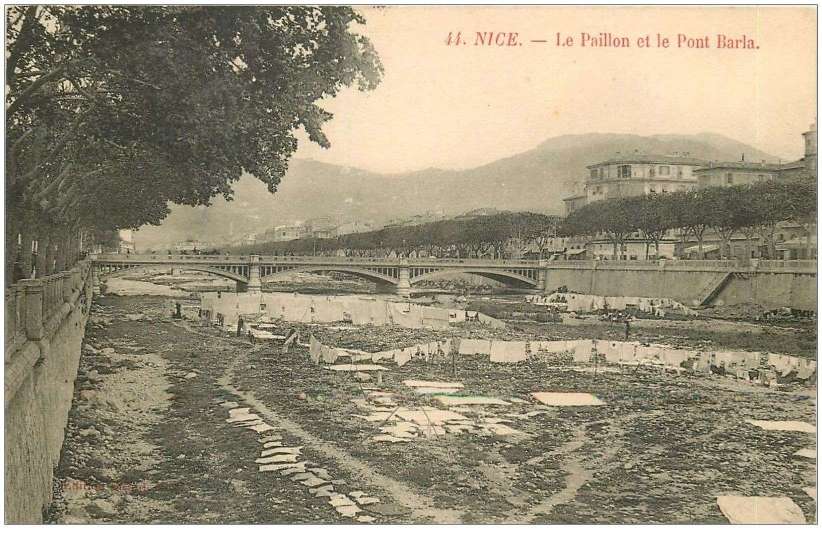
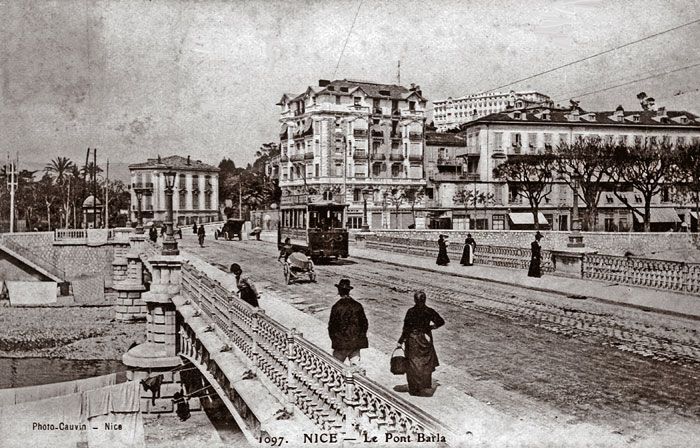
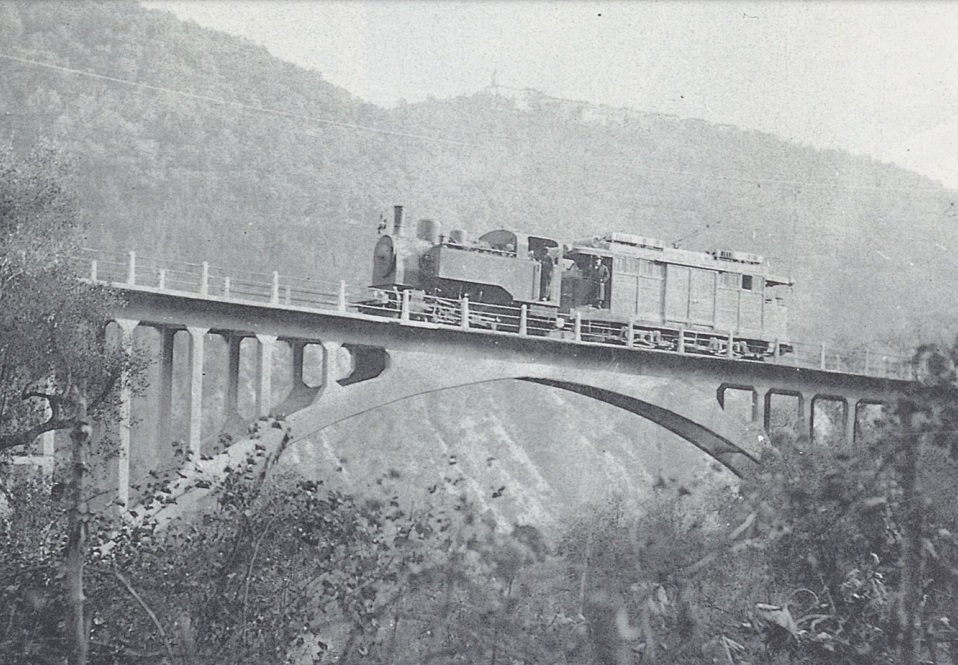
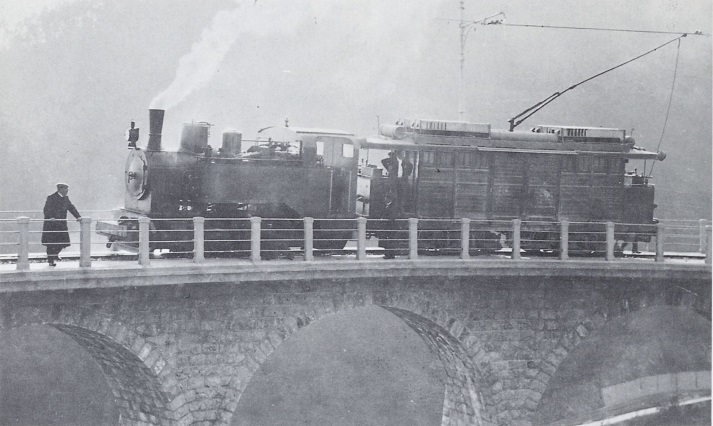
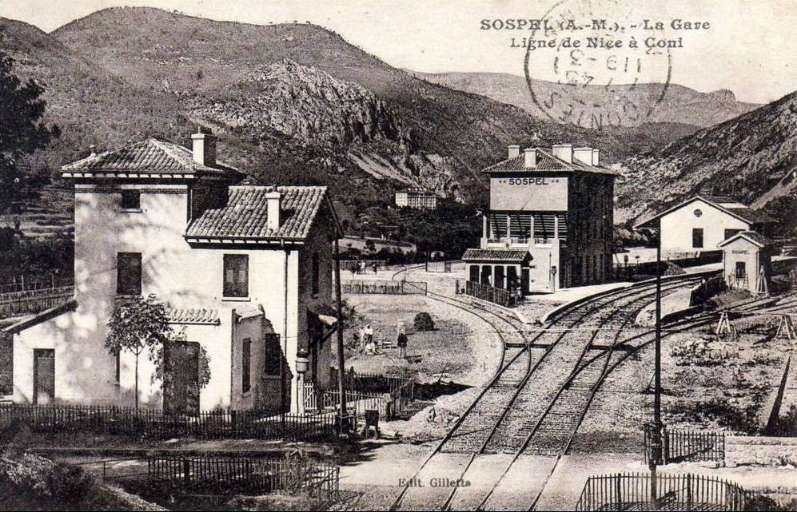
The featured image above shows an unidentified steam locomotive crossing the highly unusual Viaduc de Bevera. The train is heading toward Sospel.
In the first five articles about the line from Cuneo to the sea we covered the length of the line from Cuneo to Breil-sur-Roya and then to Ventimiglia. These articles can be found here, [9] here [10] here, [11] here, [12] and here [13]
I want to acknowledge that a series of stills from a video of the train journey from Breil-sur-Roya to Nice have been used in this article. The video can be seen here. [4]
This article begins the journey from Breil-sur-Roya to Nice.
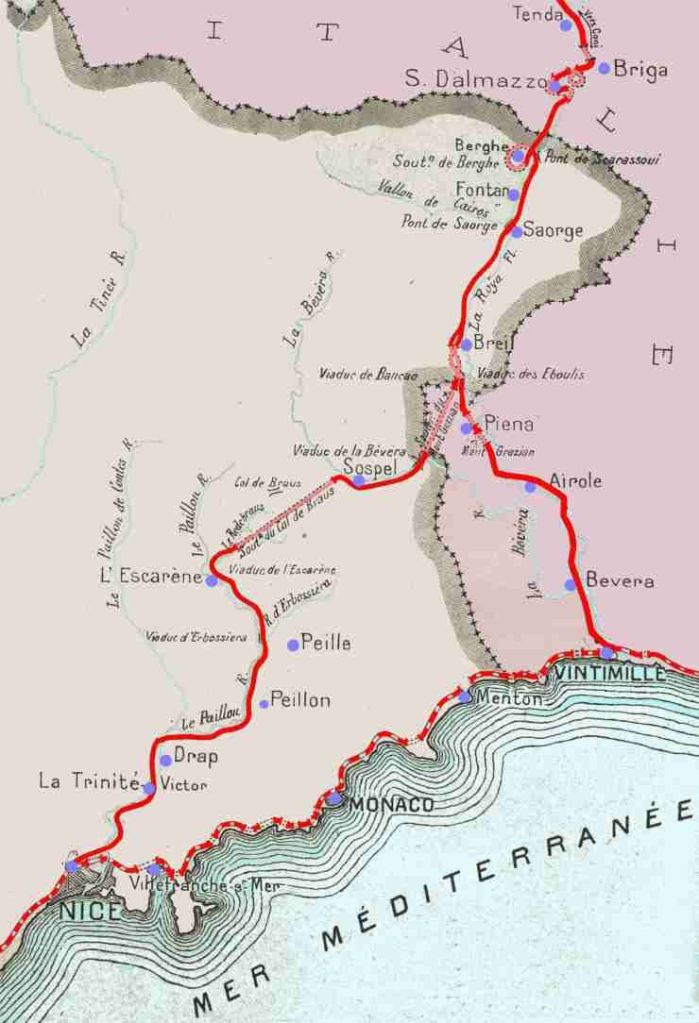
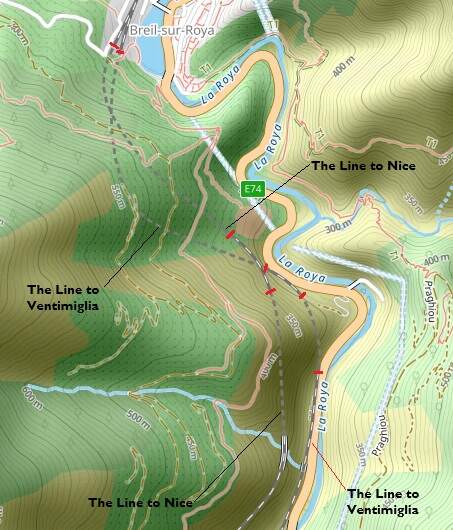
South of Breil-sur-Roya a junction allows direct access to Ventimiglia and to Nice. The map below shows the two routes as they existed prior to the alteration of the border between France and Italy after the Second World War.
The project was finally agreed by the PLM on 7th January 1907 but various portions of the work would be delayed by disputes relating to the transfer of land. “Acquisitions began in the suburbs of Nice in May 1907, at Saint-Roch … and Roccabiliera, where the PLM had decided to build a vast facility with a goods station, marshalling yard and engine depot to relieve congestion at Nice central station, whose rights of way, enclosed in the urban fabric, could no longer expand. This program for the redesign of Nice’s railway facilities also provided for a 3,610 m connection between the new Saint-Roch station, Riquier station and the port. In the hinterland, events also began to take shape and in December 1908, a section of engineers set up in Fontan and undertook the first work along the Roya the following January.” [1: p90]
Banaudo et al continue: “In 1909, Chief Engineer Paul Séjourné (1851-1939), then fifty-eight years old and already renowned for his original designs for civil engineering structures, took over the direction of the construction department. The line from Nice to the Italian border would give him the opportunity to exercise his talent in the design of structures that were as daring as they were harmoniously integrated into the landscape.” [1: p90]
In this series of articles, we have already seen Séjourné‘s Scarassoui Viaduct spanning La Roya to the North of Breil-sur-Roya.
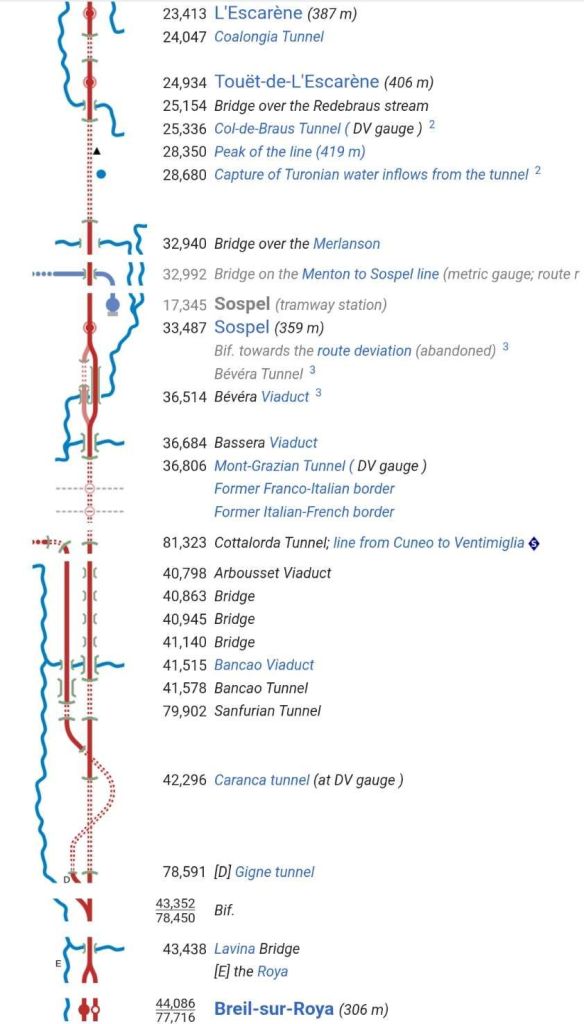
This article follows the line South from Breil-sur-Roya to l’Escarene in two parts. The first from Breil to Sospel and the second from Sospel to l’Escarene.
1. The Line South from Breil-sur Roya to Sospel
Banaudo et al tell us that, “In December 1912, tranches 8 and 9 were awarded in turn for a length of 10,500 m from Sospel to Breil to the François Mercier company, of Moulins-sur-Allier. The work included three tunnels with a combined length of 5,307 m, including the Mont Grazian and Caranca structures established at double-track gauge and equipped with defensive devices, as well as seven bridges and viaducts representing twenty-five masonry arches and two metal spans. Among them, the exceptional structure of the Bévéra viaduct. There were also three culverts and three level crossings in this section.” [1: p102-103]
Banaudo et al take up a significant part of Volume 1 of the story of the line with an album of photographs of the construction work on the French side of the border. [2: p152-331] A superb record of the work undertaken.
On the Sospel-Breil section of the line the contract works were gradually completed. By the end of 1921, the Bancao and Caranca tunnels were completed. The Mont Grazian tunnel was finished in 1923. The Bévéra viaduct’s abutments and masonry arch were ready by then and only awaited the delivery of the metalwork of the decking. [1: p141]
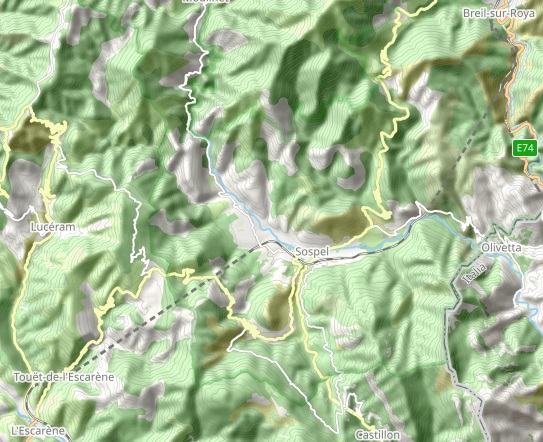
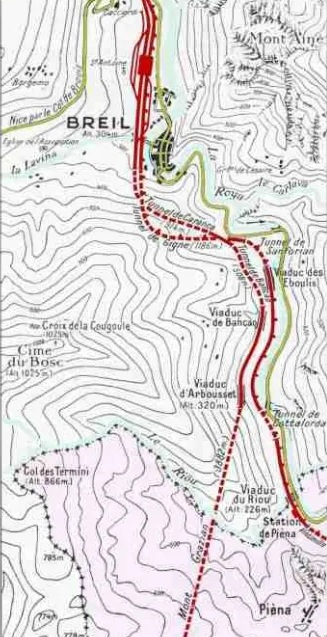
This drawing/map shows the two routes heading South from Breil-sur-Roya. [40]
As with the line immediately to the North of Breil-sur-Roya, the works to the South and Southwest were constructed by the French. Both of the lines heading South from Breil-sur-Roya entered tunnels just a short distance South of Breil.
The first length of the line South of Breil-sur-Roya is common with the line to Ventimiglia. The two lines separate at the Lavina bridge.
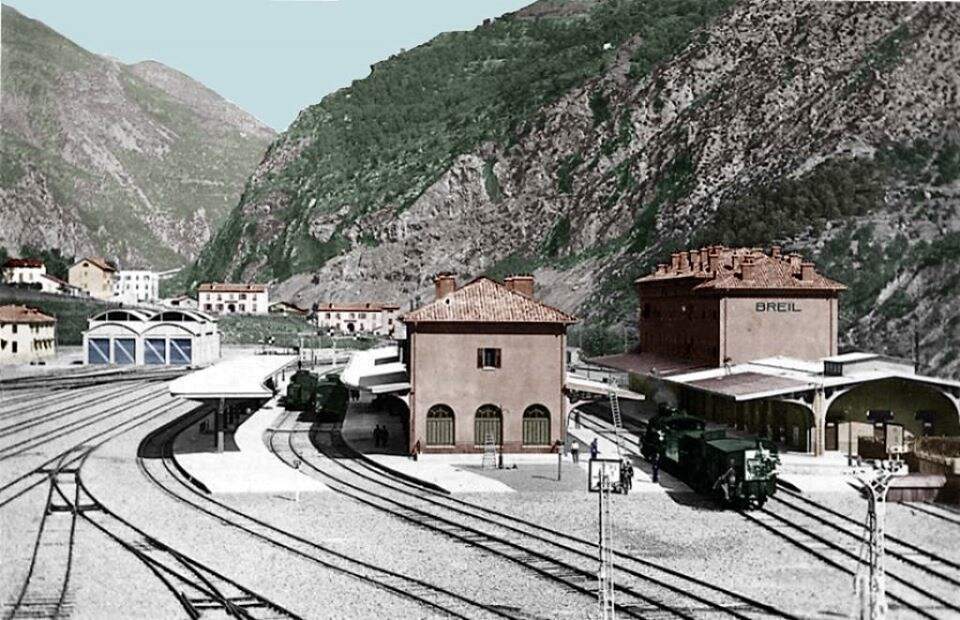
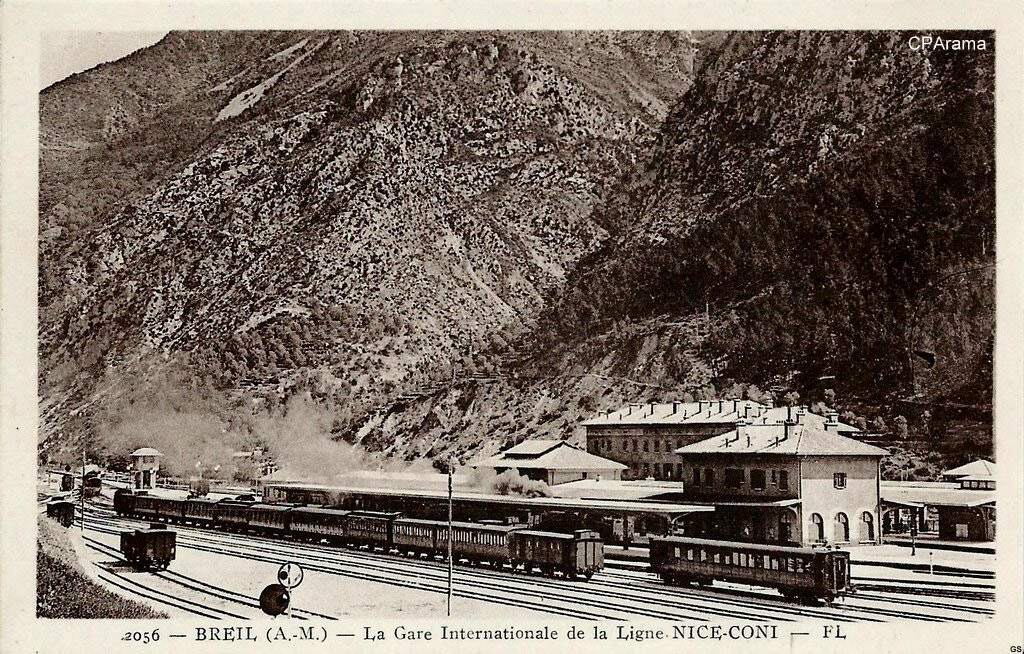
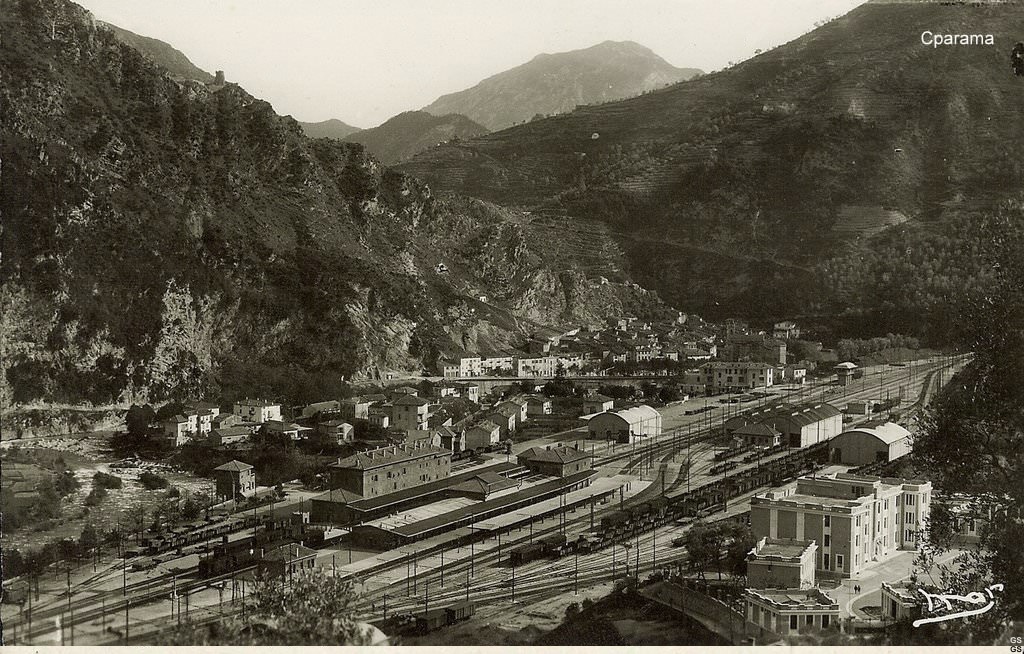
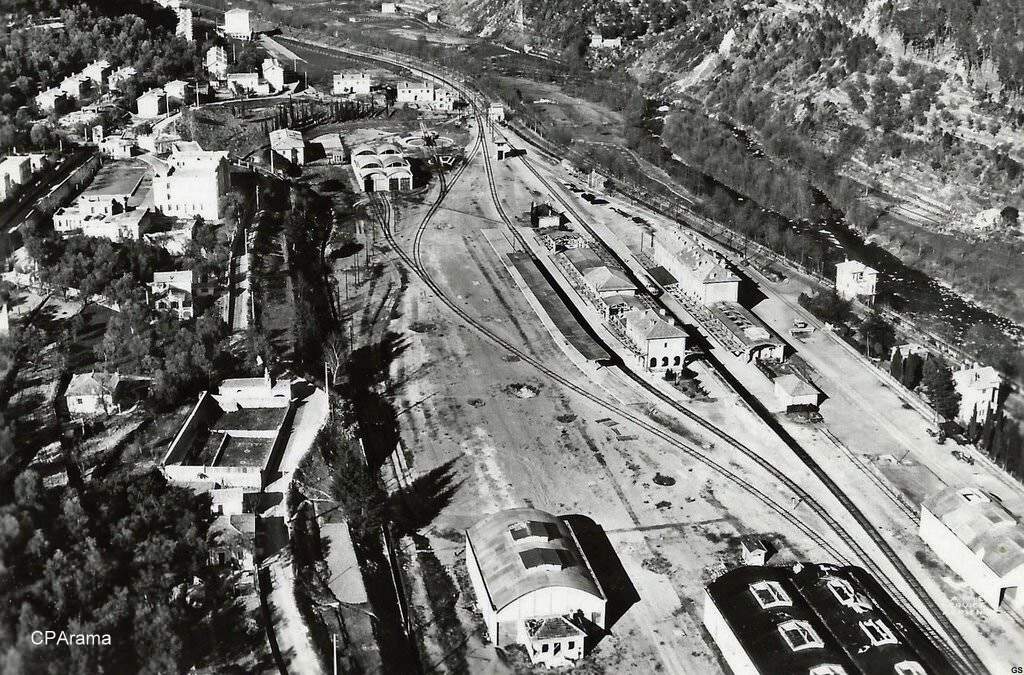
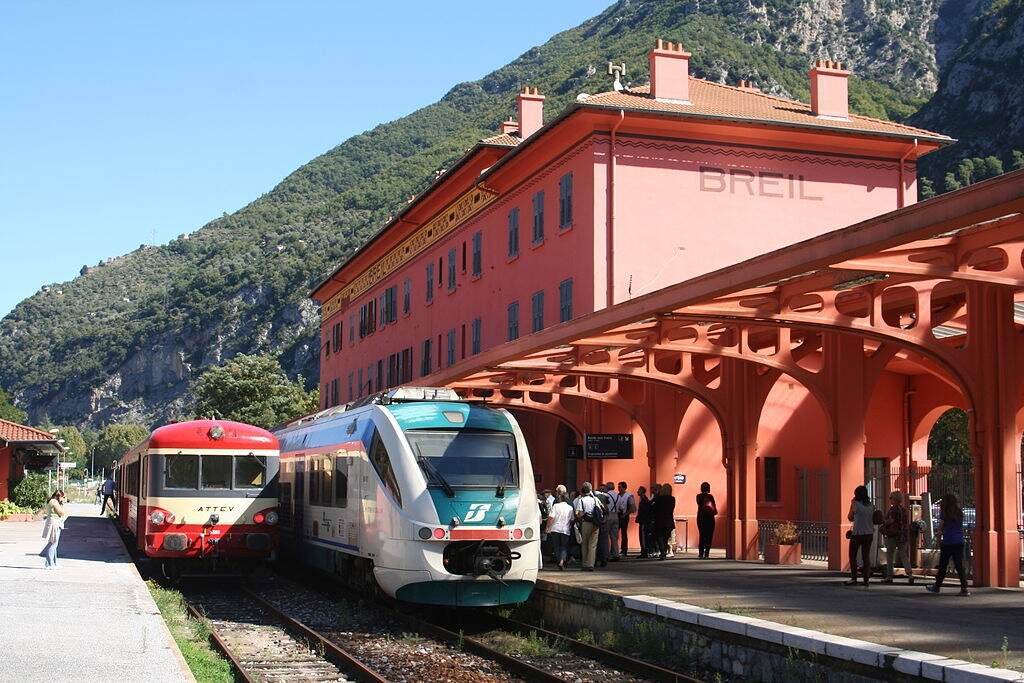






