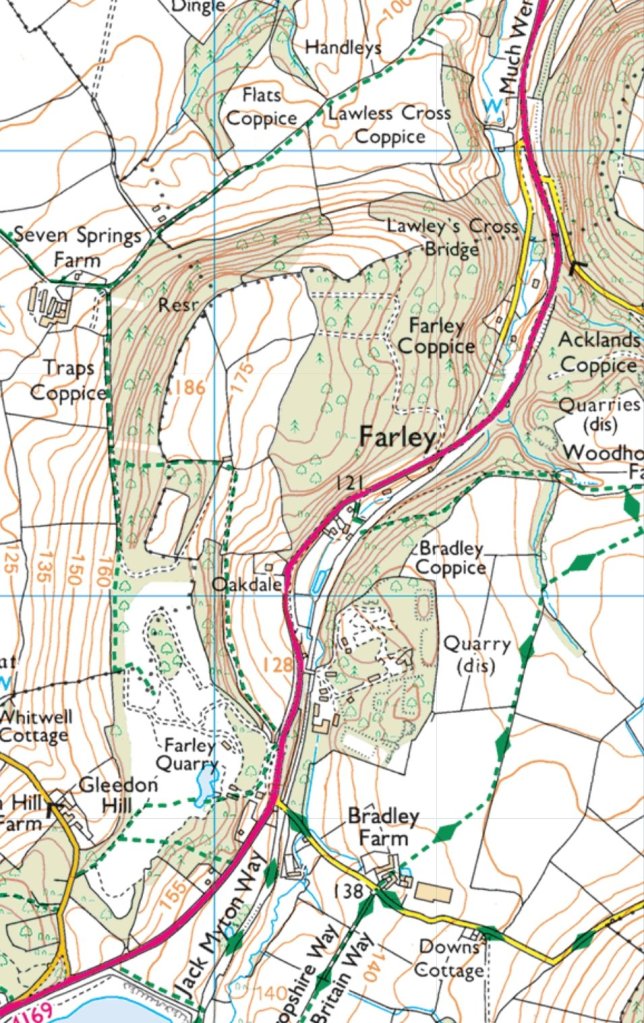
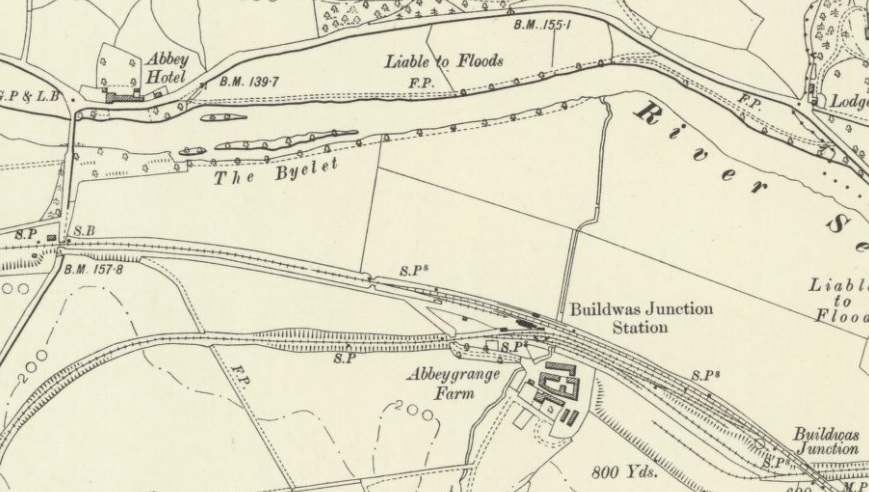
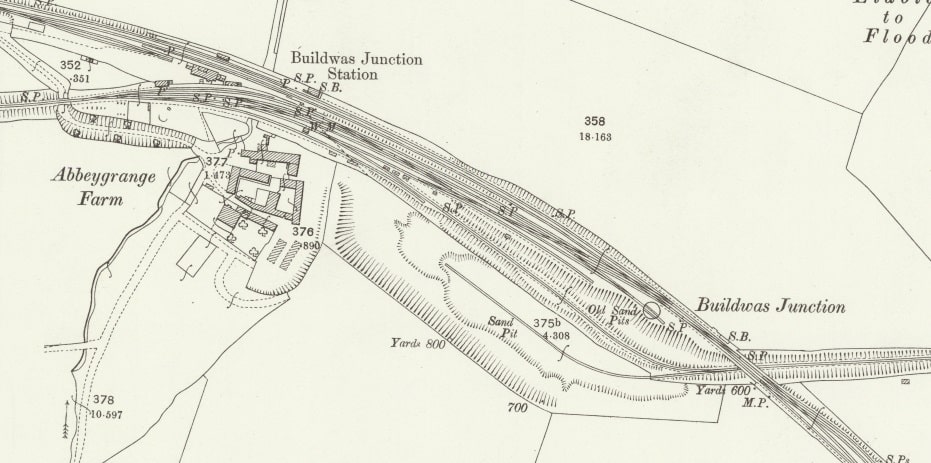
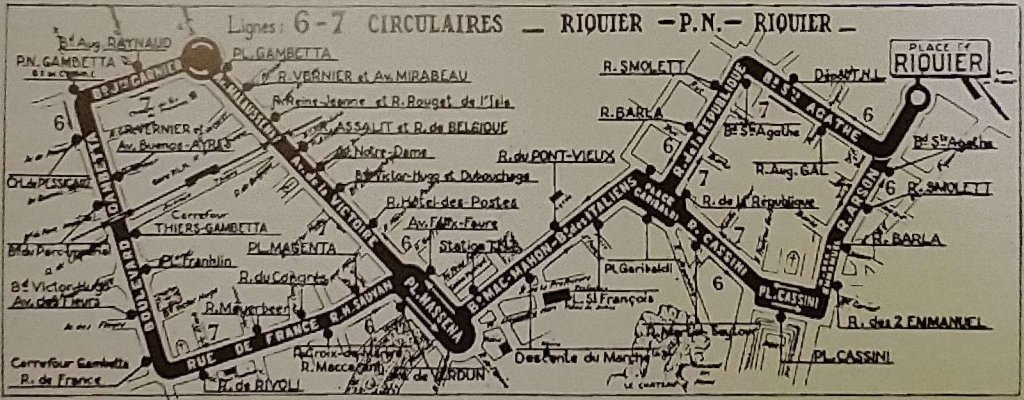
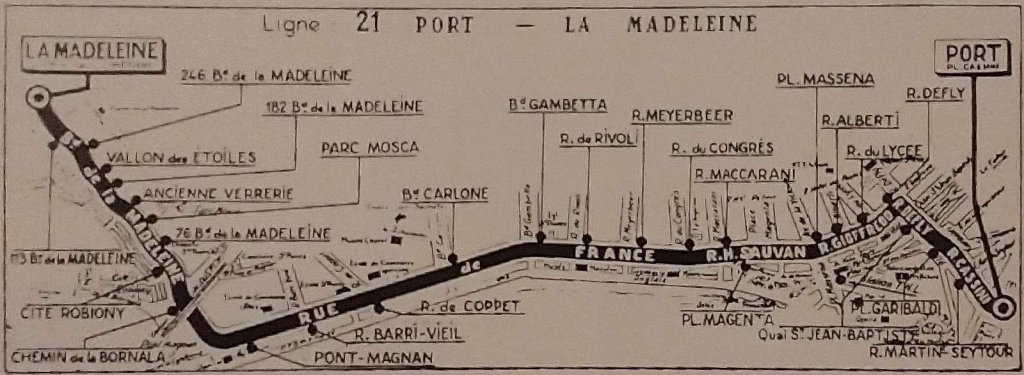
Nice is a picturesque city nestled in the French Riviera. It is renowned for its stunning landscapes, vibrant culture, and rich history. In recent years, one of the most remarkable transformations in the city’s infrastructure has been the development and expansion of its modern tram network.
In November 2017, I wrote two short articles about the History of Trams in and around Nice and the development of modern trams in Nice.
https://wordpress.com/post/rogerfarnworth.com/2332
https://wordpress.com/post/rogerfarnworth.com/2342
After those two articles about the modern trams, further articles have explored the old first generation electric tramway network in and around Nice, extending to Cannes to the West, Menton to the East and into the hinterland North of the coast. All of these can be found on this blog under the Railways and Tramways tab, and then under ‘French Railways and Tramways’ … ‘Railways and Tramways Around Nice’. Indeed at the time of writing that series of articles continues to develop. The most recent articles have focussed on the coastal tramways between Cannes and Menton.
In November 2023, it seems to be a good time to review progress on the growing tram network in and around Nice, particularly since we would be staying in the area for 10 days.
The modern tram network in Nice has undergone significant development and expansion over the past few decades. The initial line, Line 1, was inaugurated in 2007 as part of a city-wide urban revitalization project. Since then, the network has expanded to include two more lines: Line 2, which opened in 2019, and Line 3, scheduled to be operational in the near future.
I asked ChatGPT to give me a short introduction to the modern tram network, this is what that AI software came up with:
“The introduction of a modern tram network has had a profound formal impact on the cityscape of Nice. The sleek, contemporary design of the trams, characterized by clean lines and a bold colour scheme, seamlessly integrate with the city’s existing architecture. The tram tracks, which run through the heart of Nice, have been ingeniously incorporated into the urban fabric, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the city. The tram stops, with their modern structures and vibrant lighting, serve as architectural landmarks, contributing to the city’s cosmopolitan image.
The modern tram network in Nice plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and accessible transportation for both residents and tourists. Trams in Nice are known for their punctuality, frequency, and reliability, allowing passengers to reach their destinations quickly and comfortably. With dedicated lanes and priority at traffic signals, trams efficiently navigate through the city, avoiding congestion and minimizing travel times. Furthermore, the accessibility of trams is commendable, with low floors, ample space for wheelchair users, and clearly marked priority seating, ensuring that everyone can travel with ease.
The modern tram network in Nice also brings substantial environmental benefits to the city. By encouraging the use of public transportation over private vehicles, the tram system helps reduce air pollution and carbon emissions. Additionally, the trams in Nice are electrically powered, relying on clean energy sources, which further contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation system. This commitment to environmental stewardship aligns with the city’s dedication to creating a greener future.
Beyond its formal and functional impact, the modern tram network in Nice fosters social cohesion and urban integration. The trams serve as communal spaces, bringing together people from different walks of life into a shared mode of transportation. This enhances the sense of community and interaction among residents and visitors, contributing to a vibrant and inclusive urban environment. Moreover, the tram system connects various neighborhoods, enabling better access to education, employment opportunities, and cultural amenities, further promoting social and economic development.
The modern tram network in Nice has transformed the city, both in its physical appearance and its provision of efficient and sustainable transportation. With its formal integration, efficiency, accessibility, environmental advantages, and social cohesion, the tram system has become an invaluable asset for the city and its residents. As Nice continues to evolve, the tram network will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the city’s future, ensuring that it remains a model of modernity and progress.”
…….. Chat GPT
A fine, and glowing, introduction to the tramway network but which says no more than any city might want to say as an introduction to the use of trams in its urban environment. Hopefully we can add considerably more specific detail relating to Nice’s tramway network.