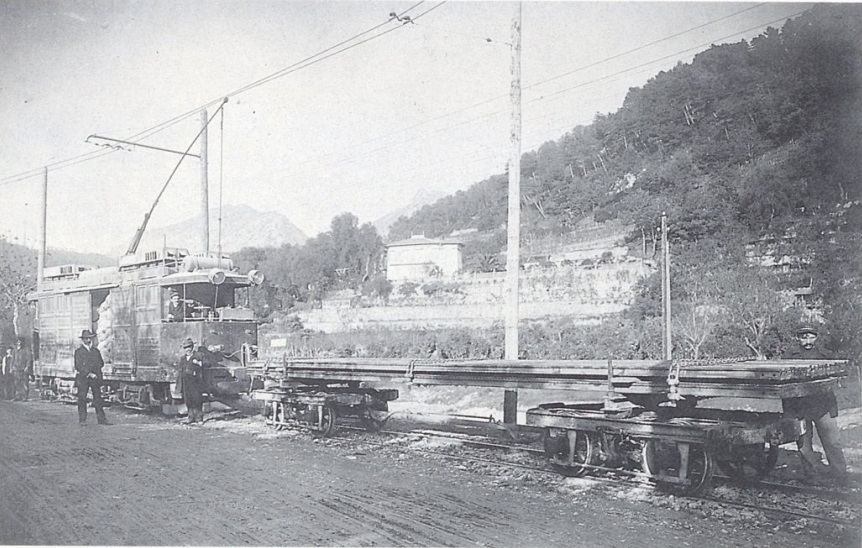
The view from the cab of a Nice-bound service waiting to set off from Breil-sur-Roya. [4]
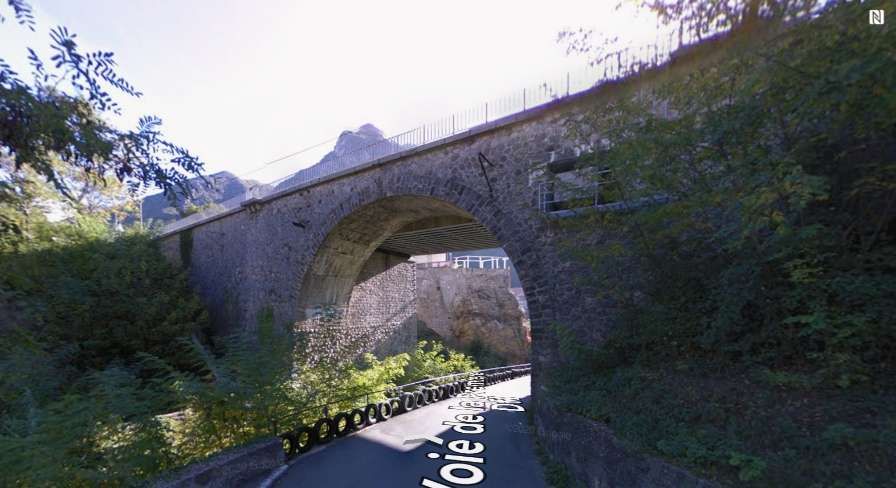
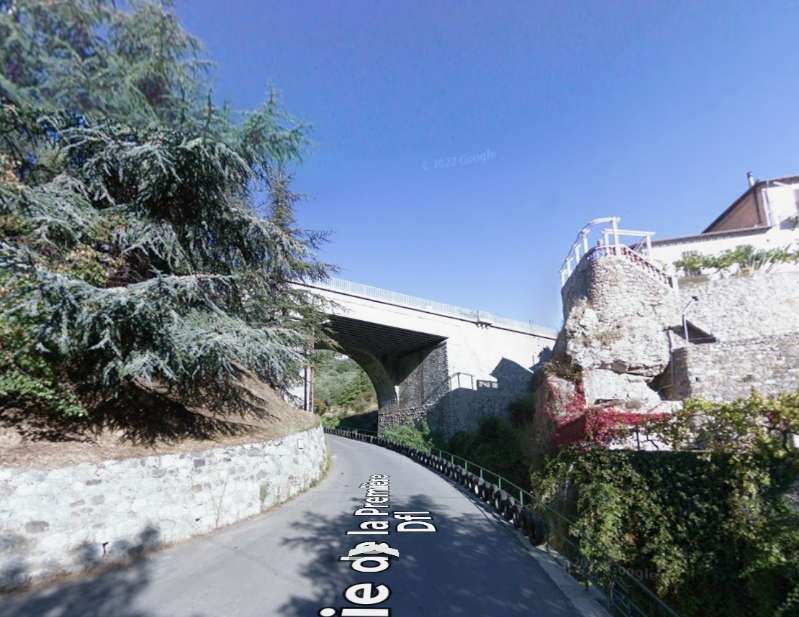
South of the station adjacent parallel bridges cross the Voie de la Première Dfl and Vallon de la Lavina (the Lavina Bridge).