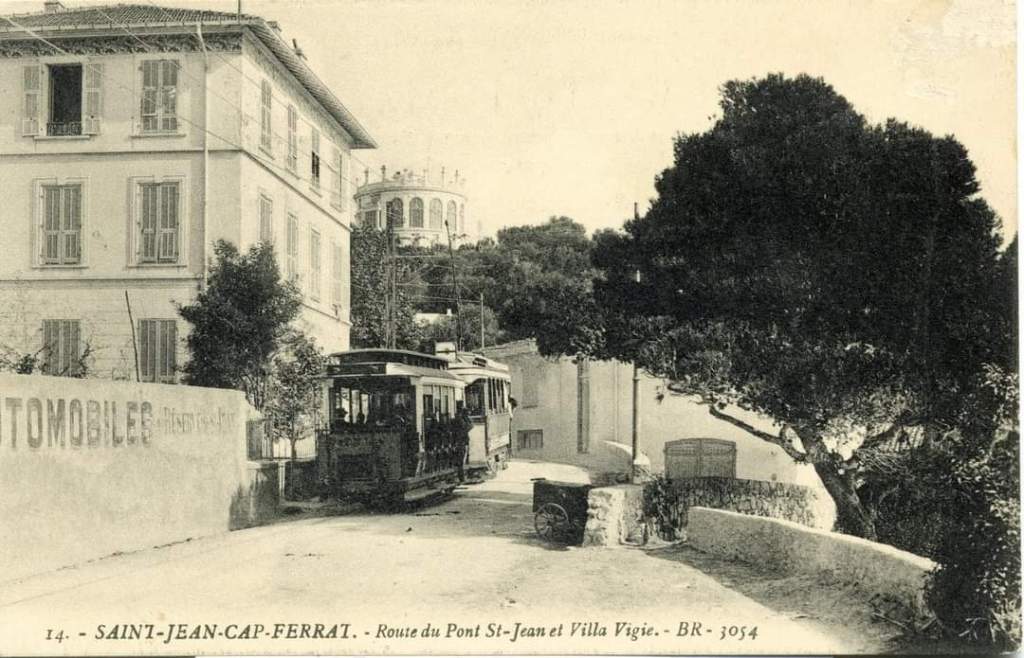
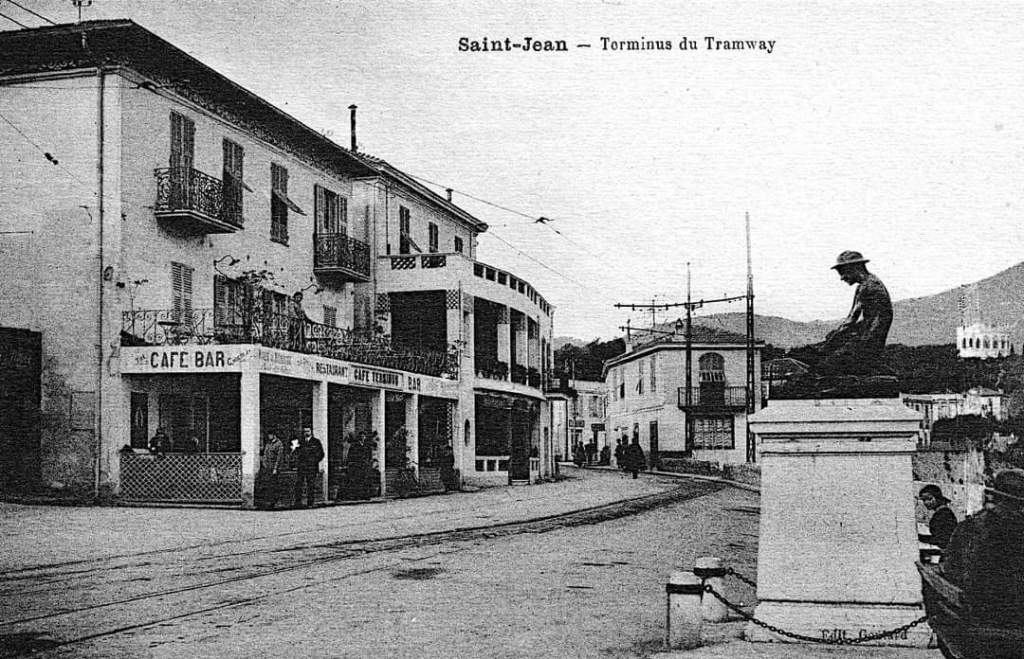
First a reminder of the history of trams and tramways in Nice:
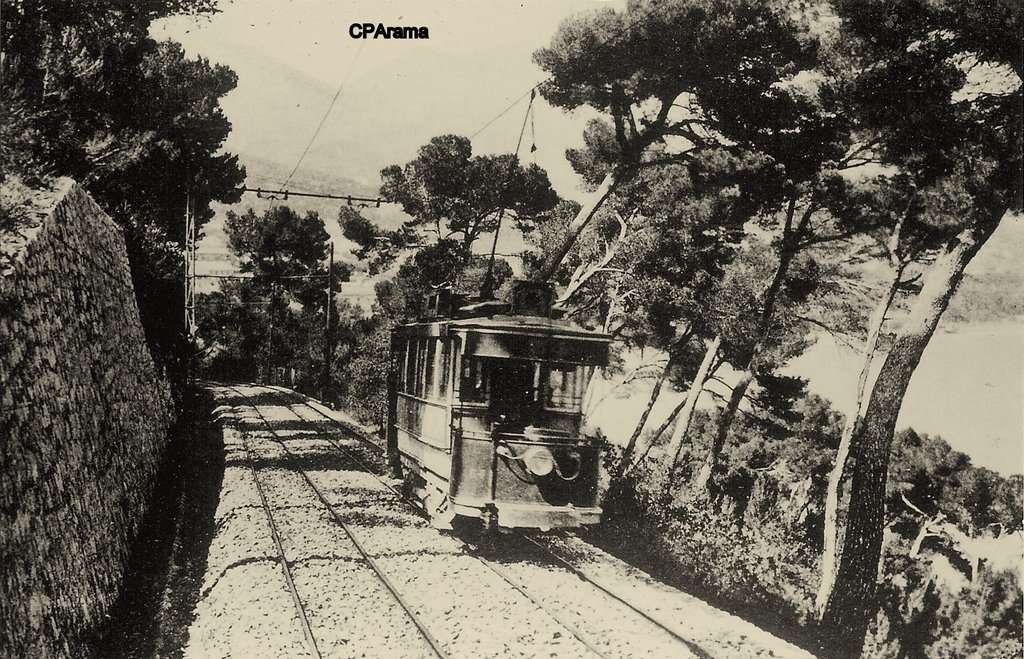
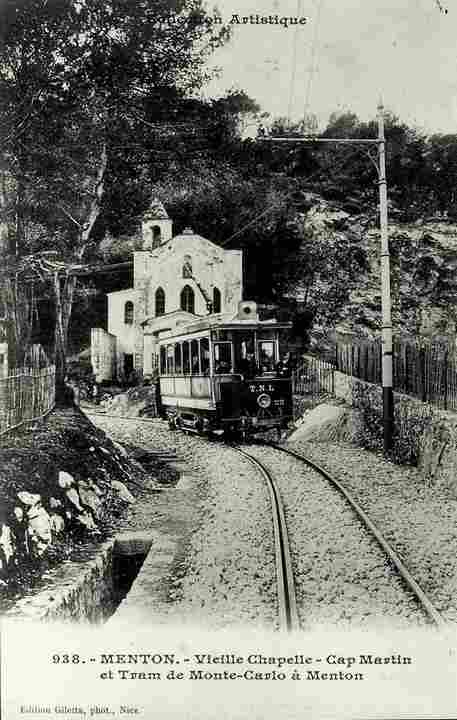
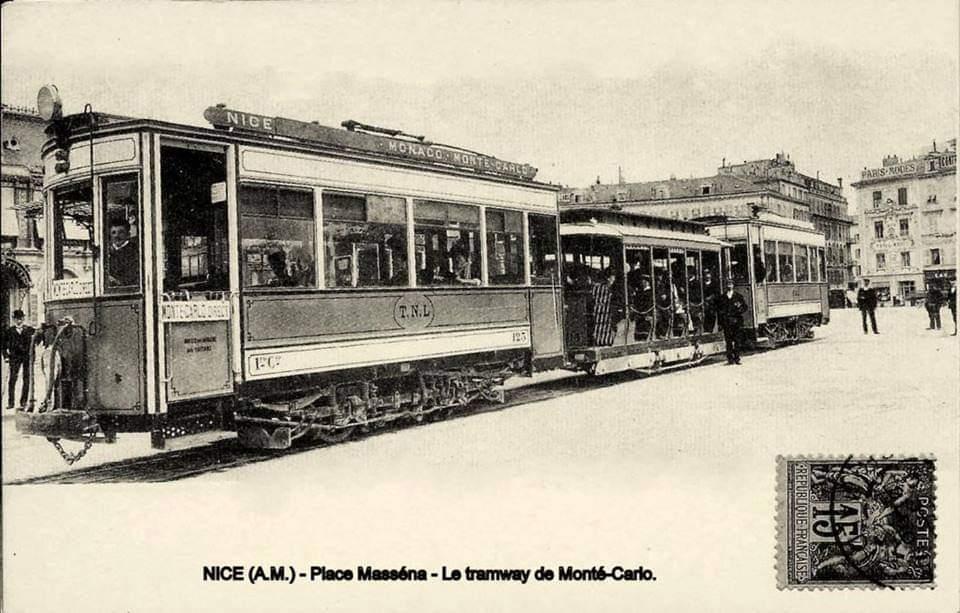
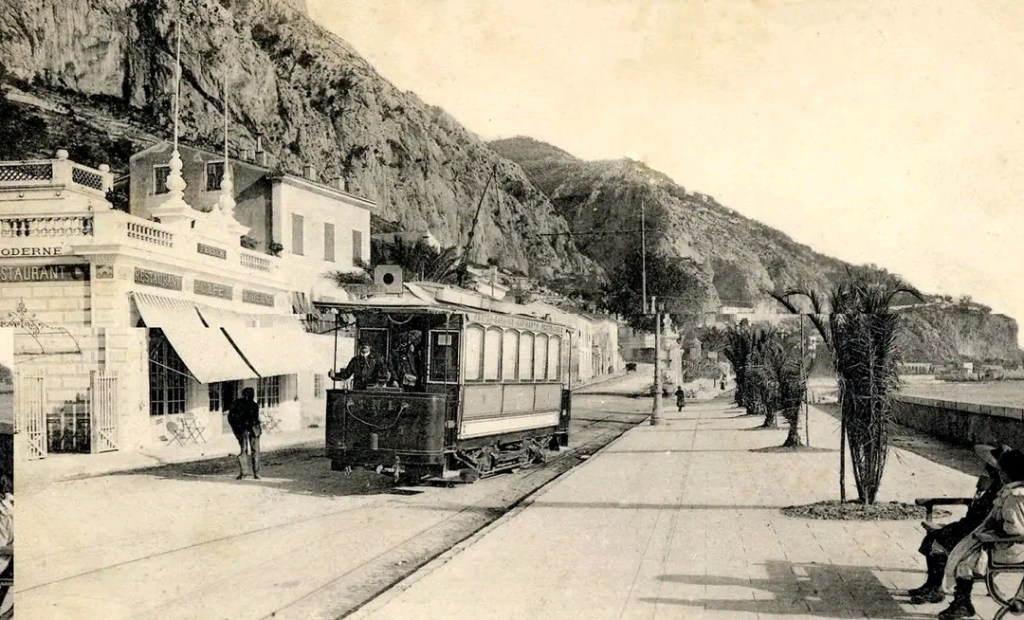
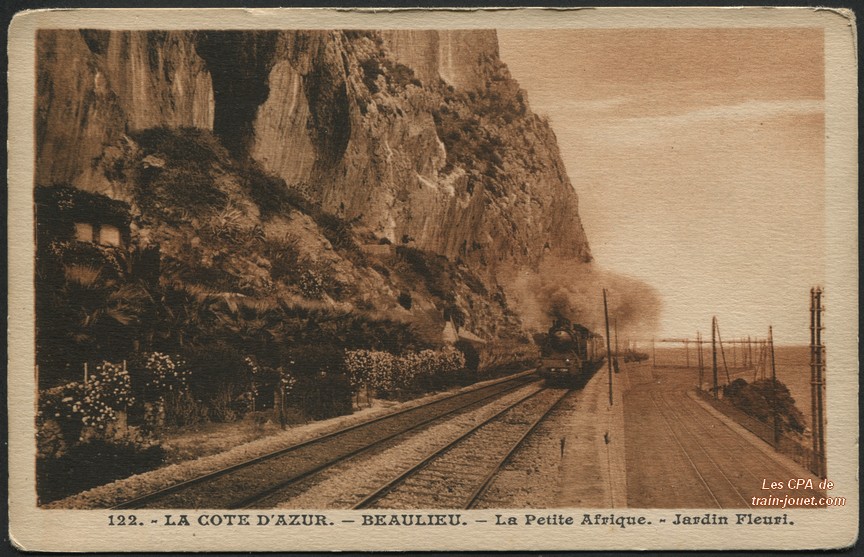
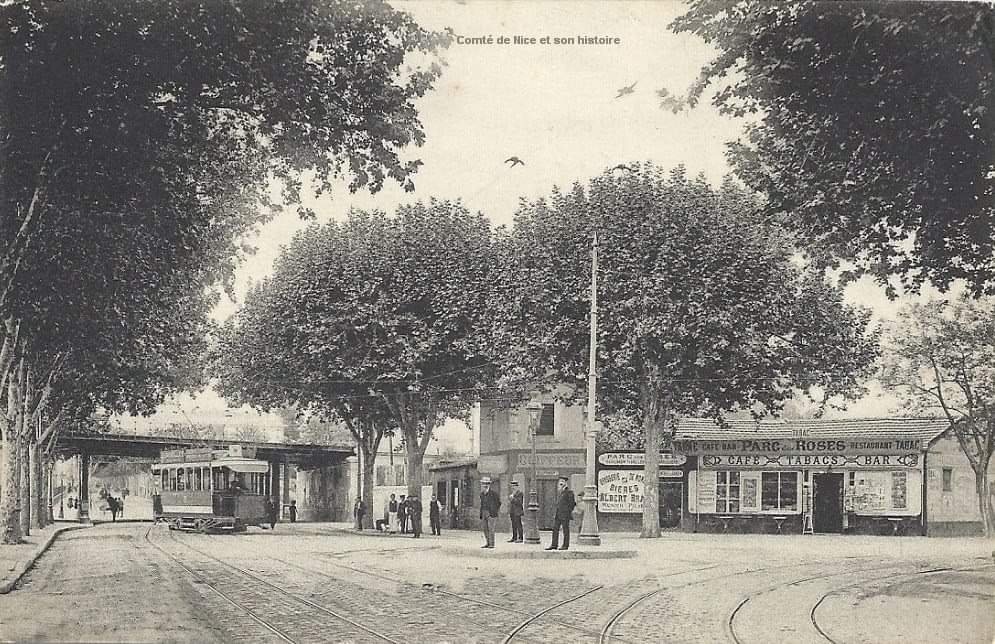
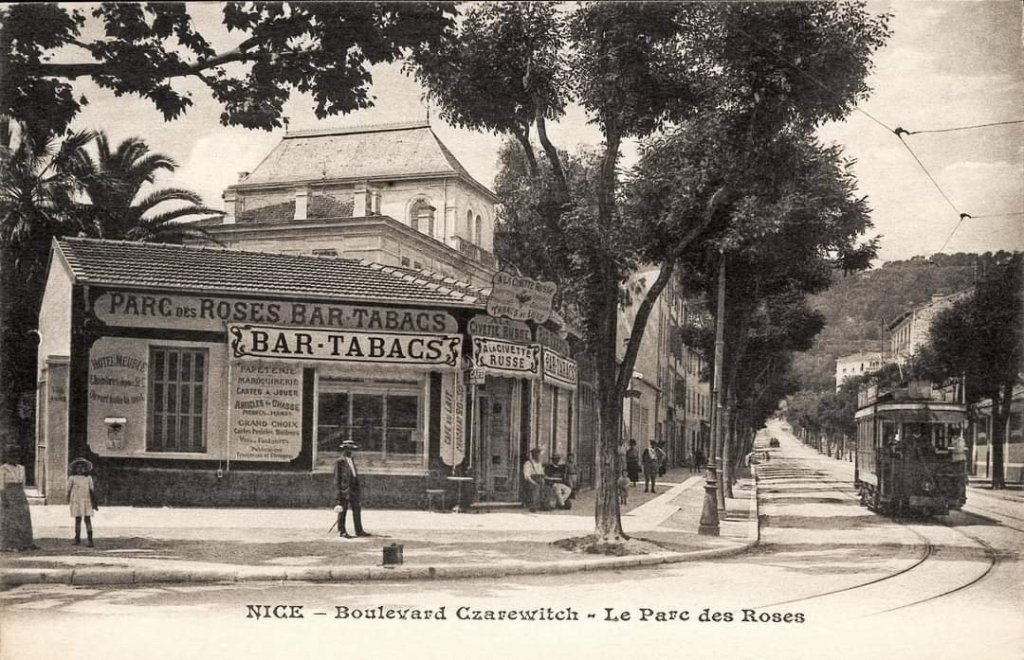
“The first tramway in Nice opened in 1879, was electrified in 1900, and was followed by a departmental network in 1906. The entire network was electrified in 1910. In the 1920s, the network had 11 lines, some of which were partially used for goods transport. However, the tram was criticised and was replaced by buses on some lines beginning in 1927. The last tramway in Nice ceased service on 10 January 1953. ” [1]
The Developing Network
The Tramway de Nice is a 27.5-kilometre (17.1 mile), tramway in Nice. It is operated by the Société Nouvelle des Transports de l’Agglomération Niçoise, which is a division of Transdev. [2] The network operates under the name ‘Lignes d’Azur‘. [1]
The first line opened on 24th November 2007 and replaced bus lines 1, 2, 5 and 18. From the start, the system had 20 No. Alstom Citadis trams in service, providing a tram every seven minutes. Wikipedia states that “since its inception, the number of passengers has increased from 70,000 per day in 2008 to 90,000 per day in 2011. The frequency has gradually increased to a tram every four minutes in 2011.” [1]
The success of the trams resulted in the city authorities deciding to create additional lines. “The West-East T2 Line serves the Nice Côte d’Azur Airport to the West through the construction of a multimodal centre and the Port of Nice to the East. This line runs through a tunnel in the centre of Nice. A future extension of the West–East line, North along the Var valley, is proposed. Another extension, running further West from the airport, across the River Var, is also proposed. [3] In addition, the Nice authorities decided to extend Line 1 to the Pasteur neighbourhood.” [1]
The extension along the Var valley mentioned in the Wikipedia article is now, in 2023, operational as Ligne 3.
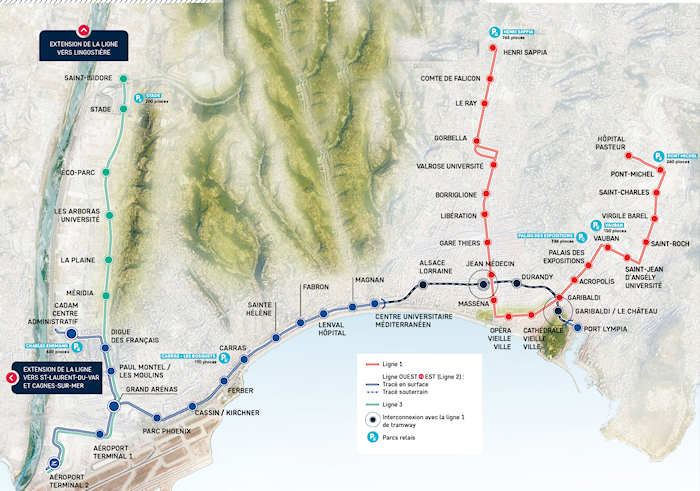
A further line, Ligne 4, is now under development with public consultation having taking place in October 2021 and archaeological investigation in St. Laurent-du-Var and Cagnes-sur-Mer undertaken between April and July 2023. [6]
The public inquiry for Ligne 4 was held in June and July 2023. [7] The proposed route is shown below. [8]
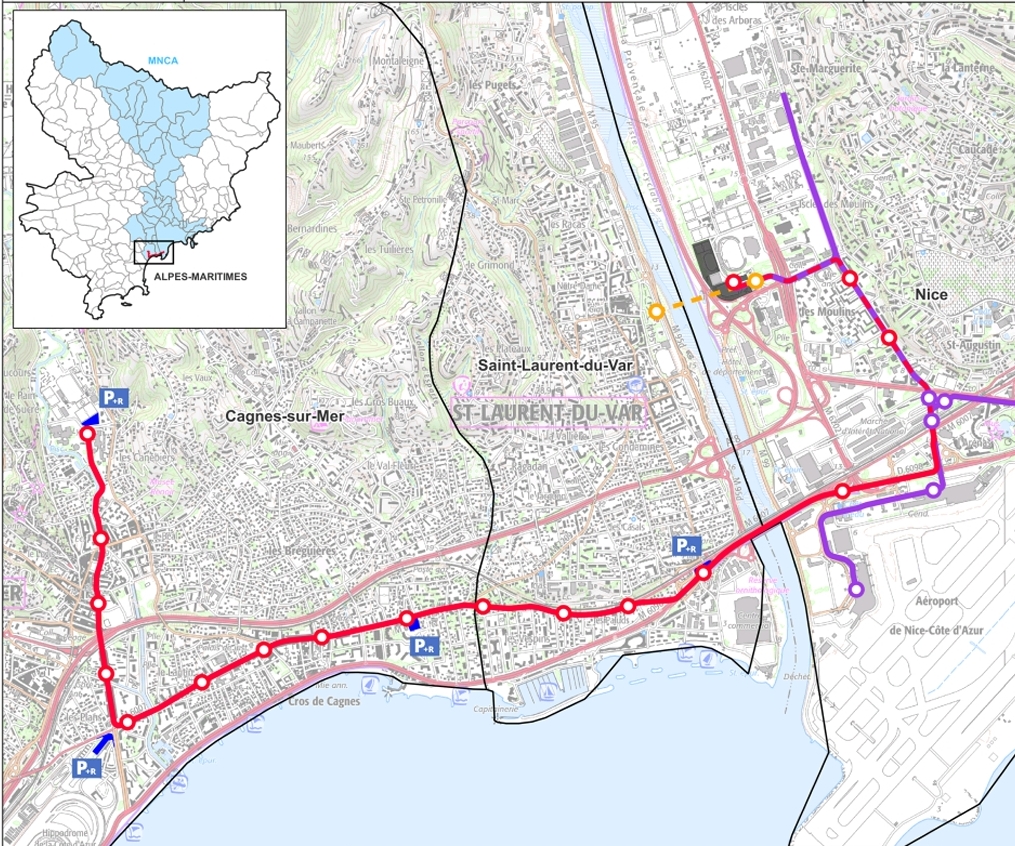
The Public Inquiry decided in favour of the creation of Ligne 4, with two reservations and one recommendation:
Reservation 1:
Boulevard Marechal Jean must be reconsidered, not as the route of the proposed line but in order to mitigate present congestion. Specifically, the authorities must: create shaded spaces; separate and reduce circulatory flows as much as possible for reasons of calm and safety; increase and promote as much space as possible reserved for pedestrians; use permeable surfacing; take advantage of the arrival of the tram to make Boulevard Marechal Juin attractive in order to revitalize businesses, professions and other activities. “The Commission, without calling into question the choice of route, requests that a new development proposal for Boulevard Maréchal Juin be submitted to public consultation at the most appropriate time.” [9]
Reservation 2:
Related to access provisions to one specific location, a clinic. The Commission required that, in addition to a ramp currently proposed, a suitable mechanised/motorised means of access from the tram stop to the clinic should be provided. [9]
Recommendation:
The current proposals only allow for one parking space for a funeral hearse for the Sainte Famille church in Cagnes-sur-Mer. The commission saw no reason why 4 such spaces could not be provided to give adequate provision for religious services without blocking the tramway. The commission also asked that the authorities give consideration to greater investment in the planned local park-and-ride provision to allow “the construction of underground parking lots, thus creating a landscaped public garden with an interesting perspective.” [9]
In the light of, often, protracted planning procedures in the UK, it is worth noting that the Inquiry finished towards the end of July and that the full report and summary report were published and available to the public by 7th September 2023, around 5 weeks after the closure of the Inquiry!