Lavina Bridge seen at rail-level from the cab of the Nice-bound train. [4]
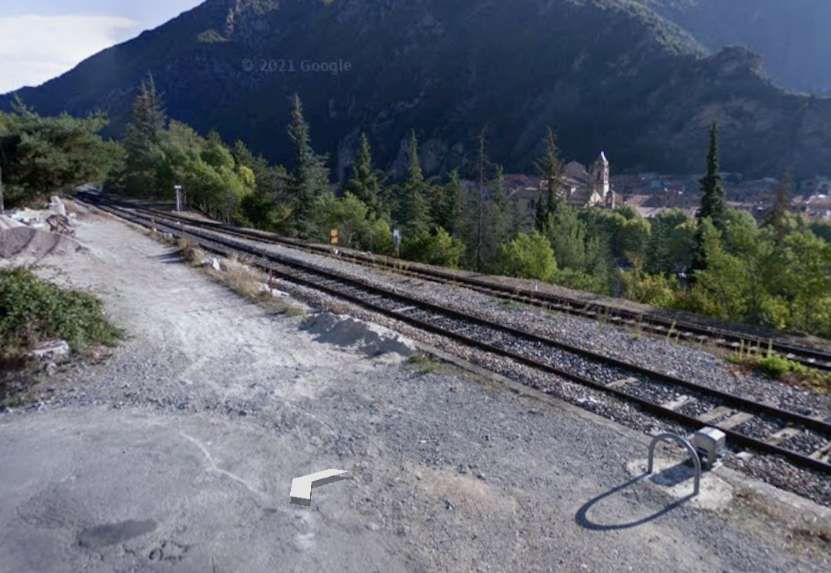
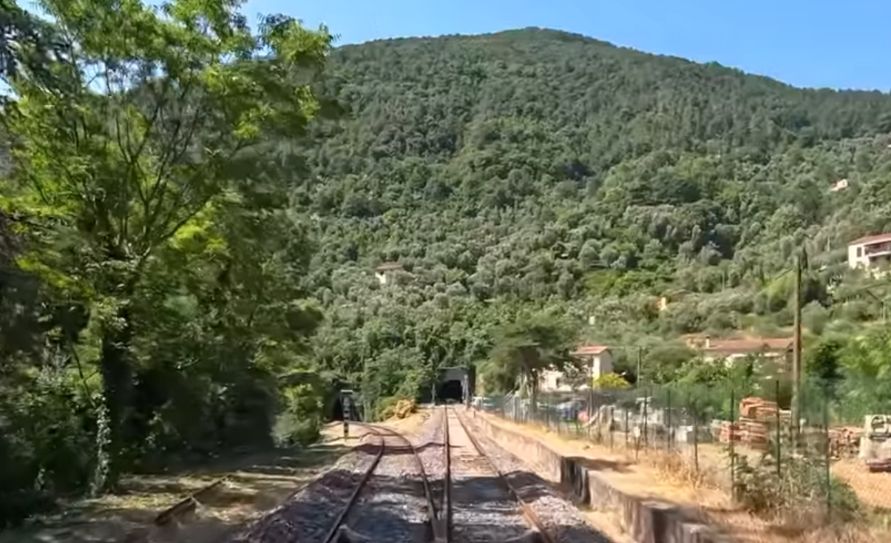






The two tunnel mouths seen from the cab of a Nice-bound service. [4]


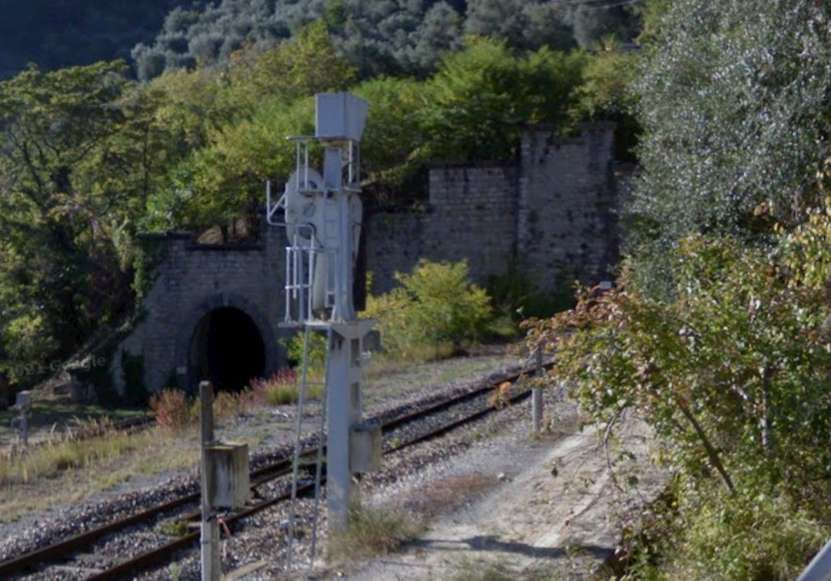
Caranca Tunnel North Portal prior to vegetation growth. The tunnel was built to accommodate double-track to allow for possible future growth in traffic. [20]

The North portal of Caranca Tunnel in the 21st century (915 metres long). [4]
The route of Caranca Tunnel crosses twice over the Gigne Tunnel which is on the Ventimiglia line. The lines to both Nice and Ventimiglia are shown as dotted lines when in tunnel. [1: p126]

Nice-bound trains exit Caranca Tunnel heading Southeast. This is the view from the cab of a Nice-bound train. [4]

Turning round to face the Tunnel portal, this is the Southeast portal of Caranca Tunnel. [20]

The next tunnel is Tunnel de Bancao (508 metres long). This is the North portal of the tunnel. [4]


The South portal of Bancao Tunnel gives way onto Viaduc Bancao. [19]

The line leaves Bancao Tunnel and immediately crosses Bancao Viaduct. [4]
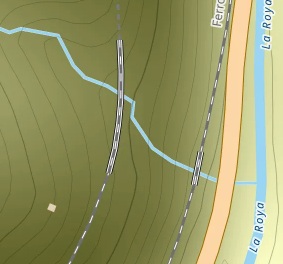
Bancao Viaduct on the line from Breil-sur-Roya to Ventimiglia is a single span arch close to the D6204 on this extract from OpenStreetMap. The line to the West is the line we are now following from Breil-sur-Roya to Nice which is at a much higher level and its viaduct is a multi-span structure. [15]

Both the Nice line and the Ventimiglia line can be seen in this image. That to Nice is at the higher level. The longer viaduct at the lower level is Viaduc Eboulis. Viaduc Bancao is at the higher level. [18]

An earlier monochrome view of Viaduc Bancao. The viaduct has eight 9 metre arches. [18]
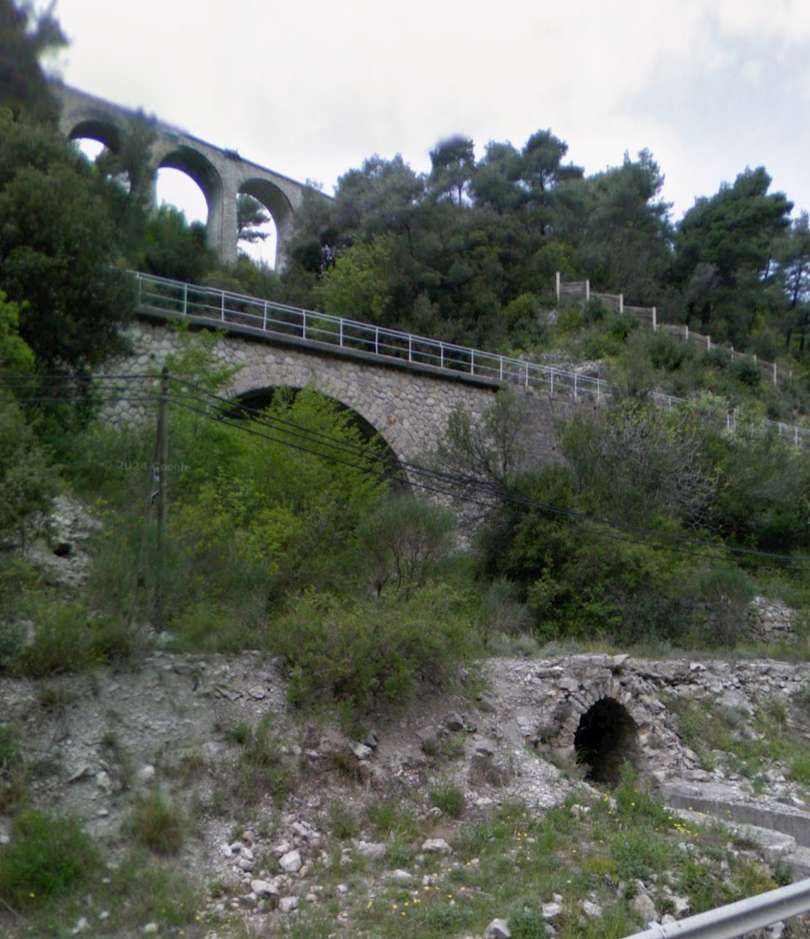

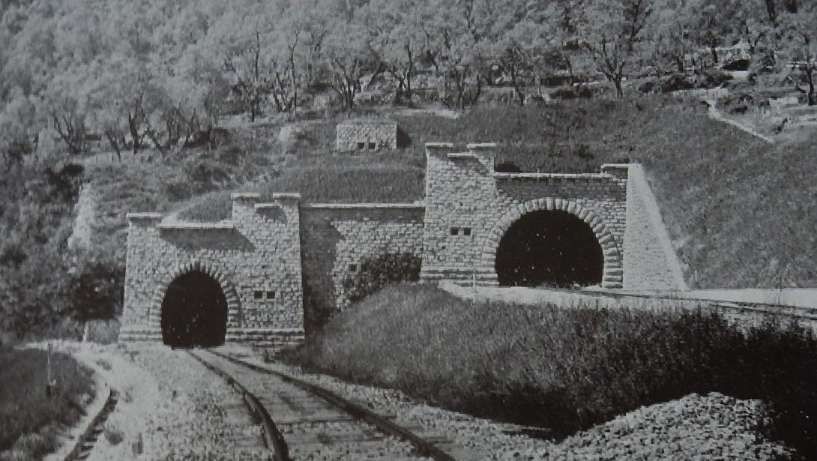
Looking West from the D6204/E74, a small culvert close to the road is dwarfed by the bridge carrying the line to Ventimiglia which in turn is dwarfed by the viaduct carrying the line to Nice. [Google Streetview, April 2008]
Viaduc de Bancao on the Nice to Breil-sur-Roya line appears, in part, at the top of this image.

The two rail lines are still running in parallel, only beginning to separate significantly at the bottom of this extract from Open StreetMap.
The line we are following enters the Mont Grazian Tunnel, bottom right of this OpenStreetMap extract. [16]
Before the Tunnel three structures are crossed – two 10 metre-span arched bridges and then Viaduc d’Arbousset none of the three are marked on this map extract. The Viaduct sits at the point where the line which has been curving round to the South begins to turn to the Southwest, just before entering Mont Grazian Tunnel. [16]

Viaduc d’Arbousset (63 metres long with three 7 metre arches). Ahead the line curves to the right and enters Mont Grazian Tunnel. [4]

The Northeast portal of the Tunnel de Mont Grazian, seen from the cab of a Nice-boud train. [4]
The Mont Grazian Tunnel was built wide enough to accommodate double-track to allow for possible future traffic growth. “It was lined with defensive measures at both ends, a precaution imposed by the major strategic importance of this structure, which connects the Roya and Bévéra valleys.” [1: p94] Details of the defensive measures can be found here. [27]

The Northeast portal of Tunnel de Mont Grazian. This view from above shows the Viaduc d’Arbousset and the high retaining wall on the right of the mouth of the tunnel. [27]
Tunnel de Mont Grazian is 3891 metres in length. [27]

The view Southeast from the cab of the Nice-bound service as it leaves the tunnel mouth. A very short distance beyond the tunnel mouth the line crosses Viaduc de Bassera. [4]

Turning through 180, the Southwest portal of the Tunnel de Mont Grazian. [27]
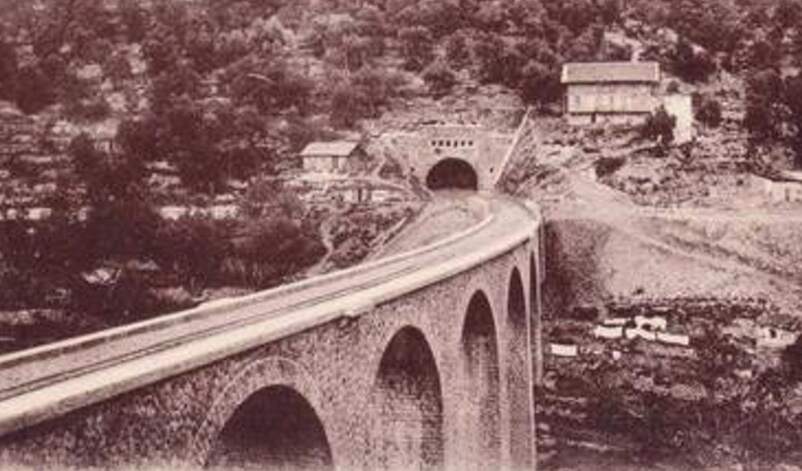
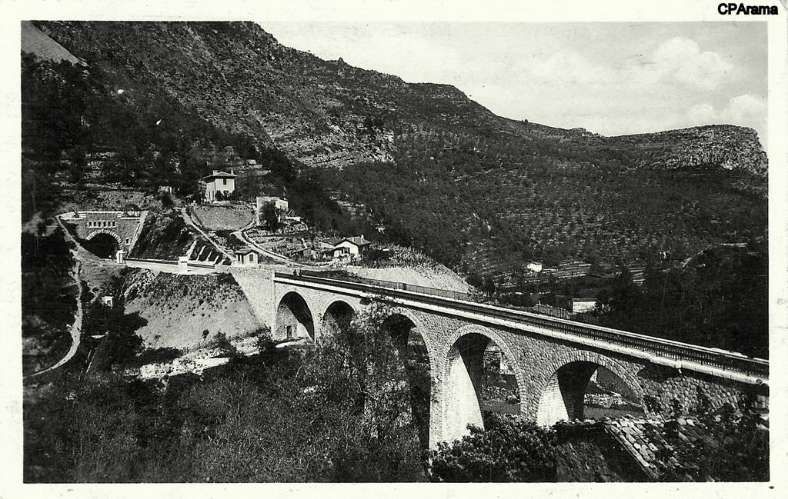


The Bassera Viaduct is curved with seven 12-metre arches and crosses the Basséra River.

A broader view of the Viaduc de Bassera at the time of its construction, (c) Public Domain. [23]

In this image, Viaduc de Bassera is on the right and Viaduc Cai (over the River Bevera) is on the left. [23]

The two bridges as seen on Google Earth. [Google Earth, August 2025]

The original bridge over the Bevera (Pont de Cai) which was built in time for the opening of the line in 1928. More details can be found here. [24]

A very short distance beyond the end of Viaduc de Bassera, the line crosses the River Bevera on another viaduct – Viaduc Cai. [4]
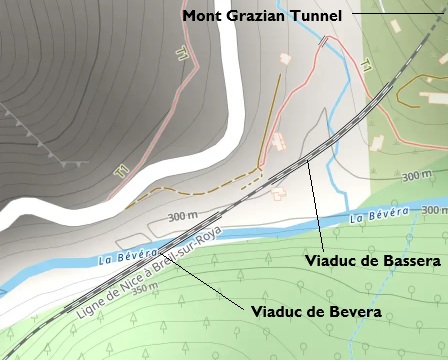
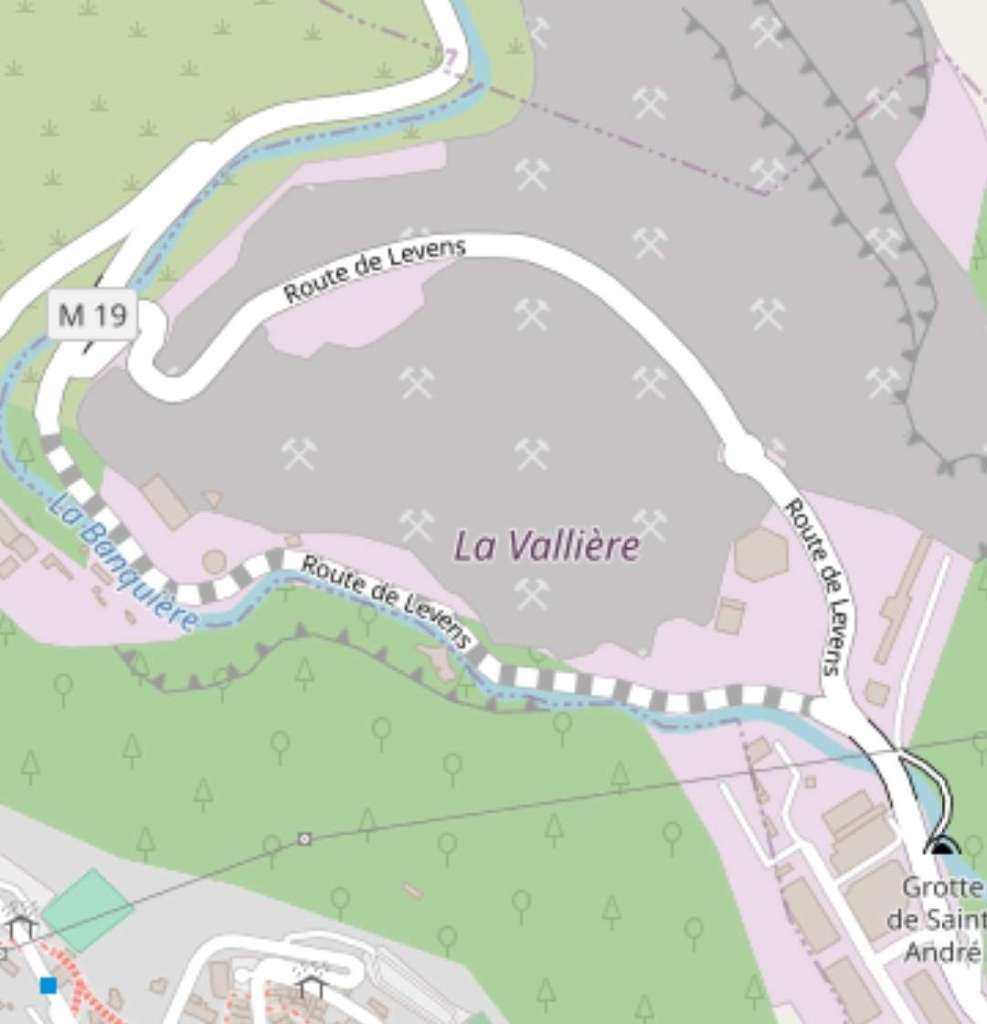
This extract from OpenStreetMap illustrates the proximity of the two viaducts and Mont Grazian Tunnel. [22]
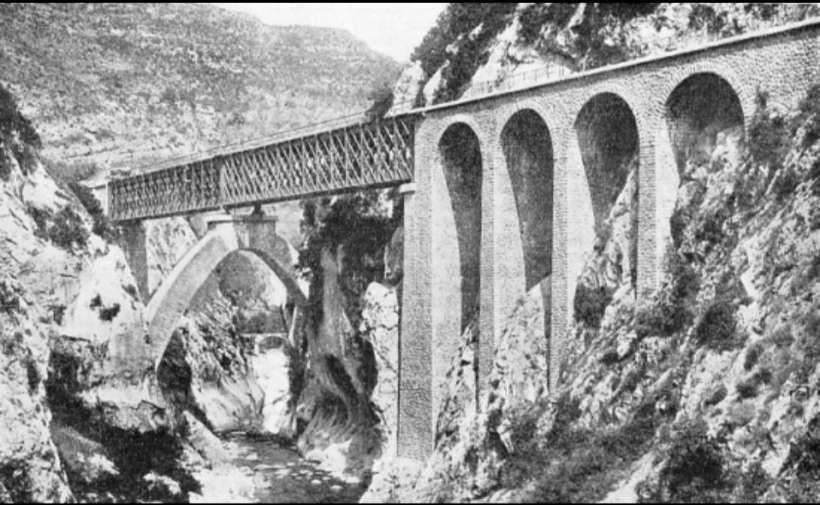
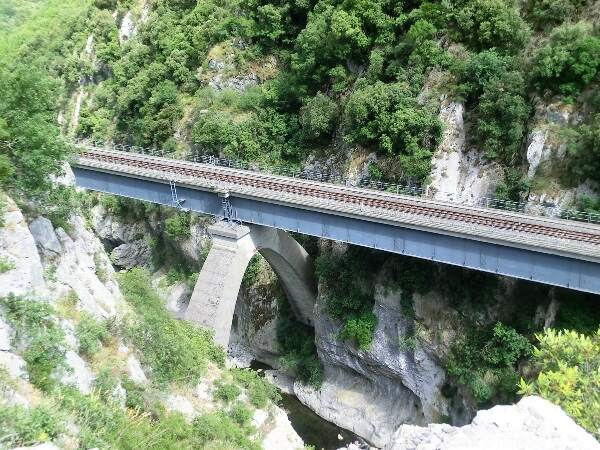
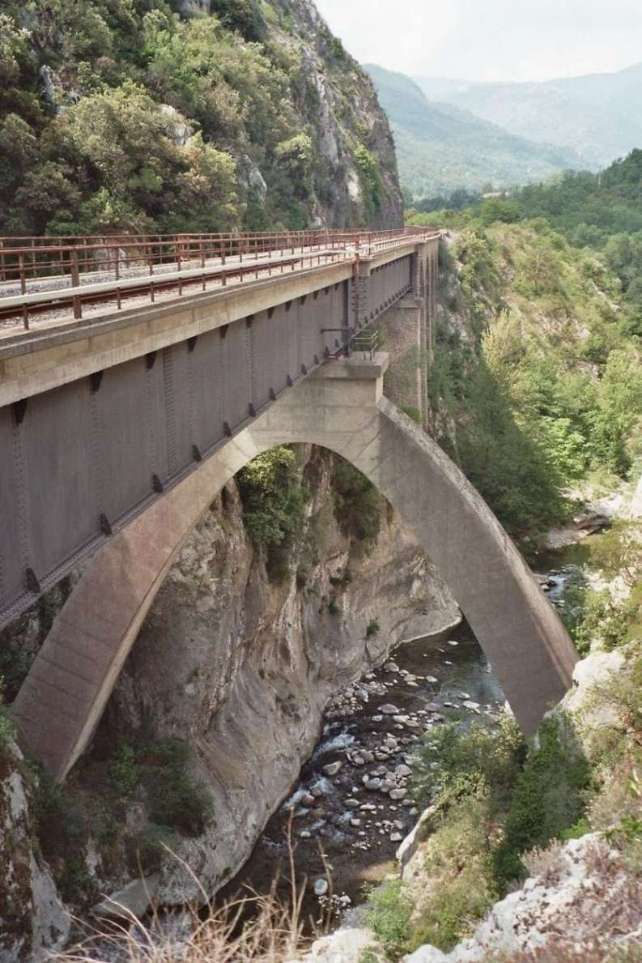