Looking further forward a fifth line is being considered. Ligne 5 will run from Drap to the eastern centre of the city of Nice.
A Focus on Ligne 1 …
On 27th May 2008, Railway Technology reported on the development of the first line which had opened in November 2007.
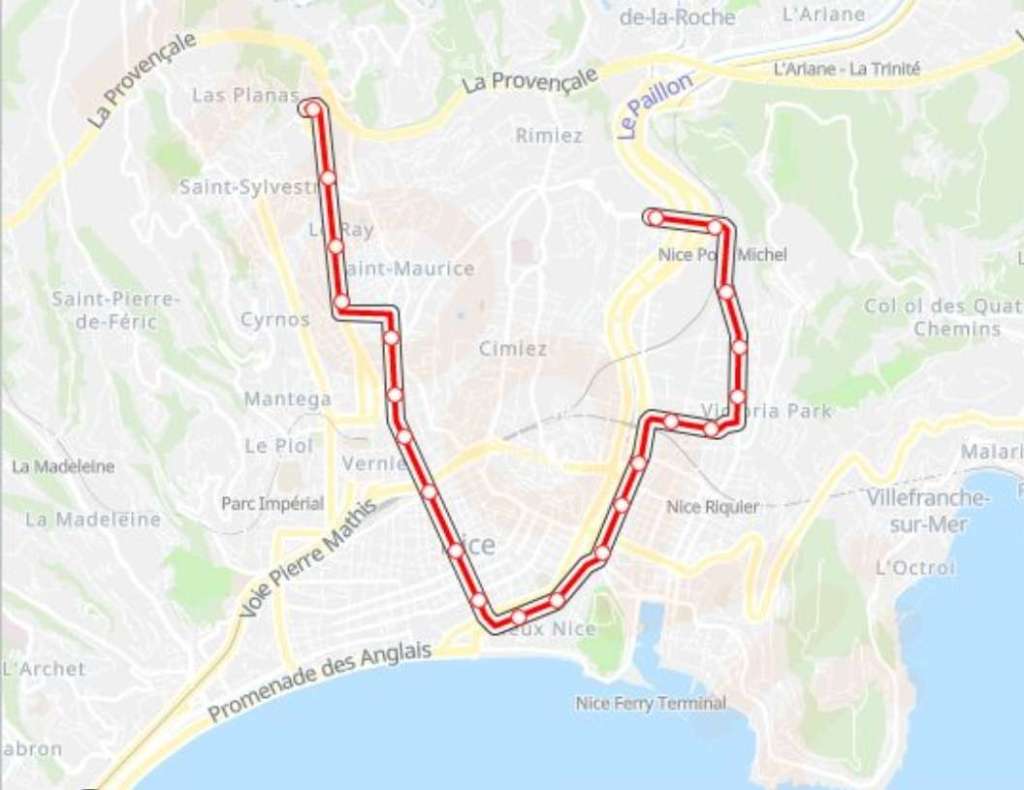
“The system’s distinguishing technical feature is the use of batteries aboard the trams to avoid the necessity of erecting overhead line equipment (OHLE) on two sections of the route. This was felt necessary to protect the character of the distinctive Italianate architecture and also because of restrictions such structures would put in the way of Nice’s carnival processions, both relevant to the area’s substantial tourism industry.” [4]
Apparently, the relatively short distances involved lent substance to the belief that battery operation was was more appropriate than the alternative Alstom OHLE-free system, APS. That alternative system has been used in Bordeaux and was due to be installed on “systems in Angers, Reims, Orléans and the Al Safooh tramway in Dubai, the more elaborate Alimentation Par le Sol/APS (ground-supply) format requires specialised equipment aboard the vehicles and also in the permanent way.” [4]
There are sections of grassed tracks throughout the system and Nice took the opportunity to undertake significant reworking of space, excluding general traffic from specific areas which then became tram/pedestrian only areas. That possibility has also been embraced in the ongoing development of the different lines which make up the system in 2023.
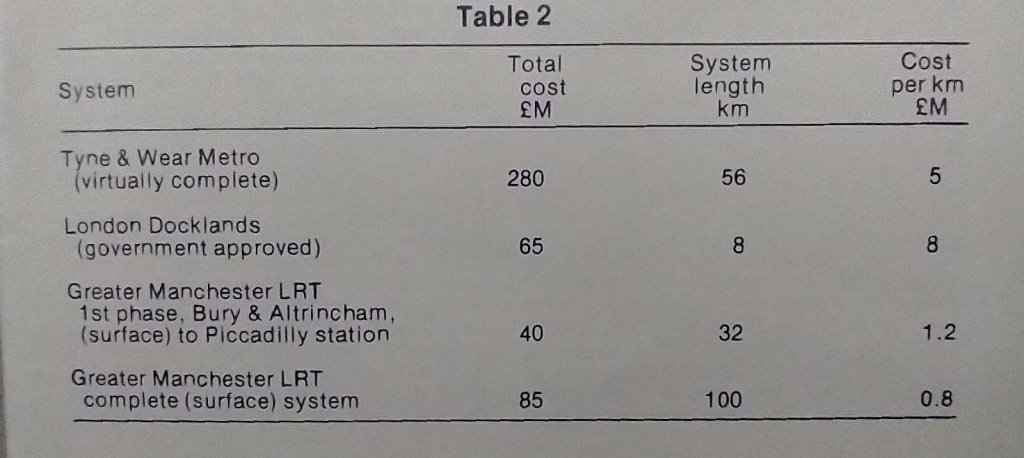
“The European Investment Bank made a €150m loan for the project which had a total cost of approximately €560m, of which just over 70% related to creating the tramway. Areas of expenditure indicative of the demands of the setting included storm water drainage works (€25m), rebuilding of Place Massena (€13m), public lighting (€4m) and tree planting (€1m).” [4]
At the time Railway Technology produced their article, they could write that, “The 8.7km double-track 1,435mm gauge line, with two brief sections where tracks diverge through narrow streets, forms a ‘U’ configuration, the two arms largely serving demand in residential areas and institutions. The base is near the southern end of the main thoroughfare Avenue Jean Médecin and the two open spaces near the Old Town, Place Masséna and Place Garibaldi, respectively 440m and 470m sections without OHLE. These ‘gaps’ are joined by a 320m section with OHLE between Opéra-Vieille-Ville and Cathédrale-Vieille-Ville stops where trams run conventionally.” [4]
Ligne 1, has only seen minor changes since it was first opened. Its western terminus is at Las Planas, and it is there that the line has its depot. “Built on sloping ground, the complex makes use of the restricted site by a line spiralling over the entry tracks beyond the Las Planas stop to give access to the depot proper and a short test track. Located close to the A8 autoroute, Las Planas also incorporates a park-and-ride facility.”
Its Eastern terminus was for some time at Pont Michel but an extension to Pasteur was completed in 2013.
Ligne 1 was initially supposed to transport 65,000 passengers/day. But it was quickly adopted by the people of Nice. Today, Ligne 1 can transport nearly 100,000 passengers/day and supports the ongoing development and attractiveness of the neighbourhoods it passes through. “Around 126,500 residents and more than 42,000 jobs, or 37% of Nice’s population and nearly a third of the city’s jobs, are less than 400 metres from the line. With 22 stations and a frequency of one tram every 4 minutes, Ligne 1 allows residents of the city to reduce their travel time.” [5]
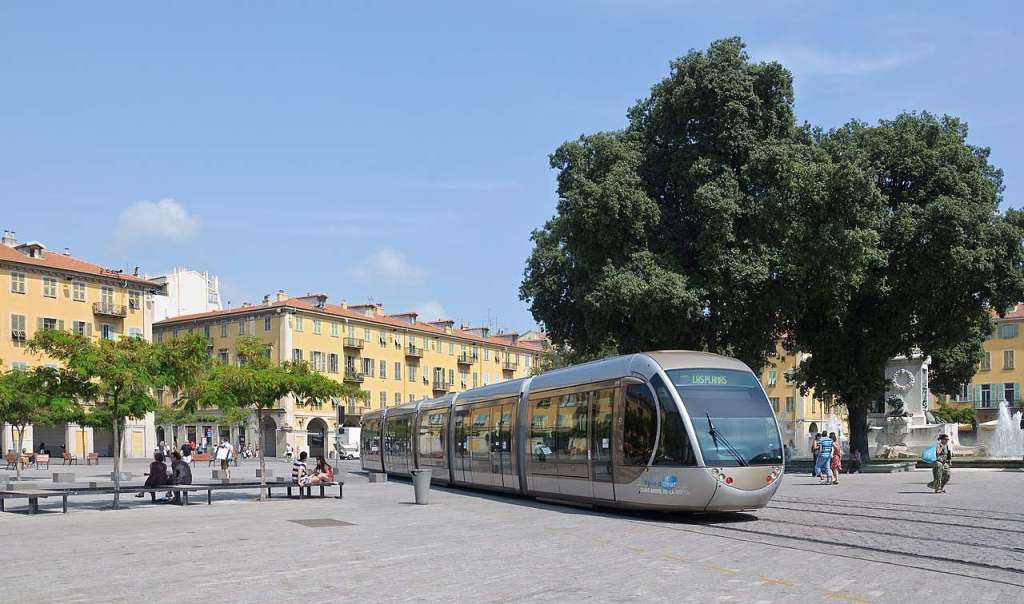

At its opening, Ligne 1 was operated by a fleet of 20 No. 20 Alstom Citadis type 302 trams. “The fully air-conditioned, 100% low-floor, modular five-unit double-ended trams could be extended in response to the high take-up of the service. Roof-mounted Ni-MH (nickel-metal hydride) traction batteries with an operational life of at least five years were supplied by Saft under a €2m contract, giving trams a range of up to 1km at a maximum speed of 30km/h with air-conditioning in operation, the switching of power being either from the overhead line or the batteries is activated by the driver, with the pantograph fully lowered when running without OHLE.” [4]
“Each tram’s driver console features visual and audio indications of the need to operate the power changeover sequence. The batteries recharge from the overhead supply while in conventional operation. There is no additional external infrastructure needed to operate the trams under battery power over the OHLE-free track.” [4]
The approximate Ligne 1 end-to-end journey time is 30min. “The control centre is at the depot, linked with trams and to the extensive network of video monitoring of the system. Benefiting from road traffic exclusions and priority at crossings, in this totally urban setting, trams can attain an average 18km/h, as opposed to 11km/h for buses.” [4]
The approximate Ligne 1 end-to-end journey time is 30min. “The control centre is at the depot, linked with trams and to the extensive network of video monitoring of the system. Benefiting from road traffic exclusions and priority at crossings, in this totally urban setting, trams can attain an average 18km/h, as opposed to 11km/h for buses.” [4]
A Focus on Ligne 2 …
Ligne 2 connects the Airport with Nice’s Port Lympia, traversing central Nice. It connects with Ligne 1 at Avenue Jean Medecin and at Place Garibaldi.