The Bevera Viaduct was an ingenious design solution to the need to thread the line through the narrow Bevera Gorge to the East of Sospel. Engineer: Paul Séjourné, © Markus Schweiss and licenced for reuse under a Creative Commons Licence (CC BY-SA 3.0). [26]

Due to its proximity to the Italian border, this unused tunnel (marked with a red arrow) was built for strategic reasons as part of the Maginot Plan for the defense of the SFAM (Fortified Sector of the Alpes Maritimes). [28]
It was intended to provide an emergency route in the event that the large neighboring Caï viaduct needed to be destroyed, and to store the metal spans of a replacement viaduct. [28]

Halfway along its length, on the left wall, it has an annex gallery (tunnel window – marked by the yellow arrow) which opens onto the western abutment of the Caï viaduct. More information can be found here. [28]
The Bevera River flows West to East (its confluence with La Roya (Roia) is adjacent to the village of Bevera which sits on the North bank of the Bevera River). Once across the Bevera River on the Cai Viaduct, the line heads up a gradient of 17 mm/m to Sospel Railway Station.
The route of the line between Breil-sur-Roya and Sospel was determined by the military. The military authorities dictated that the line should be routed to ensure that it could “be easily intercepted by the artillery of The Barbonnet fort, above Sospel, in the event of an infiltration attempt from the Roya valley.” [1: p92 & 94]
The Cai or Bevera Viaduct “crosses the river at a very acute angle. [This] inspired an original arrangement by Paul Séjourné: the deck, formed of two metal spans of 45.30 m, framed by four masonry arches of 8 m, rests 30 m above the river on a perpendicular arch of 25 m opening and egg-like in shape, resting transversely on the walls of the gorge.” [1: p94]
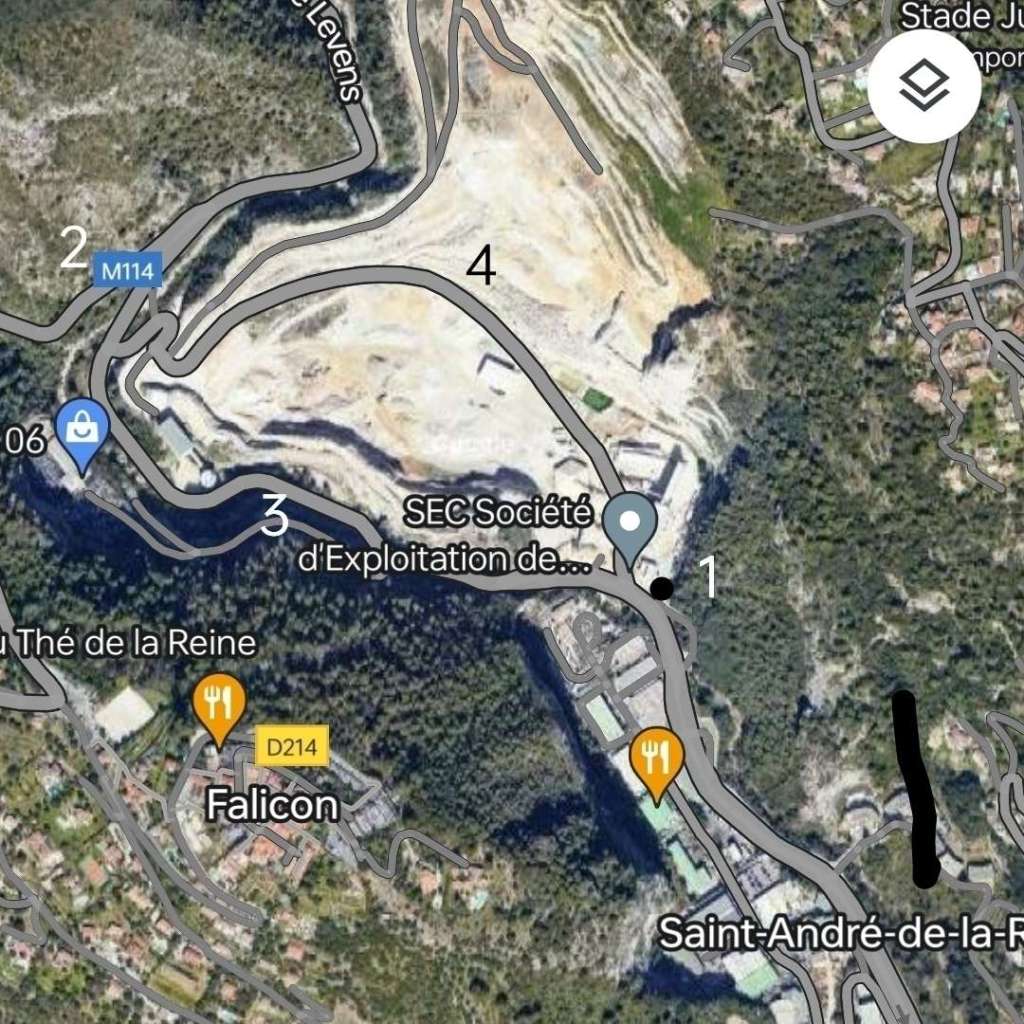
The line follows the valley side to the South of the Bevera rising, as we have already noted at a gradient of 17 mm/m. It crosses a minor road by means of a level crossing (Route de Suez).

The level crossing at Route de Suez, seen from above. [Google Maps, August 2025]

The level crossing at Route de Suez seen from the cab of a West-bound train. [4]

The next level crossing on the line is immediately at the East end of Sospel Railway Station site. [Google Maps, August 2025

The same crossing seen from the cab of the Westbound train approaching Sospel Railway Station. [4]



Further West and fully within what was the station site but which in the 21st century is an open plateau of unused land. [4]

The station passing loop seen at its eastern end from the cab of the Westbound train. [4]

The final approach to Sospel railway Station from the East. [4]

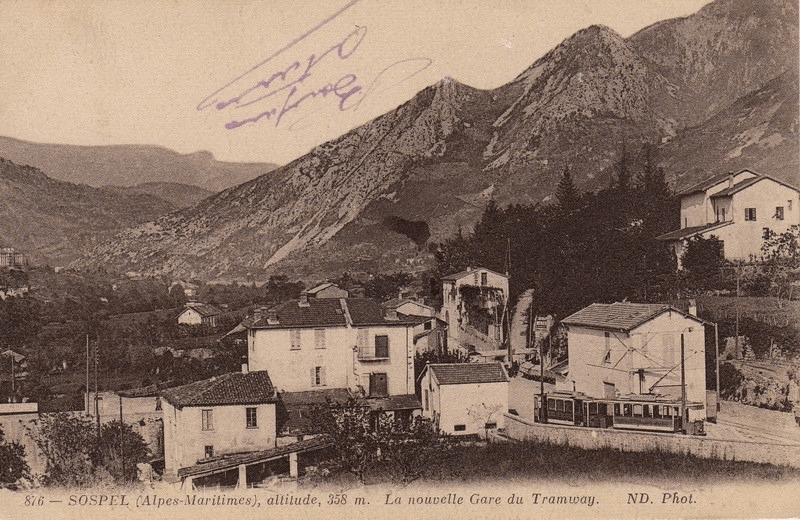
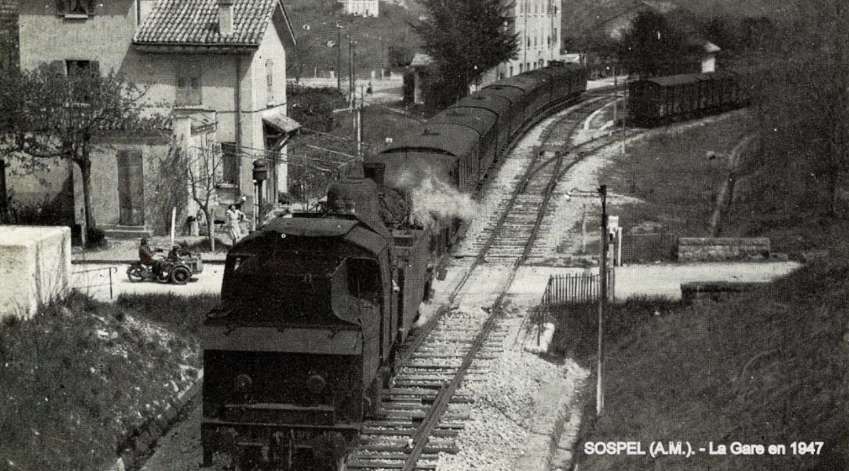
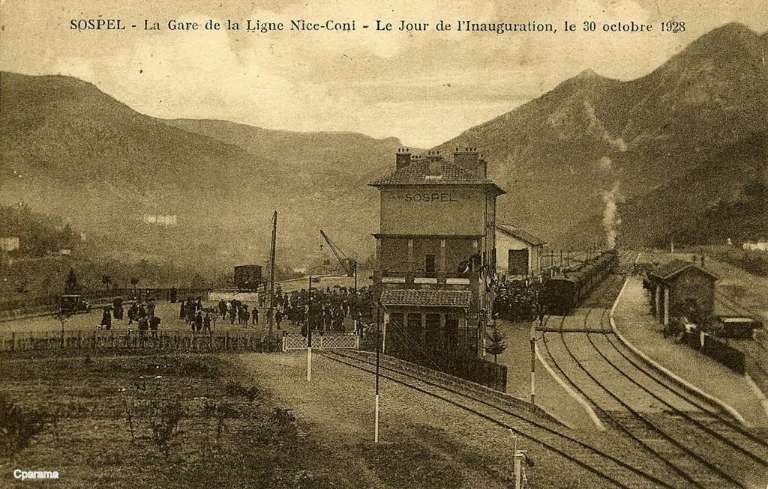
Sospel Railway Station. [4]
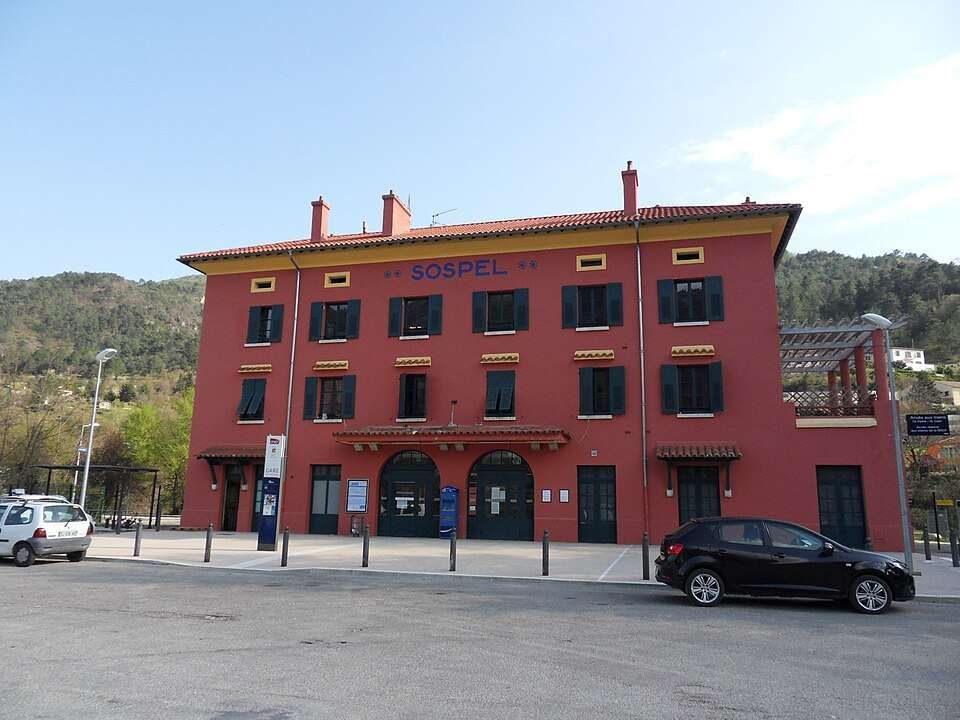
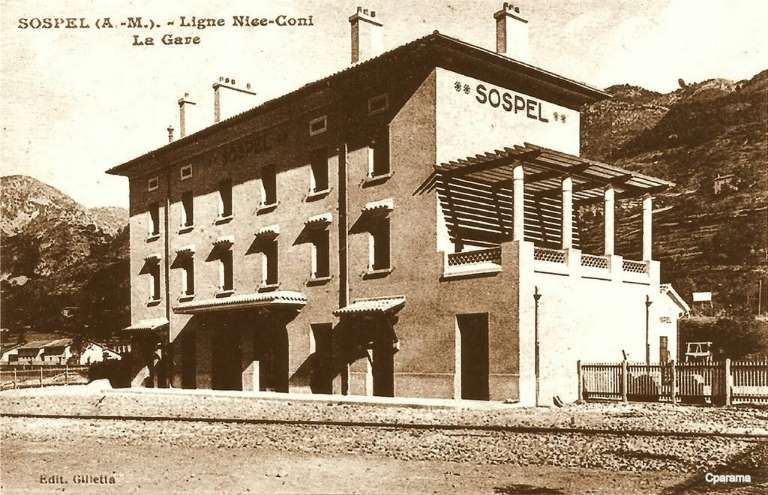