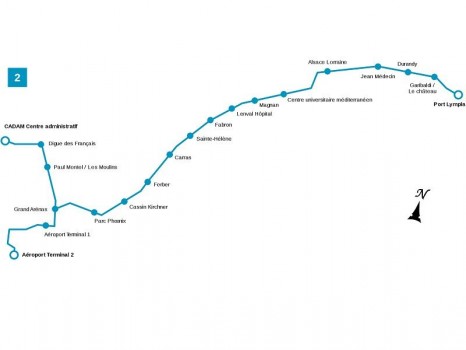
Following the success of tram Ligne 1, the mayor of Nice, Jacques Peyrat, decided to create a new line crossing Nice from east to west. This line would make it possible to serve the entire western district of the city which represents around 200,000 people, to transport more passengers (around 105,000) than with buses (around 70,000) as well as to reduce road traffic.
Between 2007 and 2008 a dedicated bus route to the Airport was provided, but the election of Christian Estrosi as Mayor in March 2008 put an end to that project. [18]
On 25th June 2008, “Christian Estrosi announced that Ligne 2 would be built on the Promenade des Anglais, which would have made it possible to reduce costs and build the line more quickly as there would have been little or no traffic preparatory work to be done. The trams would have to be powered from the ground in order to prevent an overhead line damaging the view.” [18]
“The controversial project along the Promenade was finally abandoned when on 9th October 2009, the mayor of Nice announced that Ligne 2 of the tramway would be built through the city, abandoning the route along Promenade des Anglais. The revised project meant that Ligne 2 would be 8.6 km long, including 3.6 km in tunnel. on the surface, the line would serve Nice-Côte d’Azur airport, the planned Saint-Augustin multimodal station (connection with the SNCF, the future TGV and the future tram Ligne 3) then would pass through Avenue René-Cassin, Avenue de la Californie and Rue de France. From the intersection with Boulevard François Grosso, the route would run underground with the stations Alsace-Lorraine, Musiciens, Place Wilson (near the future new town hall of Nice), Garibaldi, Île de Beauté (Port of Nice ) and Place Arson. The route would then return to the surface as far as a terminus at Nice-Riquier SNCF station.” [18]
The intention was for the work to be completed in 2016:
2013: construction of the tunnel in the city centre.
2016: commissioning of line 2 from Saint-Augustin to the port.
The Public Inquiry took place in December 2011 and January 2012 and some changes were made to the scheme as a result. These included:
- The Eastern terminus being placed on the Cassini Quay at the Port.
- A new stop being included at Sainte Helene.
- Compensation being made available to traders affected by construction work.
In 2013, the line was divided into two sections. The first part between CADAM, Magnan and the Airport was given a target completion date of 2017, the remainder was scheduled for completion by 2019. [18]

As the scheme developed the programme had to be amended. In June 2018, the length of the line between Magnan and CADAM was opened; in December 20th18, the length between Grand Arenas and the Airport terminal was completed; in June 2019 the length between Magnan and Avenue Jean Medecin was commissioned; and the final length to Port Lympia opened in December 2019. [18]
The cost of the work was estimated at 770.7 million euros, including 758.7 million euros for the work defined in 2009 and 12 million euros to cover modifications made by the public inquiry. This was financed by: the State (52.8 million); the general council of Alpes-Maritimes (50 million); the regional council of Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur (26 million); the European Regional Development Fund (3 million); and the airport company (between 10.2 and 12.6 million); the city of Nice (50 million); the General Investment Commission (4.69 million for rolling stock purchase); a loan from the European Investment Bank (250 million); and a loan from the city’s deposit and consignment fund (250 million). [18]
A New Depot
A new depot was built for Ligne 2 alongside the Ligne 1 depot at Henri Sappia.

The Henri Sappia depot is too small to accommodate all the trains from Ligne 1 and Ligne 2 simultaneously, a new depot has been built next to it. It is also the operational centre for the line. It is located between the A8 motorway and the Nikaia Palace with a total area of approximately 40,000 s². It is large enough to accommodate the 44 m trams of Ligne 2 as well as Ligne 3 and the future Ligne 4, around sixty. It is made up of a maintenance workshop, a storage centre of 2,860 m², a centralized control station of 130 s² and parking for two hundred and fifty vehicles. [18]
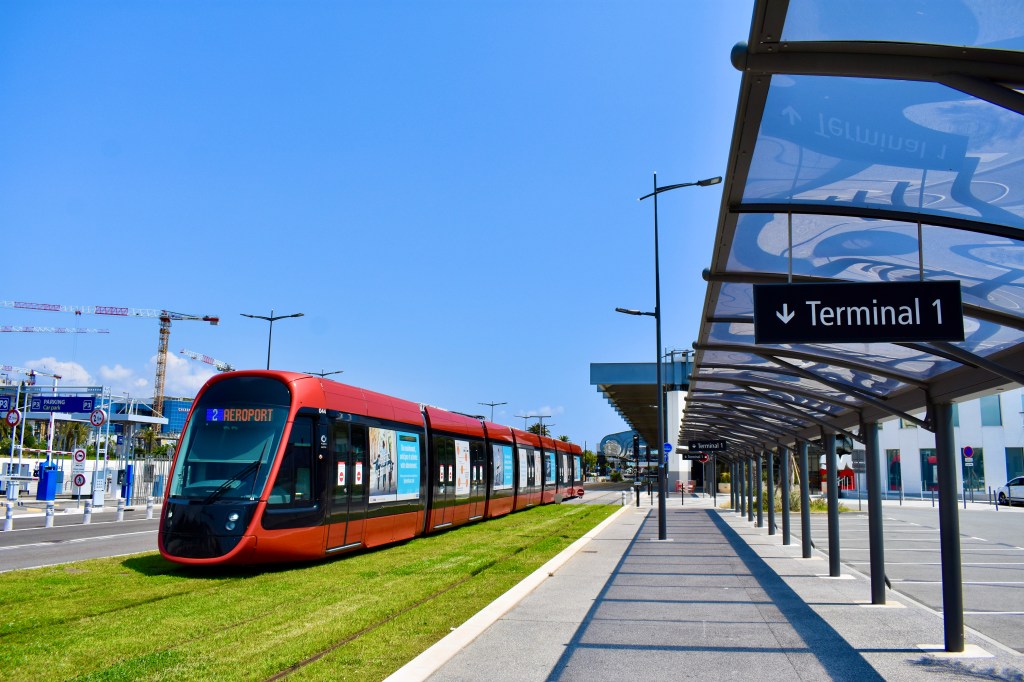

The Trams
Alstom Citadis X05 trams are in use on Ligne 2. Unlike Ligne 1, the new tramway does not feature overhead contact lines on the entire surface section of the route. This option was requested by the Nice Côte d’Azur Metropole to integrate the new tramway line into the urban landscape while preserving the city’s architecture. Instead, the line has been installed with intermittent charging in stations. [20]
Alstom supplied its latest ground-based static charging technology, SRS, which allows a tram to charge safely and automatically in under 20 seconds while stopped at a tram stop. The trams are equipped with an on-board energy storage device, Citadis Ecopack. Equipped with this technology, trams can charge up at each station as passengers get on and off, without extra stopping time and without driver intervention. [20]
Citadis X05 trams incorporate new technologies designed for lower energy consumption. The vehicles incorporate a 100% low-floor design. They have balcony-style windows, multi-purpose areas, LED lighting, CCTV cameras, emergency intercoms, electrical braking, permanent magnet motors and sensor-based air-conditioning. [21]
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems installed in the trams contain separate controls for passengers and driver zones. Each bogie offers a 750mm-wide central aisle. The entrance height of the intermediate front doors is 326mm and 342mm. The trams’ crash absorption resistance complies with the EN15227 standards. [21]
Each motorised bogie of the vehicle is fitted with two air-cooled permanent magnet traction motors. They provide a maximum acceleration of 1.3m/s² and permit deceleration of 1.2m/s², while the compression load is 400kN. [21]
The contract with Alstom was worth €91m and covered the delivery of 19 Citadis X05 trams and all necessary land-based static charging points. The contract also includes options for up to 18 further trams and associated energy charging systems and maintenance services. [21]
A Focus on Ligne 3 …
Ligne 3 connects the Airport with Saint Isidore, stopping at Allianz, Nice’s sports stadium. It connects with Ligne 2 at the airport, Grand Arenas, Paul Montel and Digue des Francais.
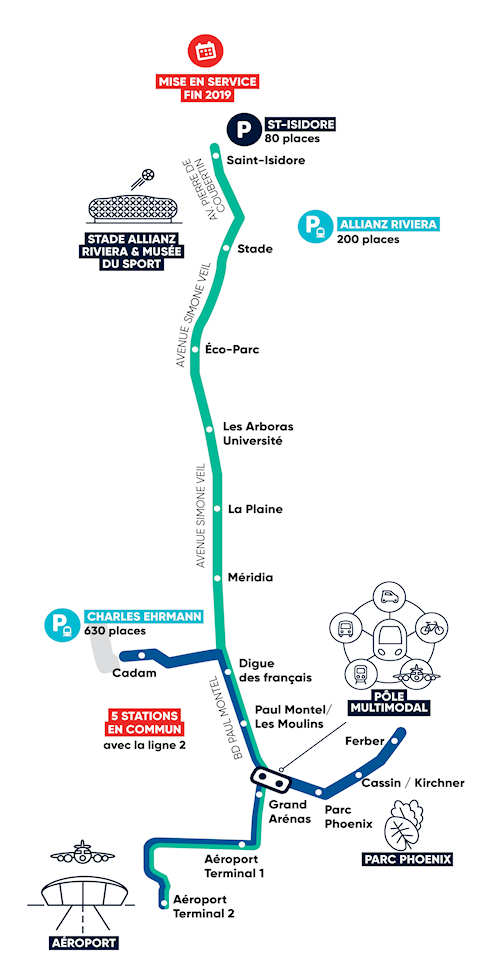
Ligne 3 is 7km long in total, stretching from Terminal 2 at Nice Airport to the heart of the Saint-Isidore district, North along the valley of the River Var. It has 11 stations in total including 5 stations in common with the West-East line. Trams travel at an average speed of 22km/hr. 12,000 passengers per day is the average usage. Trams run at a Frequency of 10 minutes and 6 trams are dedicated to the line. Additional trams are operated on march days or events and on these days a frequency of 3 minutes is sustained. It is predicted that by 2026 25,000 jobs, 11,400 inhabitants and 5,400 new homes will be served by the line. [27]
In 2017, the route Ligne 3 was finalised by the authorities. The work had an estimated cost of 56.3 million euros excluding taxes, partly subsidized by the State (3.5 million), the region (8 million), the department ( 4 million) and the city (15 million). Construction work began on 19th March 2018 and the line opened in full on 13th November 2019. [28]
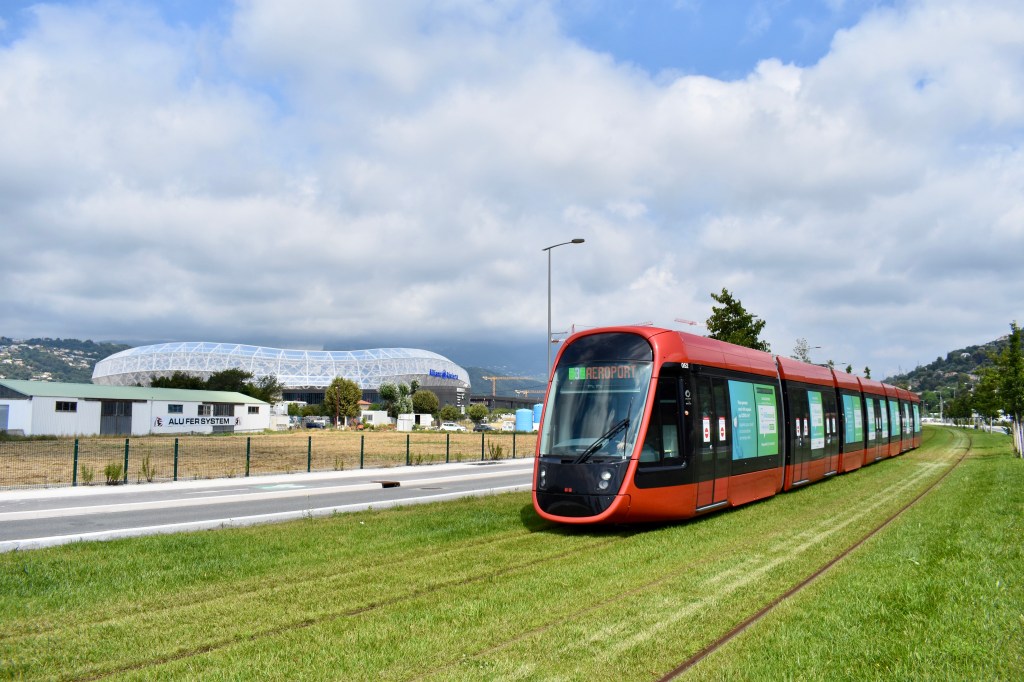

At the end of 2019, 6 additional tram sets were put into service to allow the operation of Ligne 3. These were identical to the trams in use on Ligne 2 and are powered in the same way as the Ligne 2 trams, operating without overhead contact lines.
The Charles Ginésy maintenance centre was established as part of the construction work. It is located at the Charles Ehrmann sports park and now is common to both Ligne 2 and Ligne 3, It has been designed to accommodate and maintain the whole fleet of trams on the two lines. [27]
New park-and-ride facilities accommodate 630 vehicles.
A Focus on Ligne 4 …
The city of Nice believes that the ongoing development of the tram network brings significant benefits which are focussed in 3 main areas: [10]
- Mobility: facilitating travel thanks to the tramway and cycle paths, creating new park and ride facilities, increasing intermodality, ensuring a quality, regular service to the sectors crossed,
- Quality of life : a reclassified living environment, less pollution and less noise, less car traffic, a more beautiful and peaceful city, more modern and green,
- Economic development: a more attractive city that encourages activity, a mobility offer superior to current trips to shops and businesses, a saving on travel costs, job creation during the construction phase.
Ligne 4 “will connect the three most important municipalities in the Metropolis in terms of population and jobs: Nice, Saint-Laurent-du-Var and Cagnes-sur-Mer. It will serve 18 stations, including 14 new ones, over a length of 7.1 km of track created, supplemented by 4 new park-and-ride facilities comprising 1,200 spaces (Saint-Laurent-du-Var station, Val Fleuri, Hippodrome, Parc des sports of Cagnes-sur-Mer). Thus, 40,000 passengers will be transported every day, calming traffic and avoiding 4,500 tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions per year from 2028.” [7]
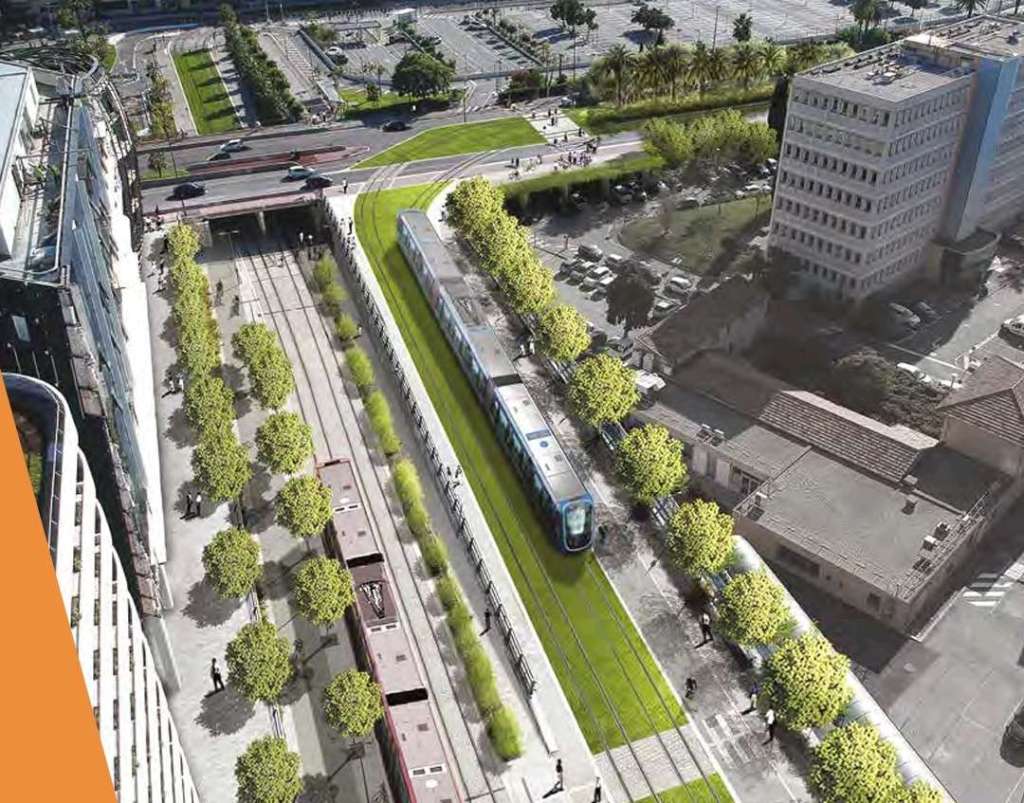
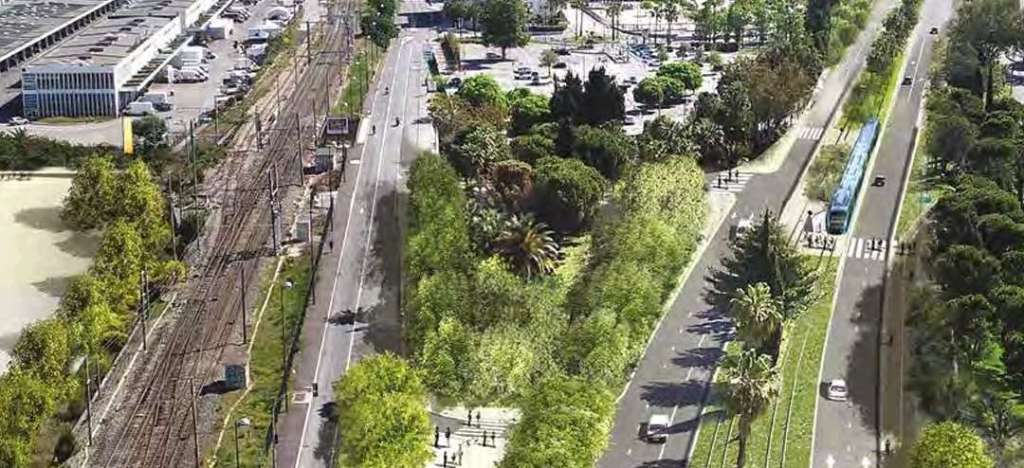



This line will be accompanied by the planting of 1,160 trees and the preservation of 365 trees along the route and 30,000 m² of green tramway.
The route will run from the CADAM (administrative center) in St. Laurent-du-Var to the Cagnes-sur-Mer Sports Park.

A Focus on Ligne 5 …
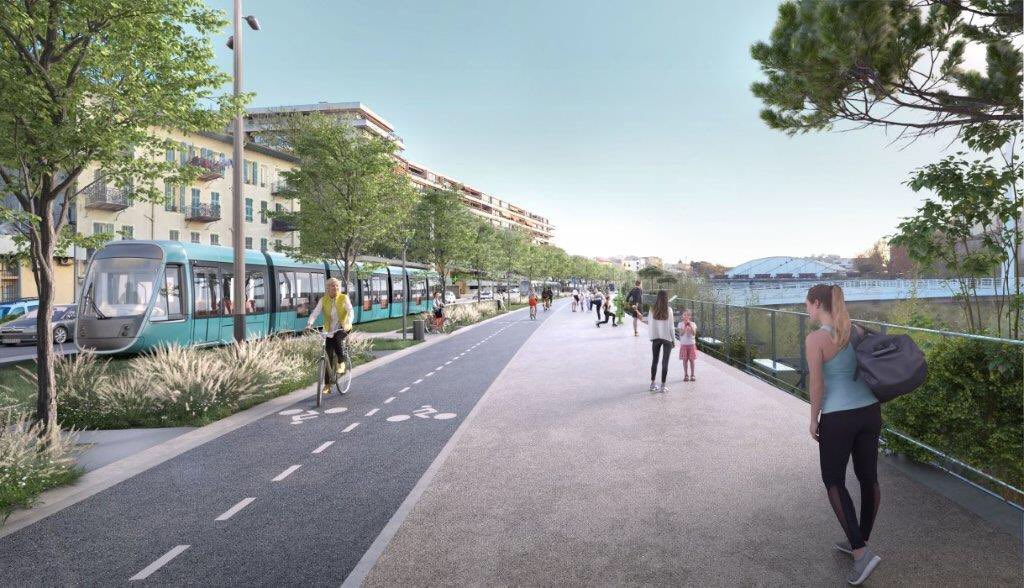
“As part of the creation of this new transport axis, it is planned, in addition to the creation of 7.6 km of additional tramway on predominantly grassed trackway tram platform,, to give more space to pedestrians and bicycles. Thus, a continuous cycle route will be created between Drap and the eastern centre of Nice. More generous pedestrian spaces will be created along this axis to rebalance the city for the benefit of local residents.” [10]
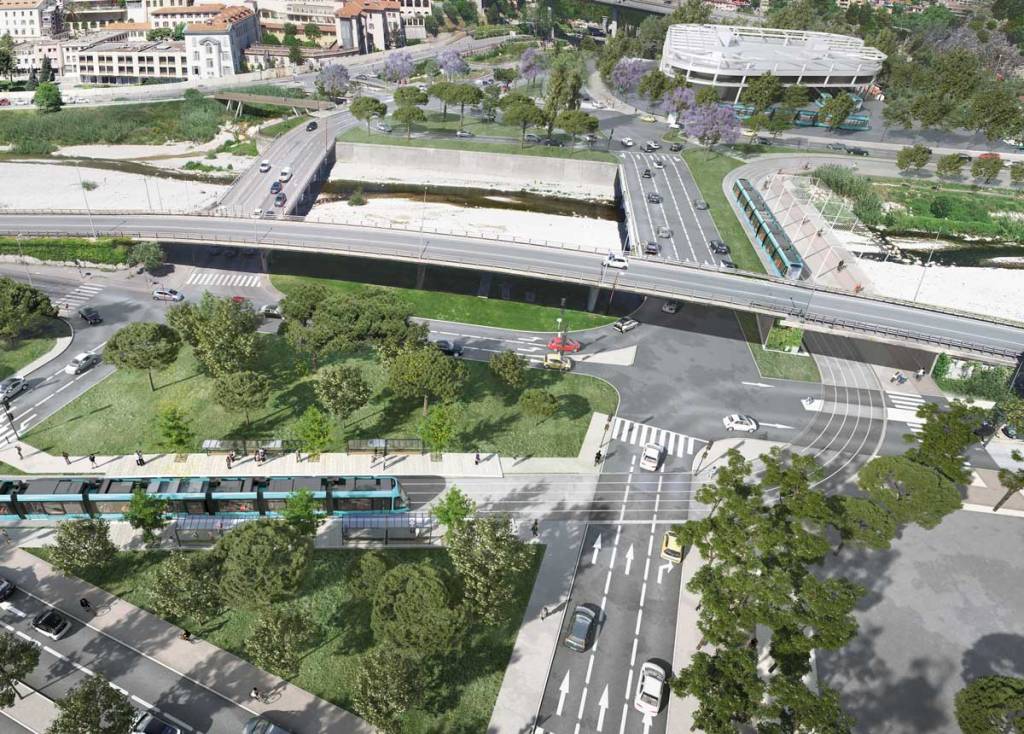
Like the other lines, the entire route will be accessible to all. Developments will be made on and around the stations to guarantee all people benefit from its presence. In the light of this additional and improved pedestrian crossing points over the River Paillon will be created specifically at two locations where tram stations will sit on significantly widened bridges: Pont Jumeaux and Pont Anatole France, which are not very accessible to pedestrians today. The objective is to encourage pedestrian crossing of the Paillon by giving more dedicated space.