Sospel Railway Station was to be a station “with substantial facilities which would allow the reception of military convoys in the event of conflict with neighboring Italy.” [1: p92] Arriving on Sospel, trains from Breil-sur-Roya pass through a large flat open area which was designed to accommodate the needs of the military.
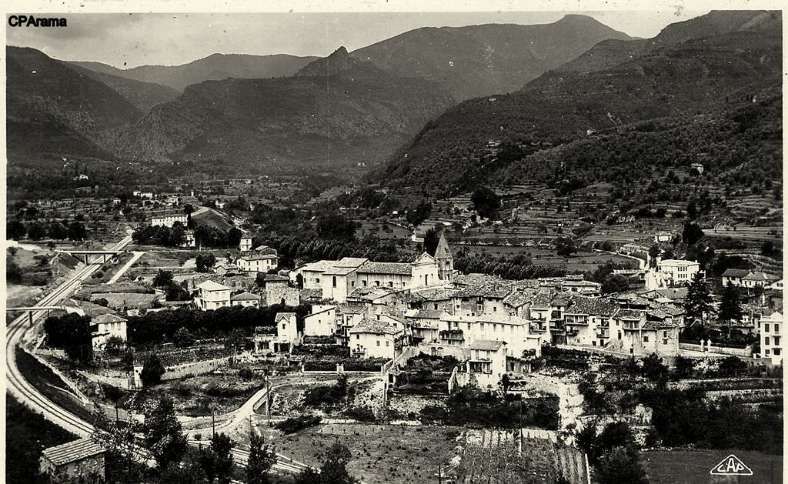
The town was, in the middle of the 19th century, the second city of the County of Nice. “The location of Sospel … in … a basin where the Bévéra Valley widens, is very unique. From wherever one arrives from France, one must cross a pass: the Braus pass coming from Nice, the Castillon pass towards Menton, the Brouis pass towards Breil and La Roya, and the Turini pass towards La Bollène and La Vésubie. Towards Italy, the Vescavo Pass road connects Piena and Olivetta, while downstream, the Bévéra flows in impassable gorges where one could only venture on foot.” [1: p101-102]
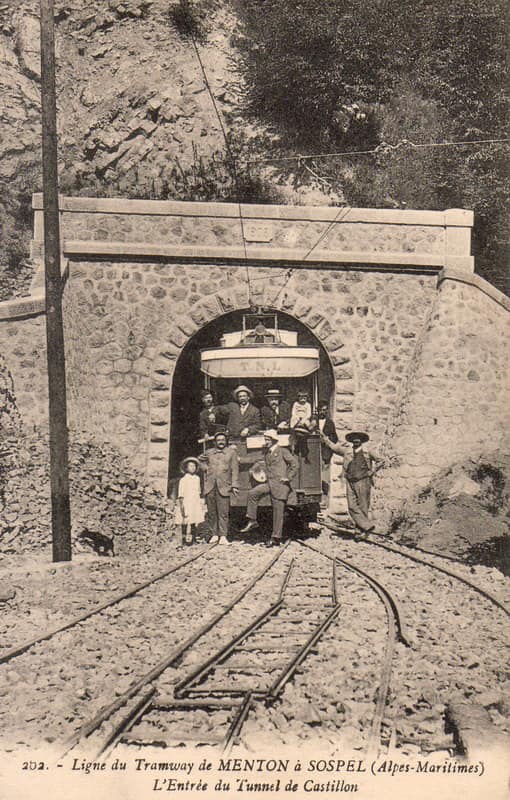
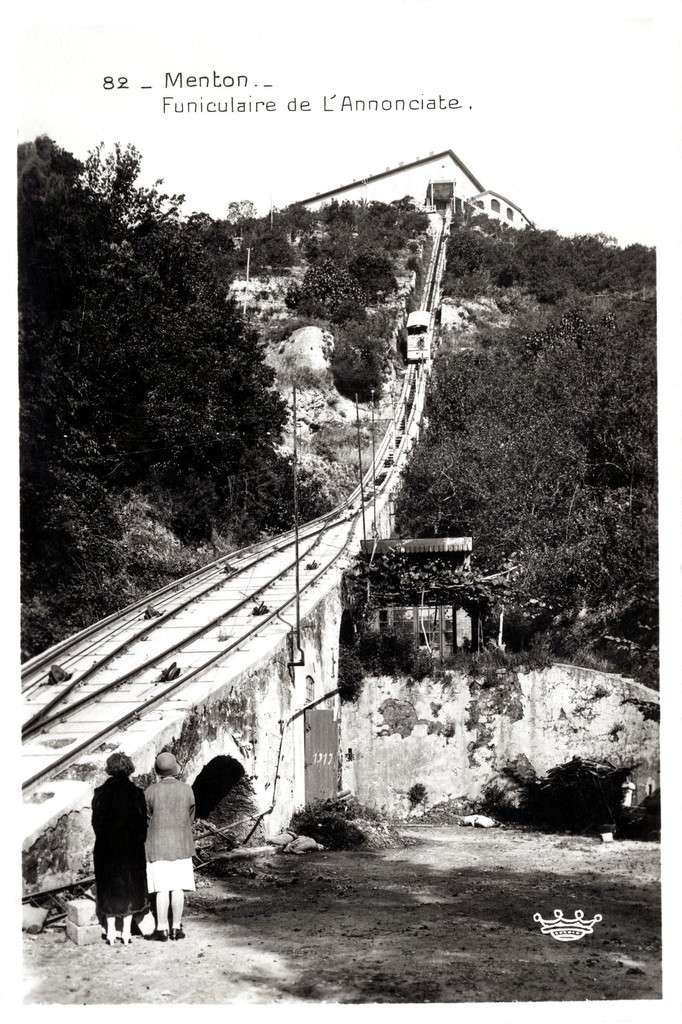
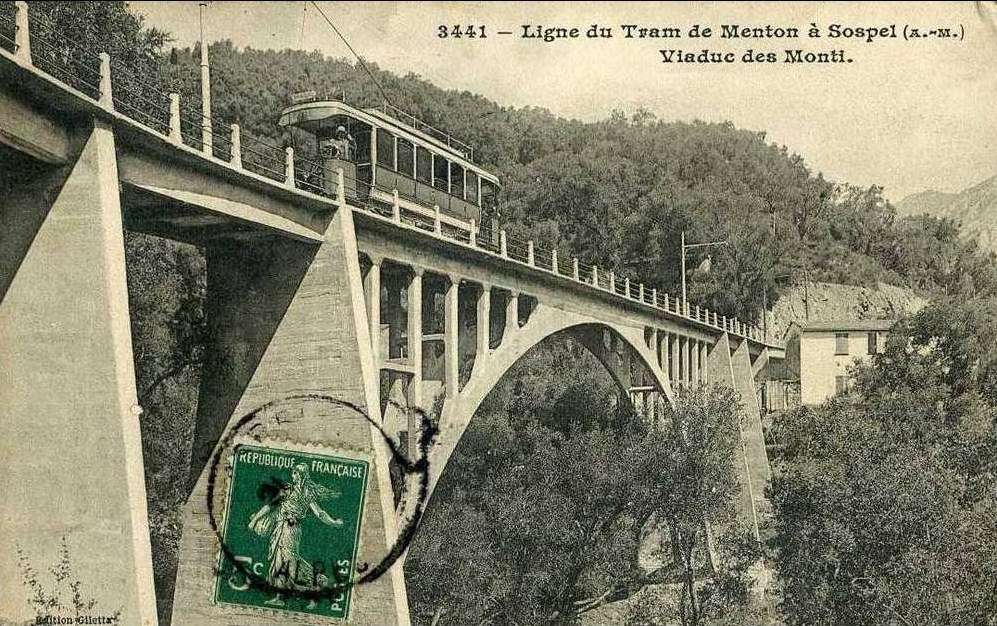
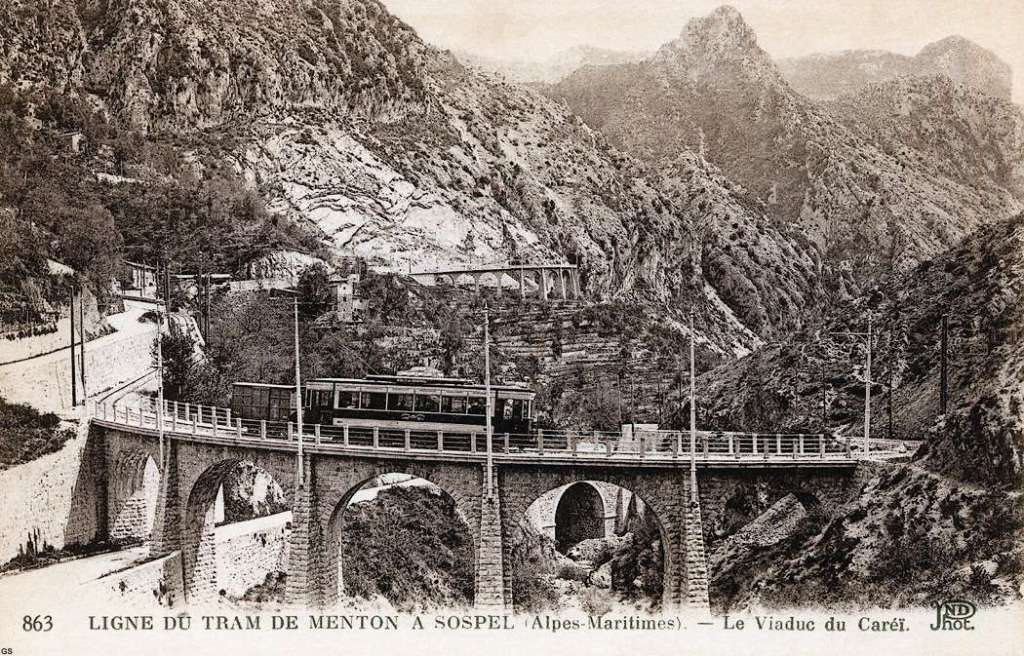
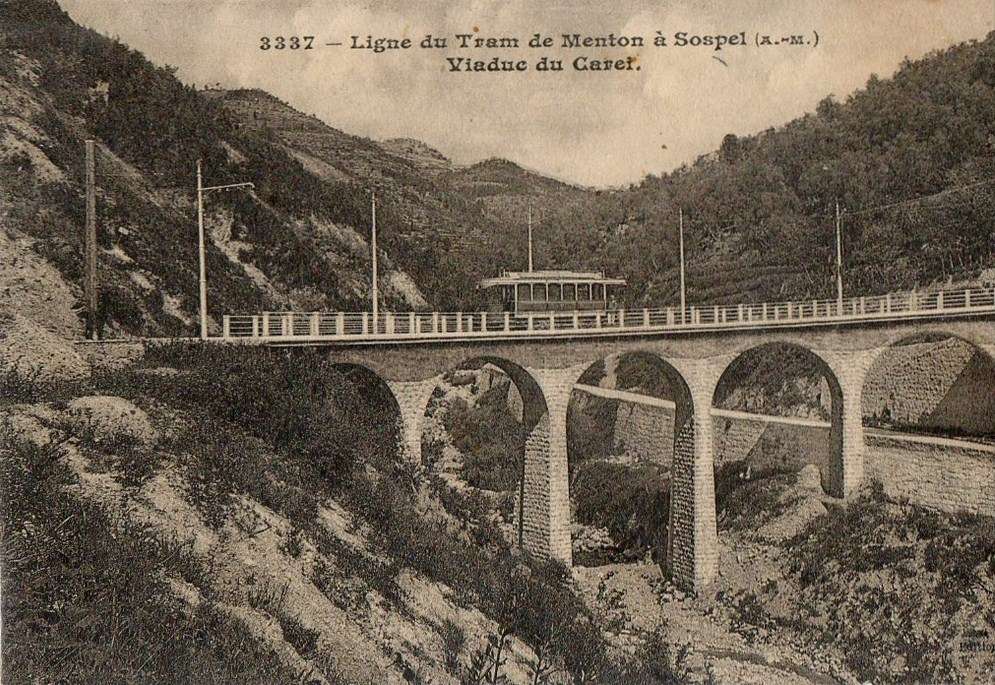
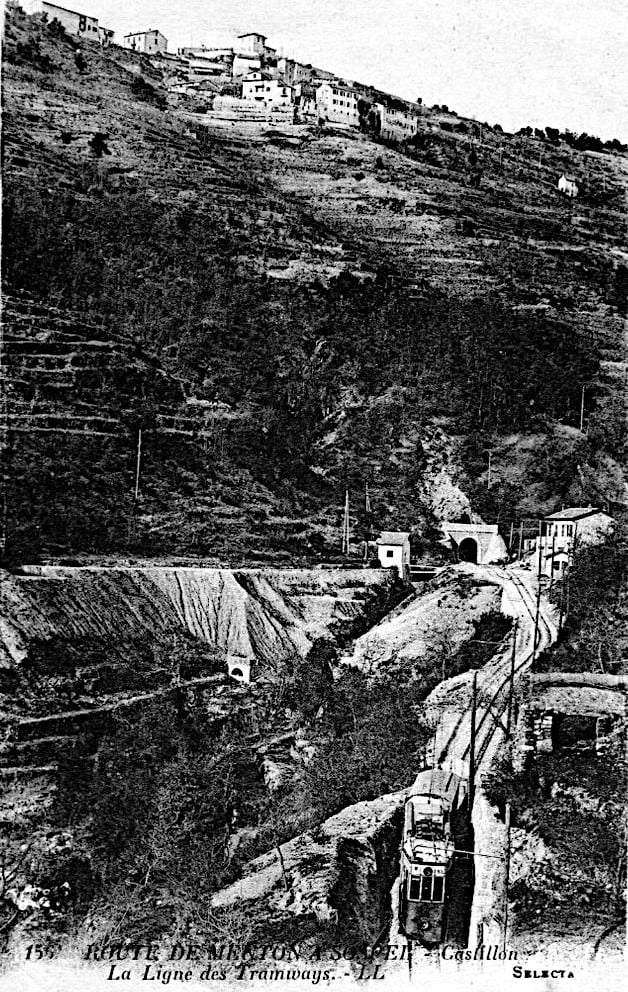
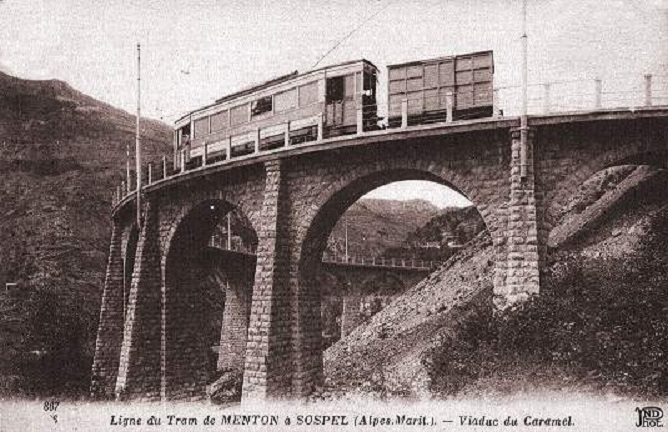
The year 1912 was quite momentous in the history of Sospel not only was construction work getting underway but on 15th April 1912 the Compagnie des Tramways de Nice et du Littoral (TNL) opened its Menton-Sospel tramway. More about the tramway can be found here, [36] here [37] and here. [38]
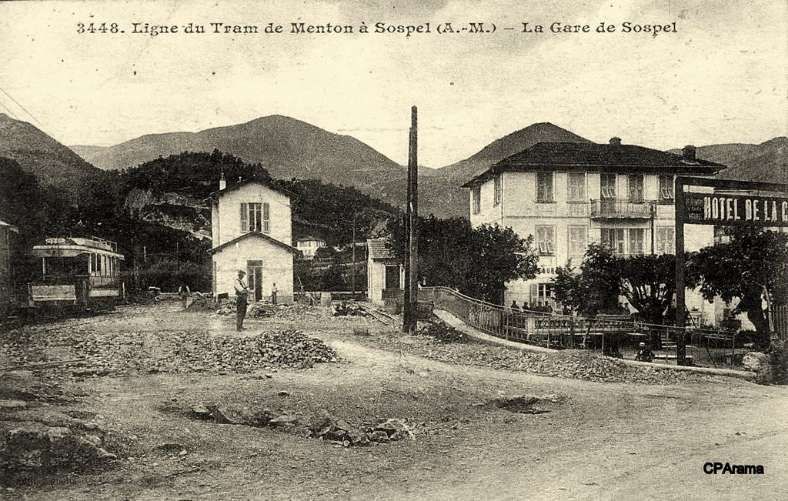

Banaudo et al comment that “The Gianotti company immediately took advantage of this opportunity to transport the tools and equipment from Nice that would be used for the construction of the Braus tunnel. … In the initial stages of the construction, the Gianotti brothers used a network of portable 0.60 m gauge railways, on which Decauville dump trucks pulled by horses ran. Later, one-metre gauge tracks were laid, on which steam locomotives pulled larger capacity trains, consisting of Koppel wagons with a load of 6 m³ or wooden-bodied wagons with a capacity of 3 m³. Several locomotives from the contractor were brought to site via the tramway, coupled to a ‘mortrice electrique’ (an electric tram engine) as a safety measure on the steeply graded tramway.” [1: p102]
“In the early months of 1913, the Mercier company got to work and obtained permission from the TNL company to open a special branch line at each end of the Menton-Sospel tramway line. The construction site’s supplies then provided the tramway with more than half of its freight traffic. In July 1913, two to three round trips ran daily, and in October, Mercier received 745 tons of materials in Sospel. In May 1914, the Gianotti brothers opened their own branch line in the Careï Valley in Menton, but soon, the saturation of the small freight yard and insufficient equipment forced the TNL to limit shipments to five wagons per day.” [1: p103]
2. Sospel to l’Escarene
The journey from Sospel to l’Escarene takes the line through and under the mountains of the Col de Braus.
The line climbs through a series of embankments and cuttings on a gradient of 9.5 mm/m and enters the Tunnel de Braus.It continues to climb within the tunnel to a high point of 420 metres above sea level. Within the tunnel the gradient then changes to a 2 mm/m downward grade towards l’Escarene. The tunnel was double-track both to aid ventilation and to allow for possible expansion of services if demand required it. At the insistence of the military defensive fortifications surrounded the two tunnel mouths. [1: p92]
Of the 12 tranches of contract work on the French side of the international border, two tranches covered the 9.7 km length between Sospel and l’Escarene – lots 6 and 7. The work was awarded in December 1911 and April 1912 to Jean and Antonin Gianotti. Banaudo et al tell us that the work included over 6.4 km of tunnel. “As well as a few secondary structures: three culverts, four level crossings, two underpasses and six overpasses, most of which were built using the new reinforced concrete technique.” [1: p101]
After waiting for a Breil-sur-Roya-bound service to clear the line ahead, we set off in a Westerly direction from the station at Sospel.

A Nice to Breil-sur-Roya service arriving at Sospel. [4]

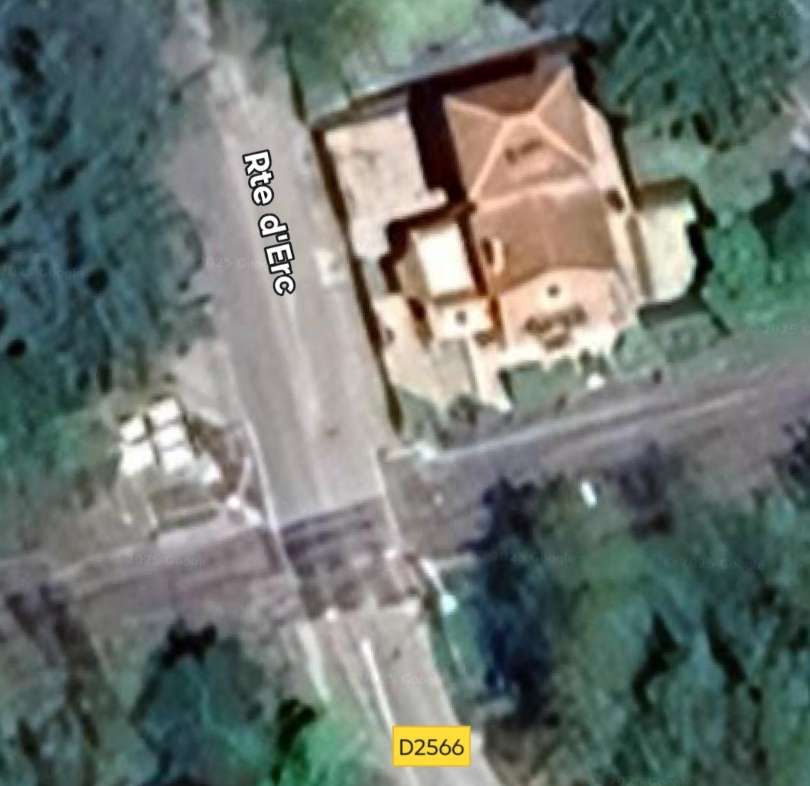
As the Nice-bound train sets off from Sospel Station it crosses Rte d’Erc at a level-crossing. [4]







A closer view of the bridge carrying Mnt des Capuchins. [4]





The bridge carrying Chemin de la Saint-Roch over the line as seen from the cab of a Nice-bound train. [4]



The next overbridge carries the D2204 (boulevard de l’Egalite over the line. [4]
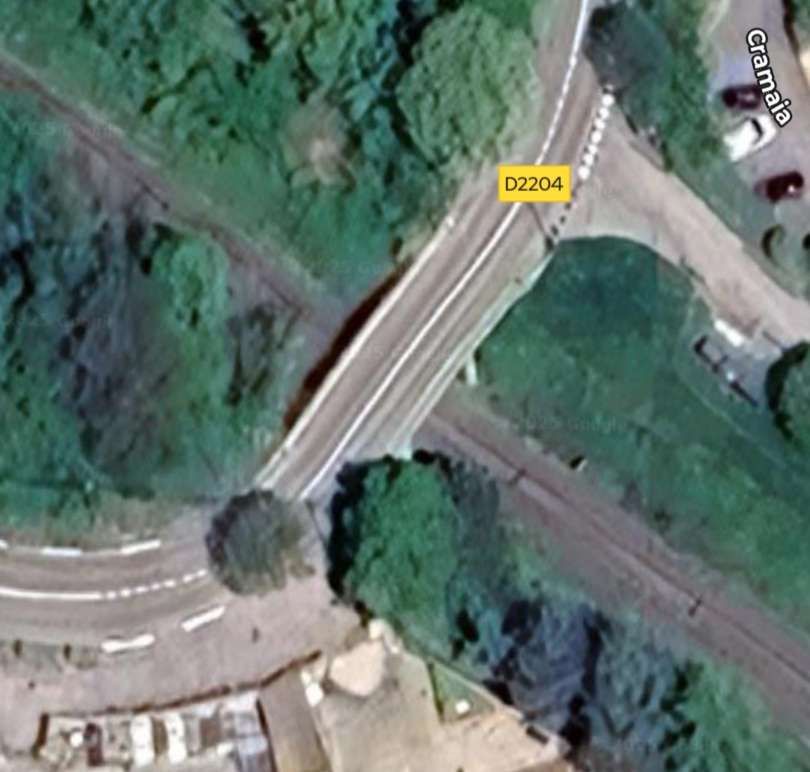
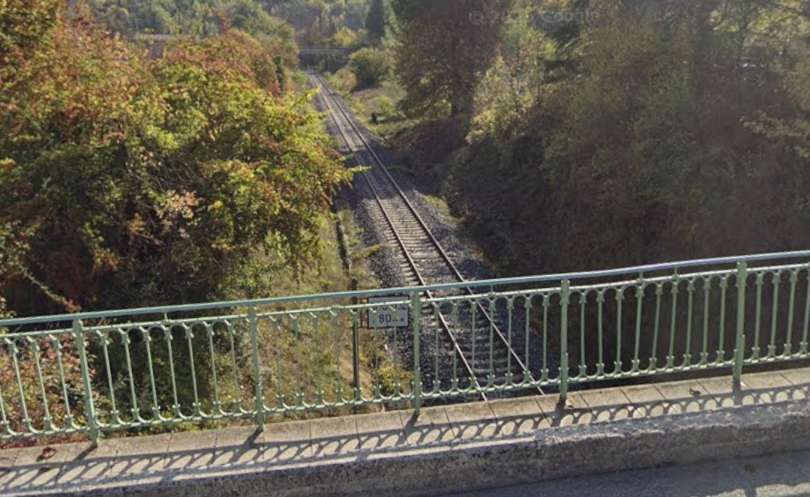
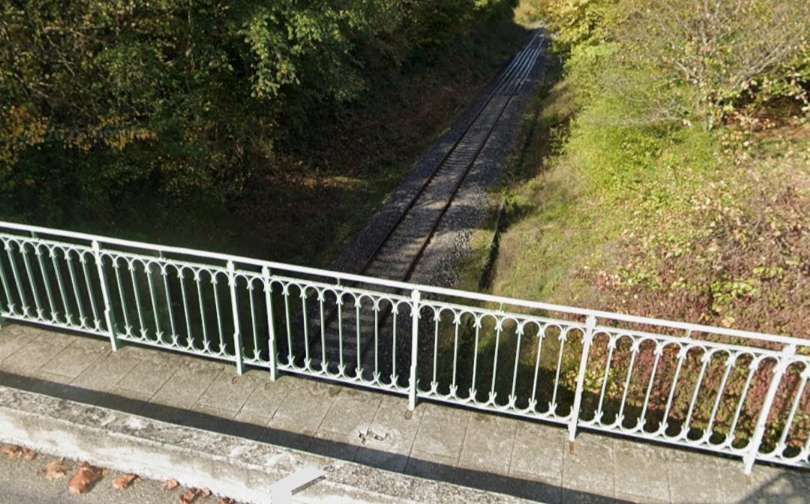




The next structure visible form the cab of the Nice-bound train is an accommodation bridge which carries a driveway to a larger property running Northeast from La Condamine. [4]
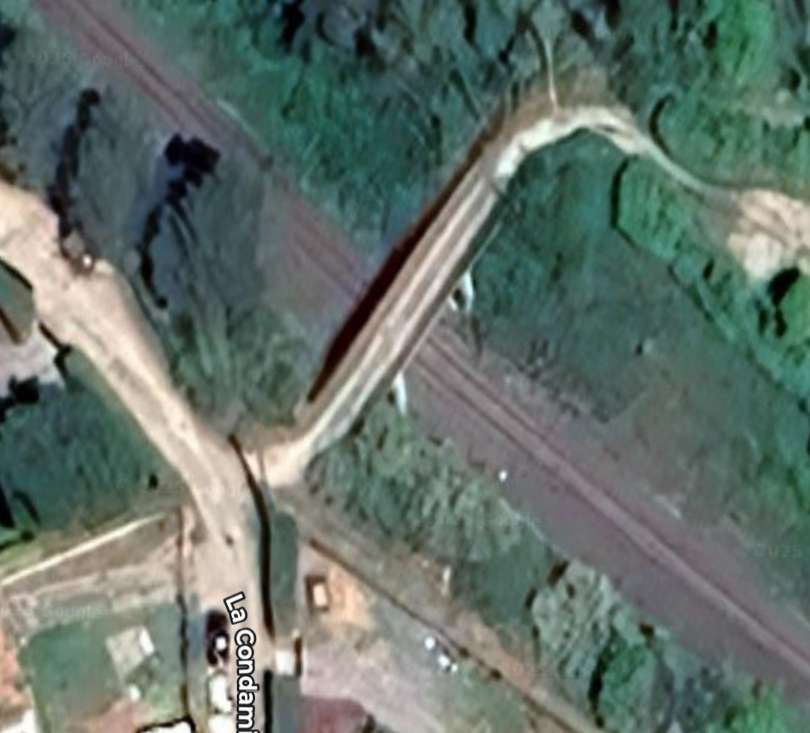
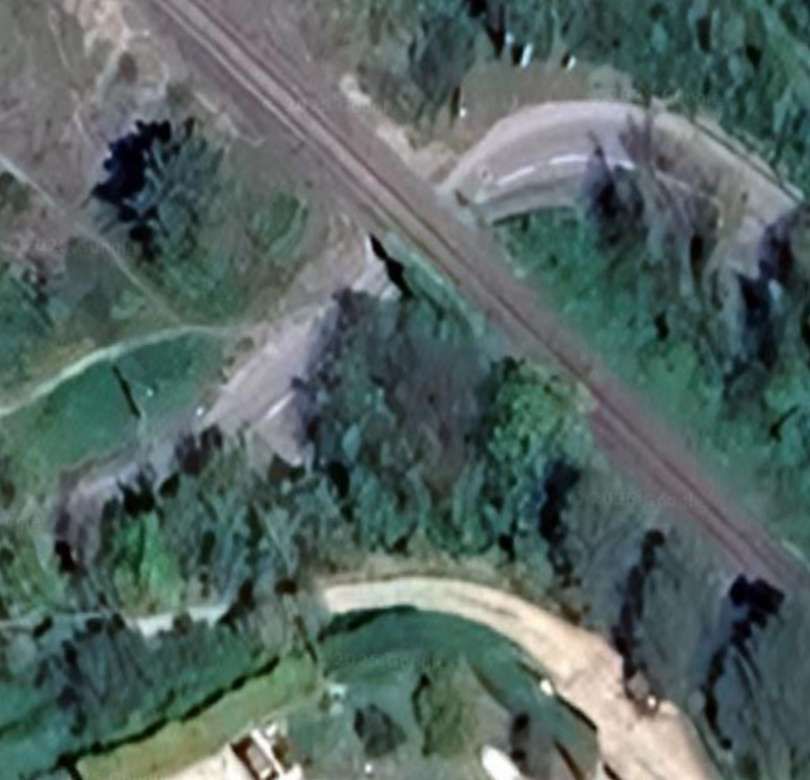
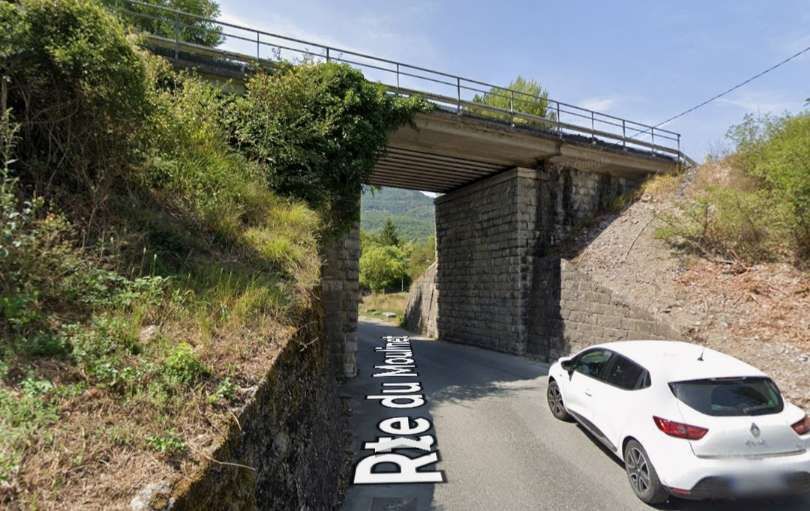
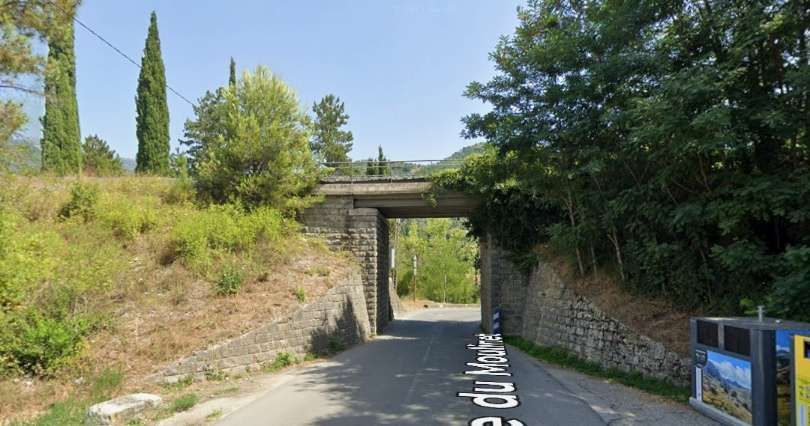