“Pont Anatole France station is a good example of this desire to connect the two banks. This station will be located on the bridge and will therefore be easily accessible from both banks via generous spaces for pedestrians.” [10]
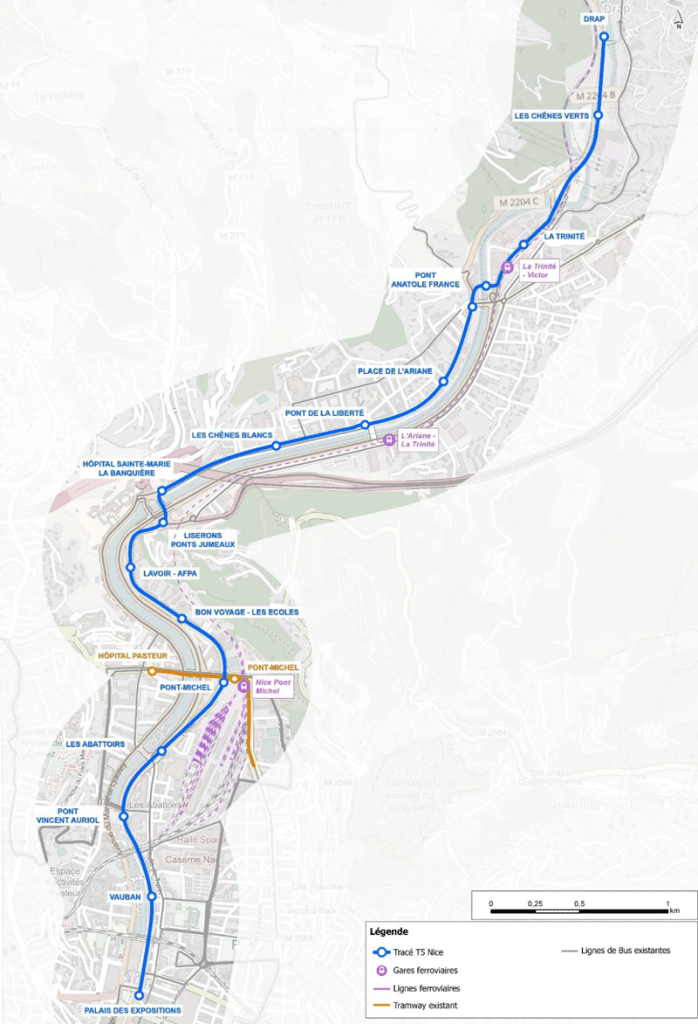
Ligne 5 could have been envisaged as an extension to Ligne 1, indeed it was seen as an extension in very early considerations for a tram network in Nice. However, Ligne 1 is acting a full capacity and would require significant alteration to accommodate the additional traffic produced by an extension to Drap.
In the light of this Ligne 5 is intended to be independent of Ligne 1 with its own terminus at the Palais des Expositions. By deviating from the route of Ligne 1, Ligne 5 includes “new neighbourhoods and both banks of the Paillon.” [10] It will, however, be “interconnected with Ligne 1 at Pont-Michel, so that Ligne 5 trams can reach the maintenance centre in Nice-Nord.” [10]
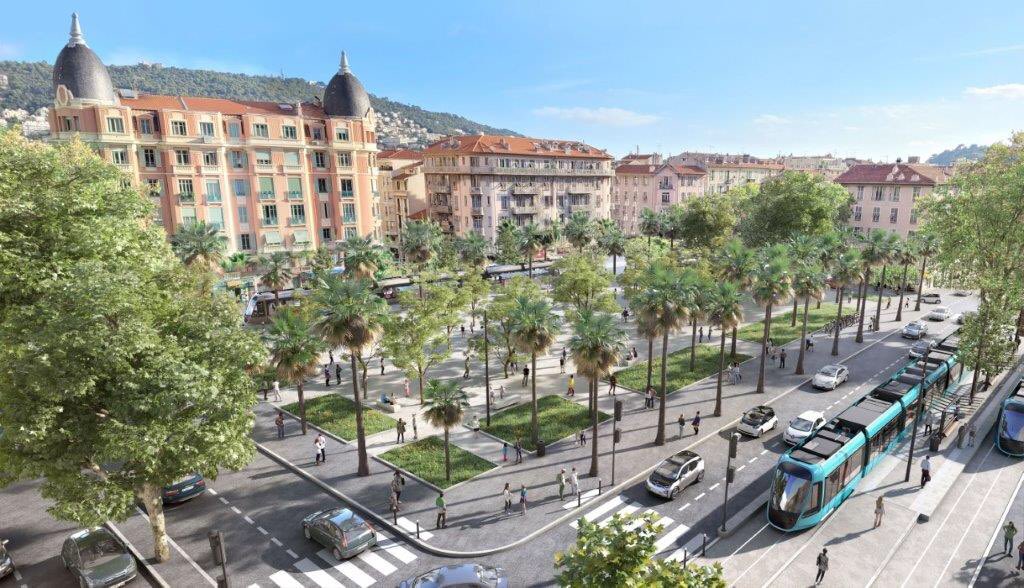
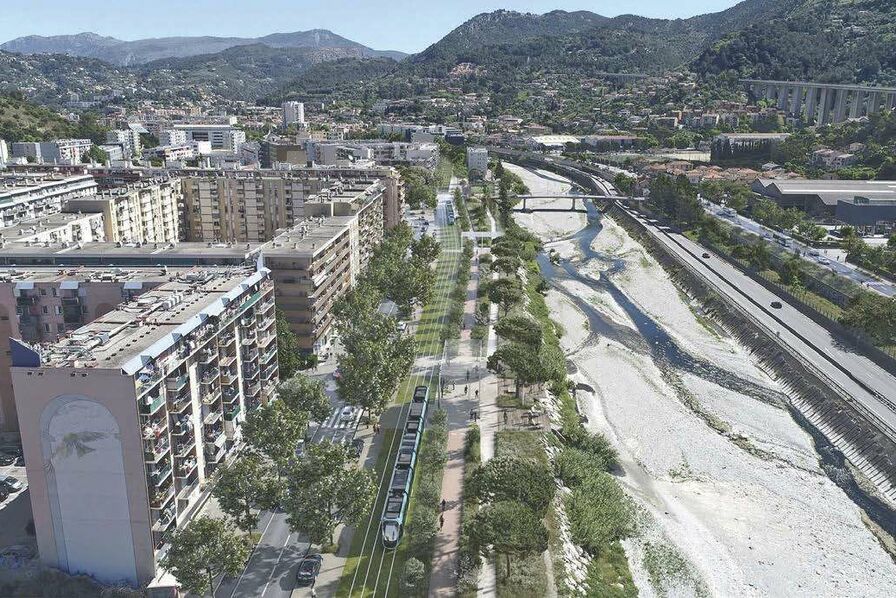
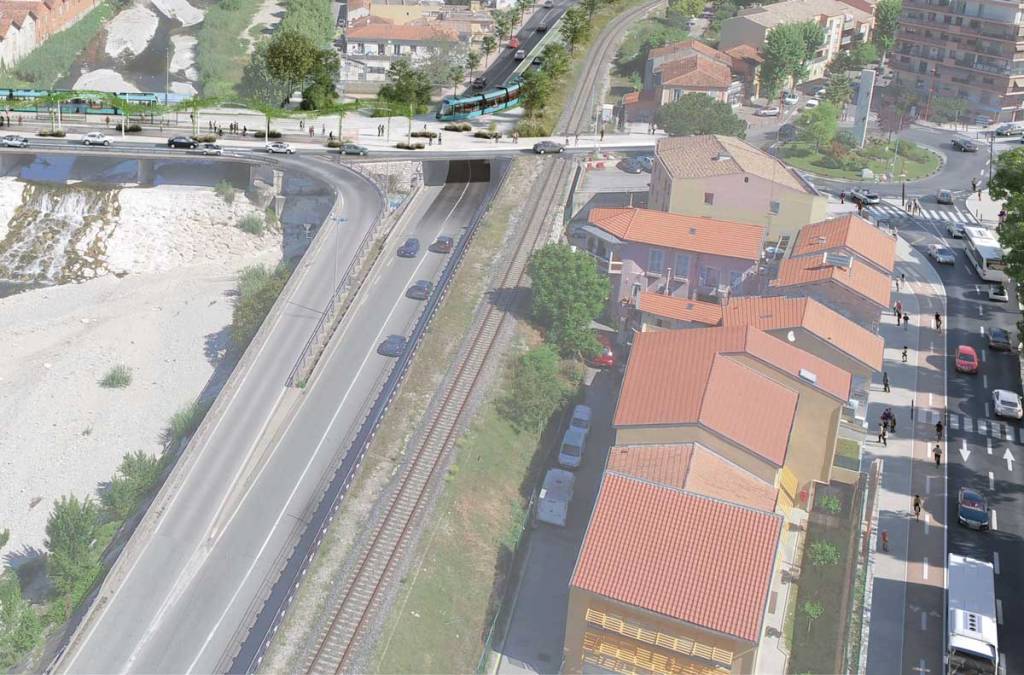
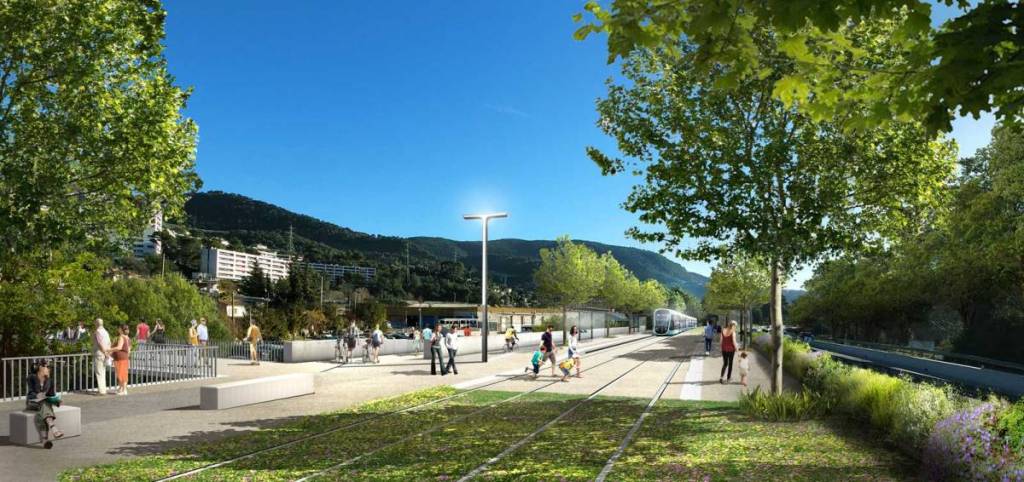
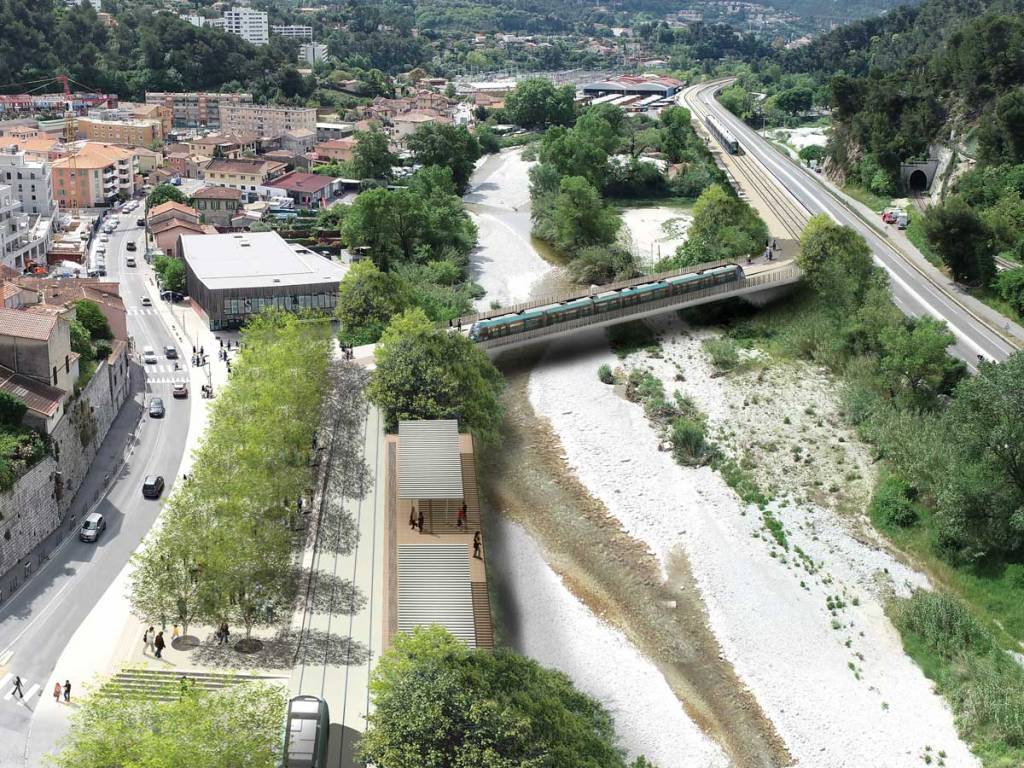









Public Consultation took place between January and March 2022 and as a result some refinements were made to proposals. Currently (November 2023) the project includes for:
– 7.6 km of tramway
– 16 stations
– 25 minutes between the two terminals
– 1 tram every 8 minutes
– 50,000 inhabitants and 28,000 jobs served
– 16,000 fewer cars every day in the Paillon valley
– 2000 tonnes of CO² avoided per year.