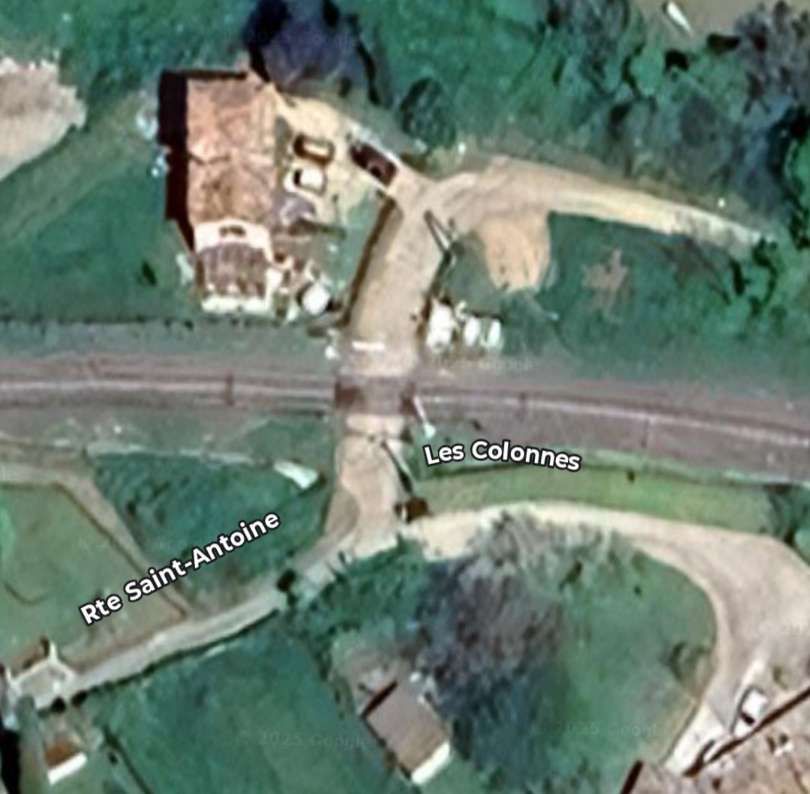
A short distance further West the line crosses Rte Sant-Antoine by means of a level-crossing. [4]
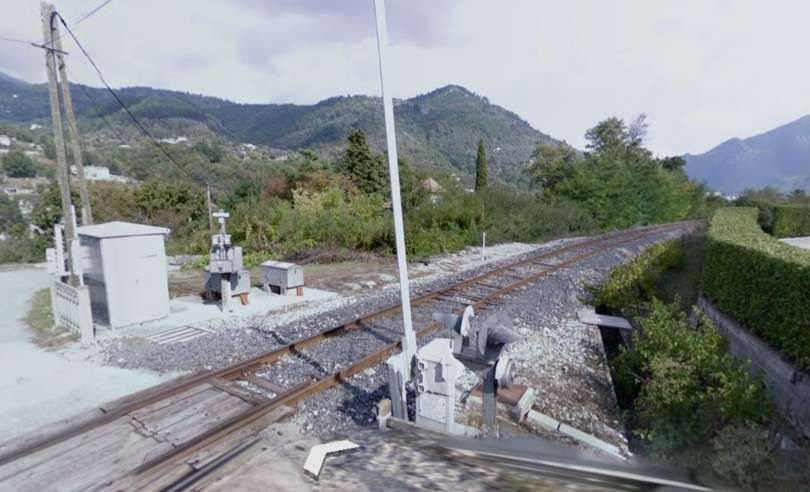
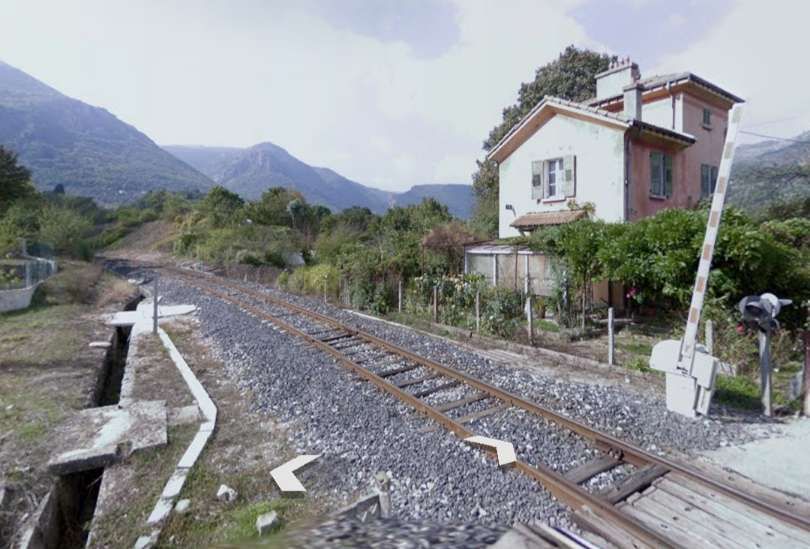
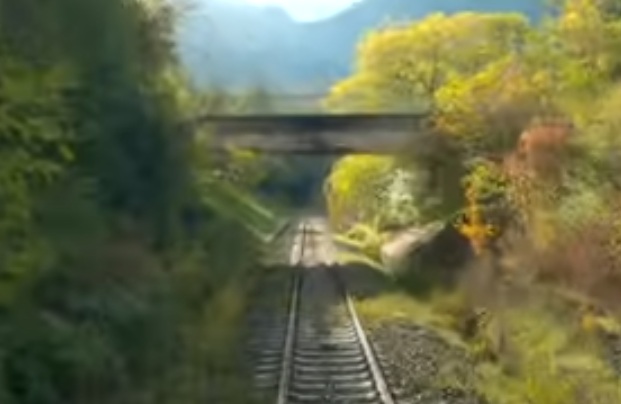




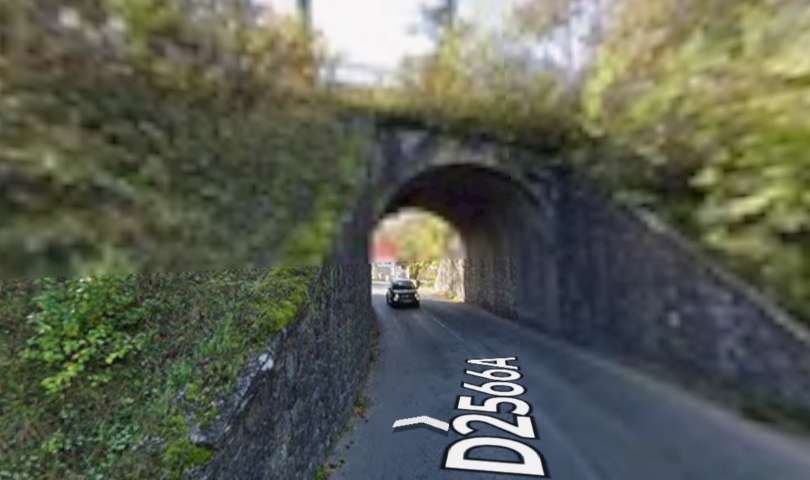
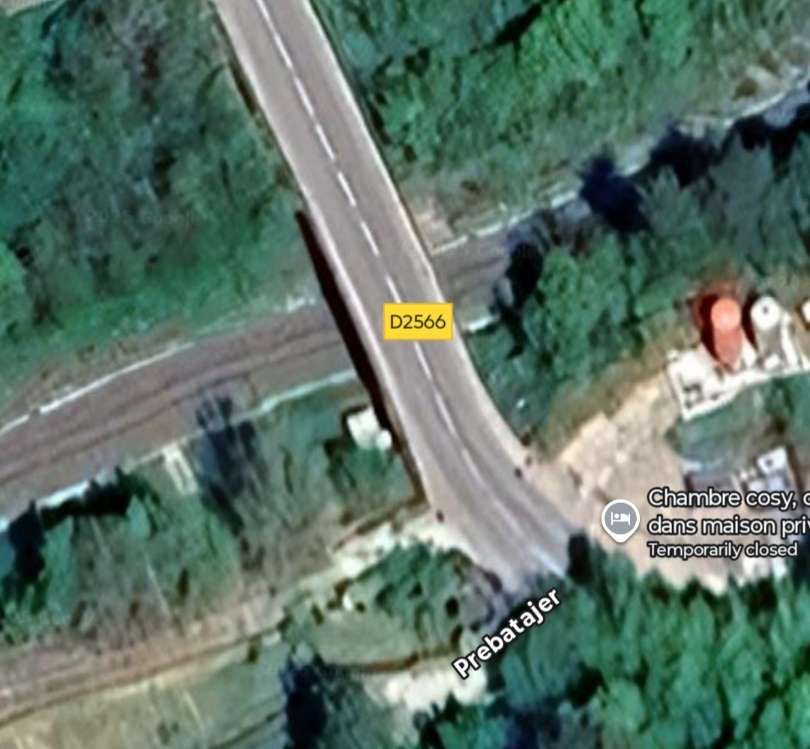
The D2566 crosses the line (heading North-northwest) with the line travelling in a southwesterly direction. [4]
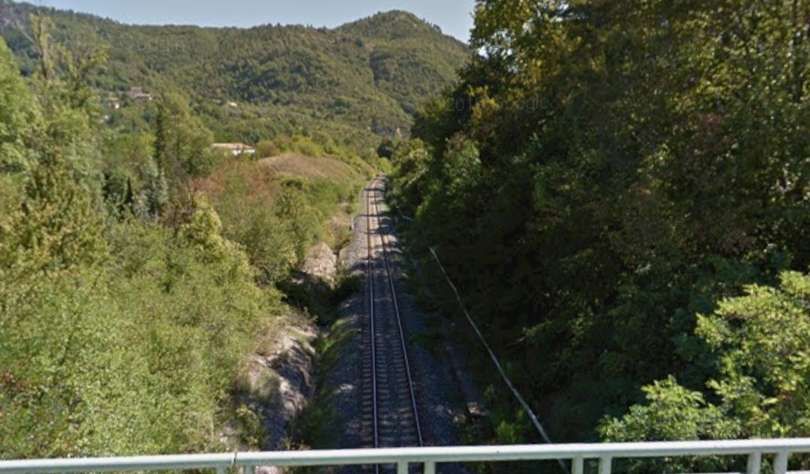
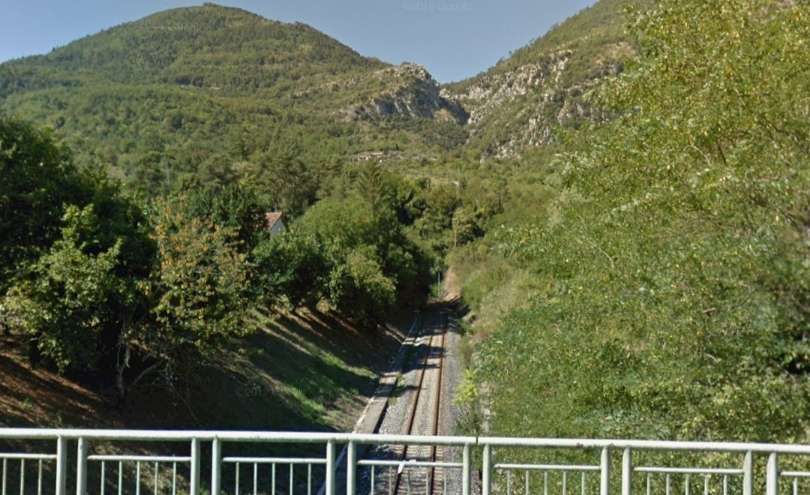




In deep shade, this is the mouth of Tunnel de Braus, seen from the cab of an approaching Nice-bound train.[4]

The same tunnel mouth in better light. [31]
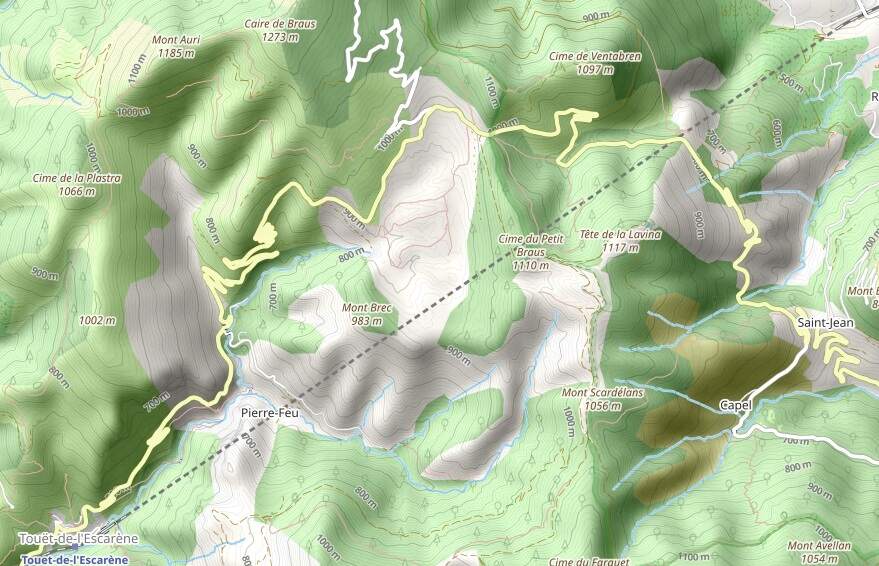
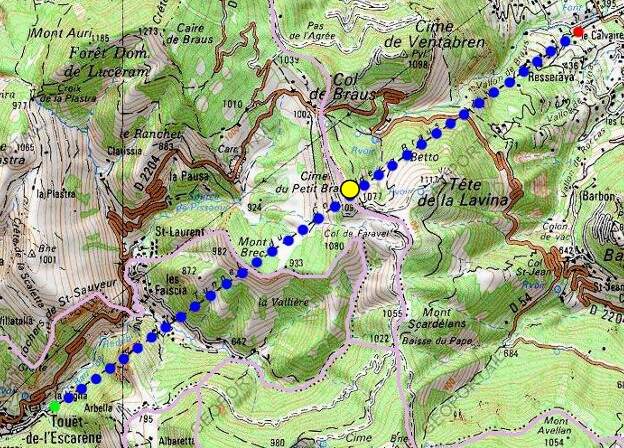
As we have already noted, both the tunnel portals were fortified at the insistence of the military. … Completing the tunnels also required significant additional work to deal with a very high level of water ingress during construction.
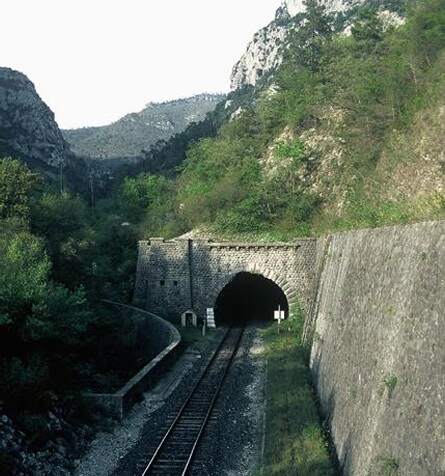

The Southwest portal of Tunnel de Braus is flanked to the Southeast by a very high retaining wall and to the Northwest by a water channel created for the Ruisseau de Redebraus. [31]
The Tunnel de Braus was built to accommodate a double-track line to allow for possible future growth in traffic.
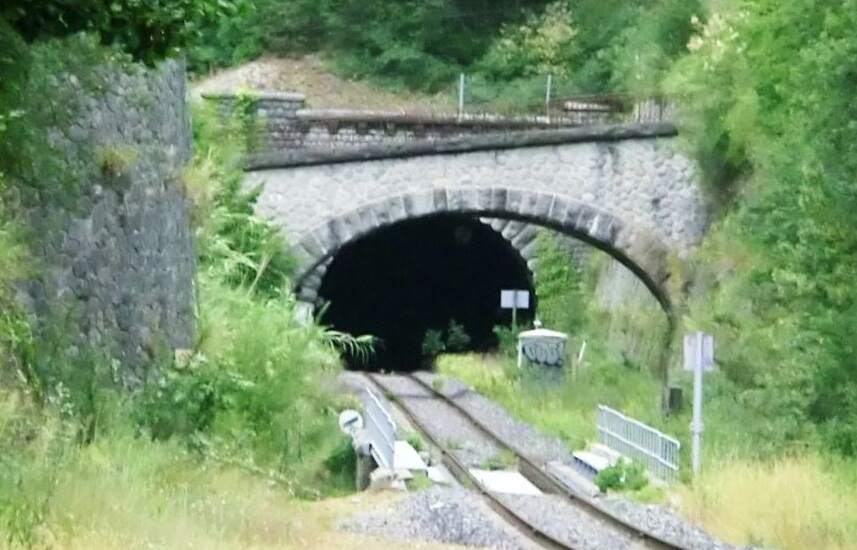
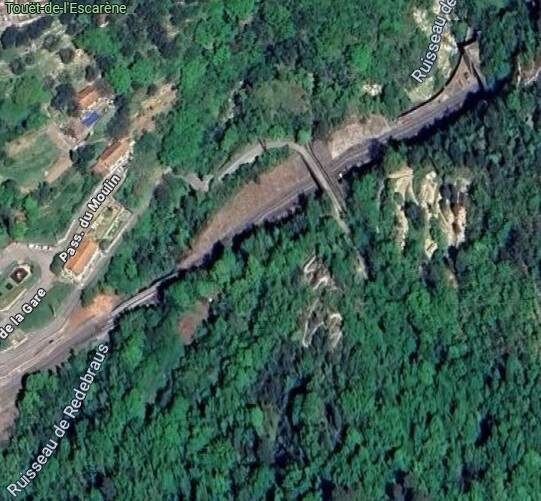


This extract from Google’s satellite imagery shows the various structures from above – the river bridge is towards the bottom-left of the image with the tunnel mouth in the top-right. [Google Maps, August 2025]

The view from the cab of the Nice-bound train as it leaves the tunnel behind. [4] The first couple of hundred metres beyond the tunnel portal are within a narrow, damp and dark defile.

The bridge over the Ruisseau de Redebraus. [4]

The Nice-bound train approaches the halt at Touët-de-l’Escarène. [4]
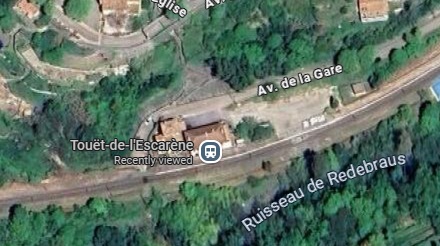
Touët-de-l’Escarène Railway Station (Halt). The village is to the North of the Station. [Google Maps, August 2025]

Touët-de-l’Escarène Railway Station. [4]
Three older images of Touët-de-l’Escarène follow. Two while the station was under construction. …
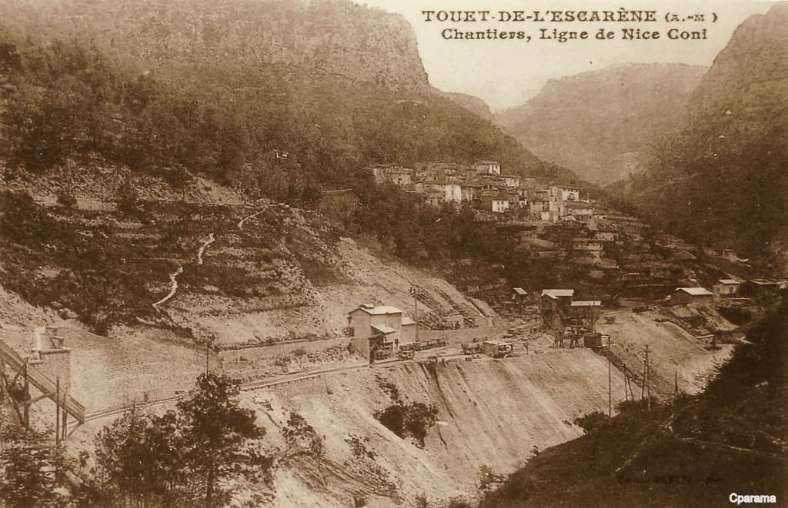
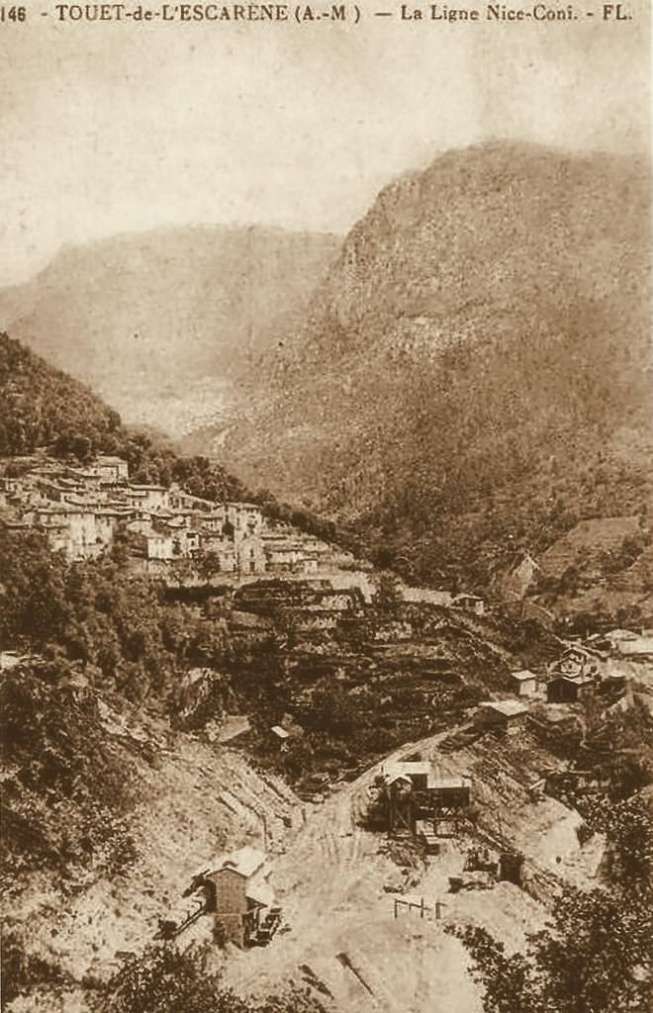
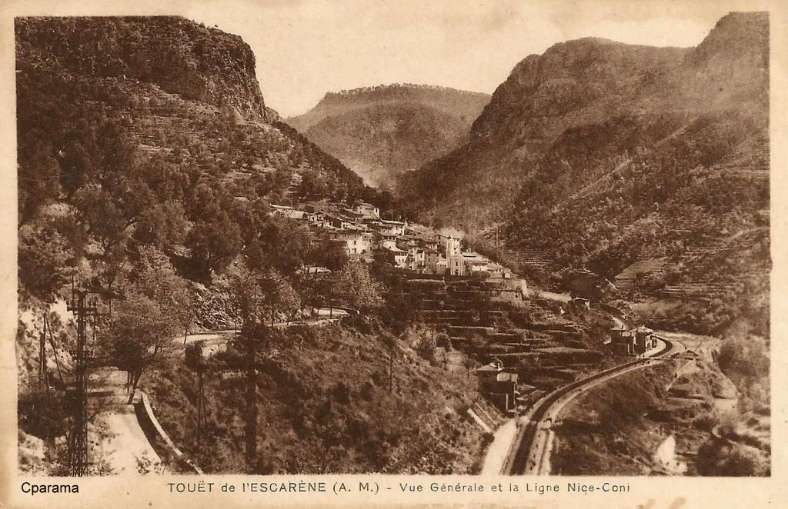



The line beyond Touët-de-l’Escarène continues West along the North side of the Ruisseau de Redebraus towards the next tunnel. …
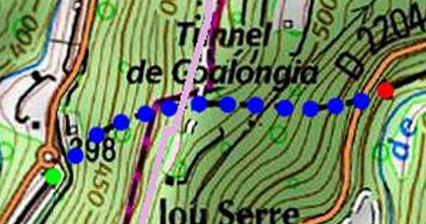
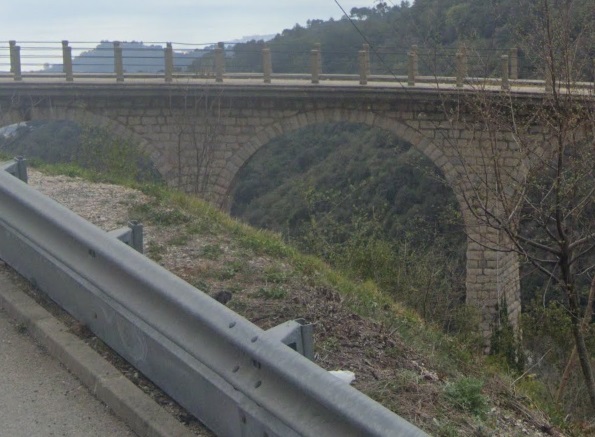
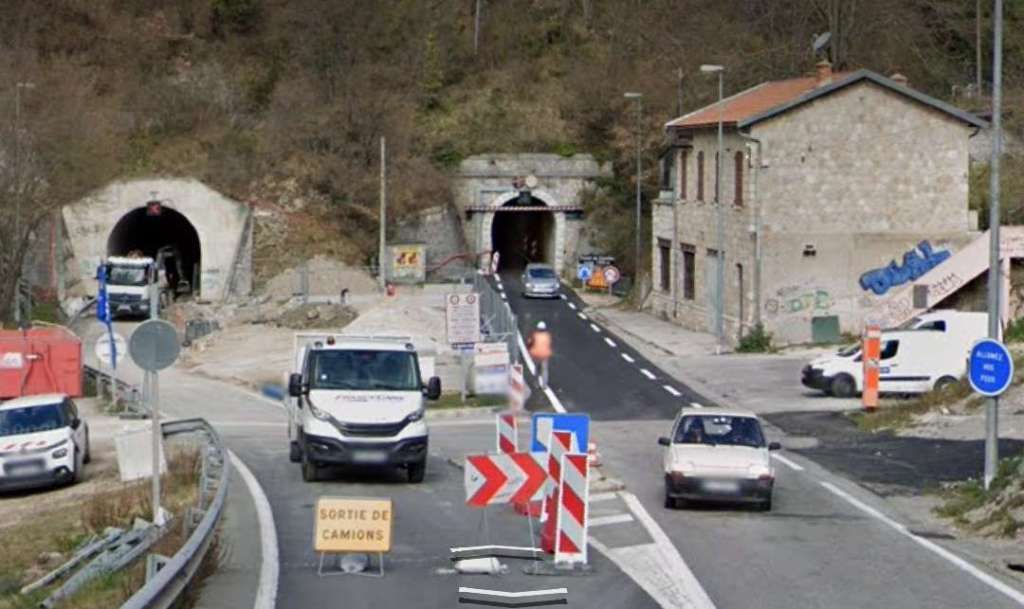
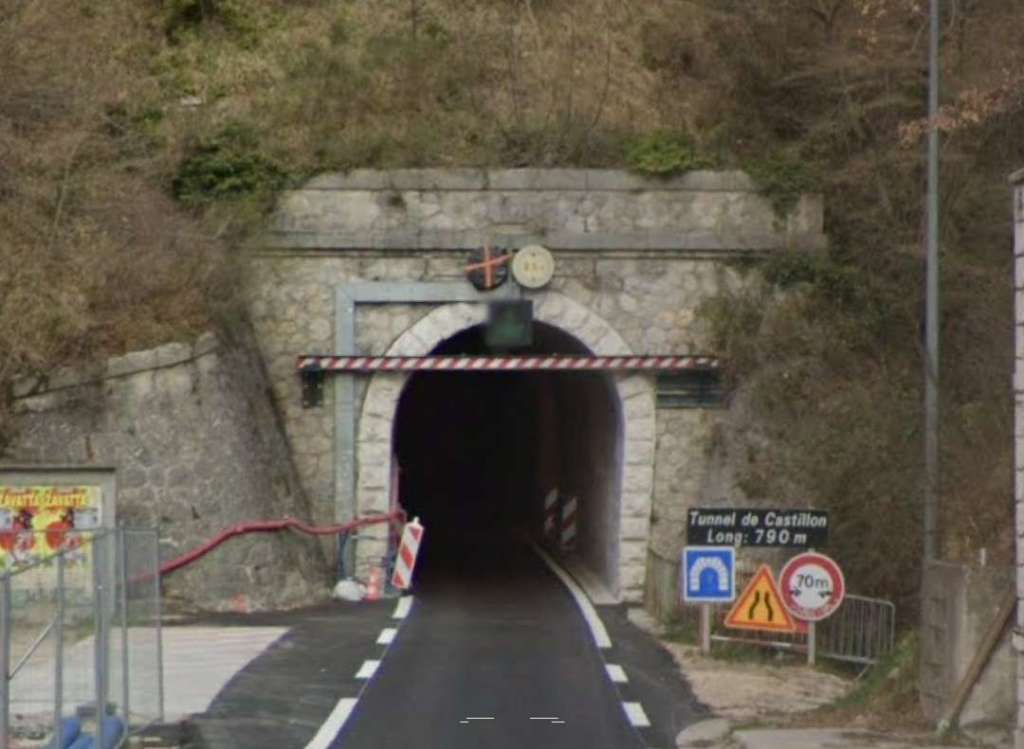
The next tunnel is Tunnel de l’Escarène or Tunnel de Coalongia (527 metres in length). [34]

The East portal of the Tunnel de l’Escarène. [4]

The view from the cab of a Nice-bound train as it leaves l’Escarene Tunnel. The points which provide the passing loop at l’Escarene Railway Station sit just outside the tunnel mouth. [4]

The West portal of the Tunnel de l’Escarène. [34]
Within the tunnel the line has begun to turn towards the South and the relatively tight curve continues until between the platforms at Sospel Station the line is on a North-South axis.

The final approach to l’Escarene Railway Station. [4]

L’Escarene Railway Station. [4]
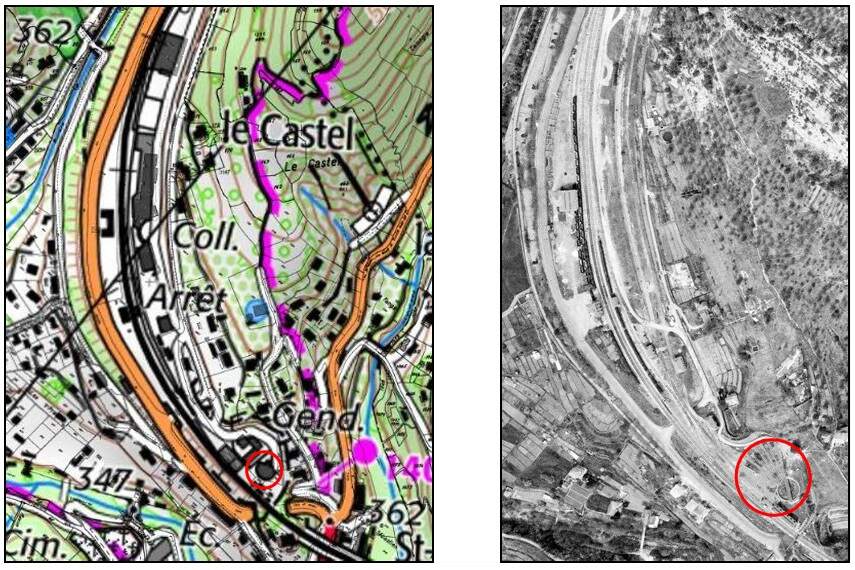
L’Escarene sits at the top of a long climb from Nice. We will follow the line through to Nice in the next two articles in this series. (The next article can be found here. [5]) Like Sospel, l’Escarene Railway Station had substantial facilities on a wide open plateau designed to allow the reception of military convoys in the event of conflict with neighboring Italy. [1: p92]
References
- Jose Banaudo, Michel Braun and Gerard de Santos; Les Trains du Col de Tende Volume 1: 1858-1928; FACS Patrimoine Ferroviaire, Les Editions du Cabri, 2018.
- Jose Banaudo, Michel Braun and Gerard de Santos; Les Trains du Col de Tende Volume 2: 1929-1974; FACS Patrimoine Ferroviaire, Les Editions du Cabri, 2018.
- Jose Banaudo, Michel Braun and Gerard de Santos; Les Trains du Col de Tende Volume 3: 1975-1986; FACS Patrimoine Ferroviaire, Les Editions du Cabri, 2018.
- https://youtu.be/rLXAEz-n4mM?si=RLQC31jynGeM_lQR, accessed on 26th August 2025. Permission to use still images from this video has been sought via YouTube.
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2025/09/26/the-railway-between-nice-tende-and-cuneo-part-7-lescarene-to-drap-cantaron-railway-station/
- Not used.
- Not used.
- Not used
- https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=12/43.8804/7.4395&layers=P, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2025/07/22/the-railway-from-nice-to-tende-and-cuneo-part-1.
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2025/07/26/the-railway-from-nice-to-tende-and-cuneo-part-2.
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2025/08/06/the-railway-from-nice-to-tende-and-cuneo-part-3-vievola-to-st-dalmas-de-tende
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2025/08/16/the-railway-between-nice-tende-and-cuneo-part-4-st-dalmas-de-tende-to-breil-sur-roya
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2025/08/25/the-railway-between-nice-tende-and-cuneo-part-5-breil-sur-roya-to-ventimiglia
- https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=15/43.93077/7.51647&layers=P, accessed on 18th August 2025.
- https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=17/43.923820/7.520512&layers=P, accessed on 19th August 2025.
- https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=16/43.91950/7.51623&layers=P, accessed on 20th August 2025.
- F. Honore; Le Rail a Travers Les Alpes: De Nice a Coni par la Voie Ferrée; L’Illustration, No. 4470, 3rd November 1928, p499.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/mx06/06023.04D.pdf, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/tu06/06023.1.pdf, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/tu06/06023.2.pdf, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://structurae.net/en/structures/bevera-viaduct-1962, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=17/43.886948/7.487220&layers=P, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/mx06/06136.03Y.pdf, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/kc06/06136.04W.pdf, accessed on 26th August 2025.
- https://www.railwaywondersoftheworld.com/link-mediterranean.html, accessed on 26th August 2025
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Viaduc_de_Bevera01.jpg, accessed on 26th August 2025
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/tu06/06136.2.pdf, accessed on 27th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/tu06/06136.1.pdf, accessed on 27th August 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gare_de_Sospel.JPG, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=14/43.86371/7.40071&layers=P, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/tu06/06142.1.pdf, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/144697687618, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://structurae.net/en/structures/col-de-braus-tunnel, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/tu06/06057.2.pdf, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://www.inventaires-ferroviaires.fr/pt06/06057-02U.pdf, accessed on 28th August 2025.
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2013/12/10/sospel-to-menton-tramway
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2018/02/23/the-sospel-to-menton-tramway-revisited-chemins-de-fer-de-provence-51
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2018/06/08/the-menton-to-sospel-tramway-revisited-again-chemins-de-fer-de-provence-61
- https://ebay.us/m/GvQ7Pv, accessed on 29th August 2025.
- Franco Collidà, Max Gallo & Aldo A. Mola; CUNEO-NIZZA History of a Railway; Cassa di Risparmio di Cuneo, Cuneo (CN), July 1982.
- Franco Collidà; 1845-1979: the Cuneo-Nice line year by year; in Rassegna – Quarterly magazine of the Cassa di Risparmio di Cuneo; No. 7, September 1979, pp. 12-18.
- Stefano Garzaro & Nico Molino; THE TENDA RAILWAY From Cuneo to Nice, the last great Alpine crossing; Editrice di Storia dei Trasporti, Colleferro (RM), EST, July 1982.
- SNCF Region de Marseille; Line: Coni – Breil sur Roya – Vintimille. Reconstruction et équipement de la section de ligne située en territoire Français; Imprimerie St-Victor, Marseille (F), 1980.
- https://www.geneanet.org/cartes-postales/view/194490#0, accessed on 29th August 2025.
- https://www.cparama.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=898, accessed on 29th August 2025.
- https://www.cparama.com/forum/sospel-t898-20.html, accessed on 29th August 2025.
- https://www.cparama.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=898&start=40, accessed on 29th August 2025.
- https://www.cparama.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=24506 , 29th August 2025.
- https://www.cparama.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=24506, 29th August 2025.
- https://fr.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sch%C3%A9ma_de_la_ligne_de_Nice_%C3%A0_Breil-sur-Roya, 15th September 2025