The calendar for the development and implementation of the project is:
2024: public inquiries (environmental, water law, public utility, land, etc.)
2026: Construction of the length through Pont-Michel to Pont Garigliano
2028: Construction of the remaining length to Drap. [11]
The public consultation resulted in a near unanimous approval of the project. 98% of the opinions expressed by the public were favourable. And 100% of elected representatives supported the scheme. [16]

“This project is eagerly awaited by residents and we know how to recognize when a consultation is going well,” said the leader of the environmentalists, Juliette Chesnel-Le Roux. [16]
“The Nice Côte d’Azur Metropolis has obtained European funding of 823,924 euros to finance all the studies carried out for the tram project linking the Ariane district to the city center of Nice and La Trinité. This funding comes from the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) which aims to strengthen economic, social and territorial cohesion within the European Union as part of the Integrated Territorial Investment of the Nice Côte d’Azur Metropolis.” [17]
And further into the Future? … Towards Monaco? …
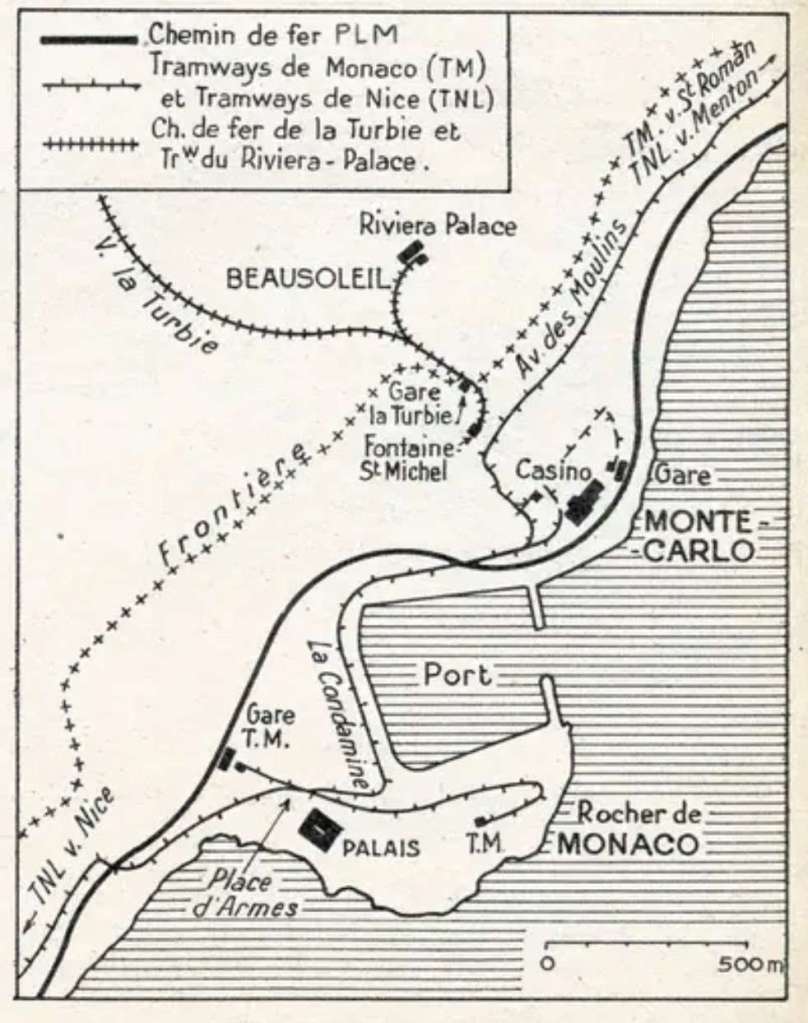
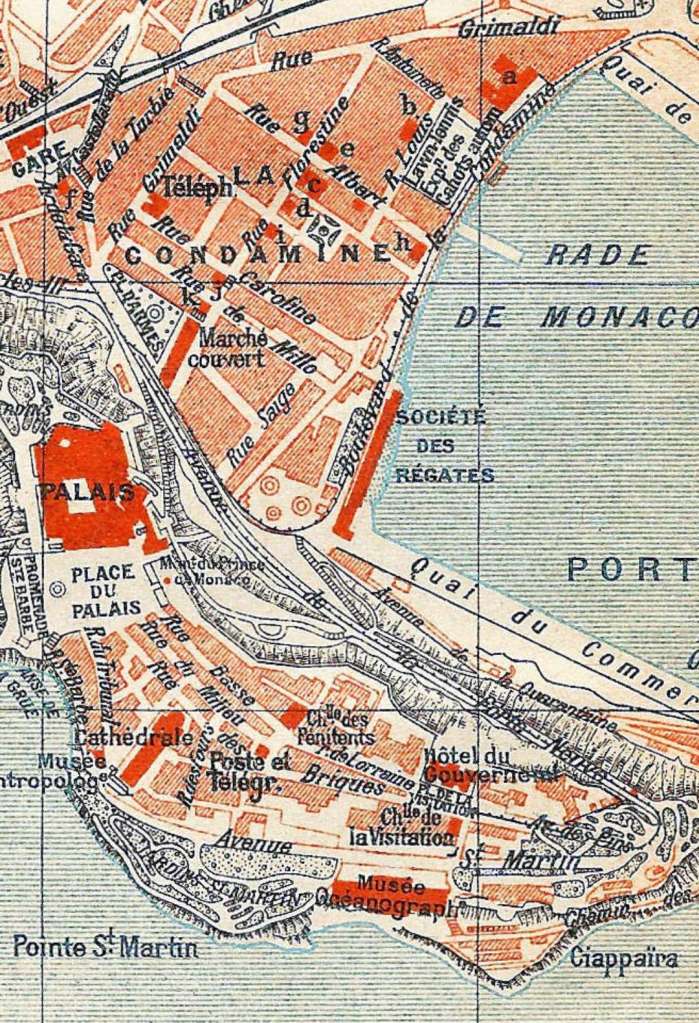
It is possible that Ligne 2 may be extended. Some consideration is being given to an extension to Ligne 2 of the tramway, beyond the current eastern terminus of the Lympia port, towards the principality of Monaco. “It would provide a second rail line between the metropolis of Nice Côte d’Azur and Monaco, and be an alternative to the TER PACA network.” [20]
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nice_tramway, accessed on 26th October 2023.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20130515035144/http://www.lignesdazur.com/presentation/?rub_code=9&thm_id=7&gpl_id=, accessed on 26th October 3023.
- https://www.frenchrivieratraveller.com/Nice/Transport/Tramway.html, accessed on 26th October 2023.
- https://www.railway-technology.com/projects/nice-trams/?cf-view, accessed on 24th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/ligne-1/hier-aujourdhui, accessed on 24th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/actualites, accessed on 24th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/ligne-4/enquete-publique-du-lundi-12-juin-au-vendredi-21-juillet-2023-inclus, accessed on 24th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Ligne-4-tramway-rapport-d-enquete.pdf, accessed on 24th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Ligne-4-tramway-CONCLUSIONS-DUP-MECDU.pdf, accessed on 24th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/questions-reponses/#faq_27231, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/ligne-5/le-projet-de-la-ligne-5-de-tramway-nice-la-trinite-drap, accessed on 25tj November 2025.
- https://projets-transports.nicecotedazur.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/MNCA_TRAM-L4_BROCHURE_TT-SAVOIR_A4_BD.pdf, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://saintlaurentduvar.fr/blog/ligne-4-du-tramway-l-enquete-publique-est-lancee, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://twitter.com/Elodieching/status/1484215486867021824?t=JFKe_qZVQzGO-STX2SqQrQ&s=19, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://www.lemoniteur.fr/article/metropole-de-nice-la-t5-une-ligne-de-tram-vertueuse.2215172, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://www.nicematin.com/transports/approuve-a-lunanimite-trace-prefere-craintes-exprimees-bon-depart-pour-le-projet-de-tramway-entre-drap-et-nice-777378, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://www.investincotedazur.com/ligne5-tramway-nice, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://fr.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligne_2_du_tramway_de_Nice, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://www.pss-archi.eu/forum/viewtopic.php?pid=835184, accessed on 25th November 2023.
- https://www.intelligenttransport.com/transport-news/18414/tram-design-revealed-for-the-east-west-line-of-the-nice-cote-dazur-metropole, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://www.railway-technology.com/projects/citadis-x05-light-rail-vehicles, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nice_tramway_place_Garibaldi.jpg, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ligne_2_Tram_de_Nice_07-20.jpg, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://moovitapp.com/index/en/public_transit-line-L1-Nice-3260-854686-771043-0, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://www.batiactu.com/edito/ligne-2-tramway-nice-arrive-a-aeroport-54985.php, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://www.frenchrivieratraveller.com/Nice/Transport/Tramway.html, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://www.nice.fr/fr/transports-et-deplacements/la-ligne-3, accessed on 26th November 2023.
- https://fr.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligne_3_du_tramway_de_Nice, accessed on 26th November 2023.