The Railway Magazine, August 1922. [1]
An unattributed article about these LNWR units was carried in the August 1922 issue of The Railway Magazine. From 6th February 1922 a ‘reversible’ or ‘push-and-pull’ train was in use for working locally between Manchester (Victoria) and Atherton.
Courtesy of Mr. Ashton Davies, M.Β.Ε., General Superintendent (Northern Division) of the LNWR, The Railway Magazine was able to illustrate and describe the equipment of the train employed:
“The train normally consists of a tank engine adapted to run with two bogie coaches, but can be increased to four or six coaches when the volume of traffic calls for further accommodation. The vehicles adapted for use in this way are arranged in pairs, providing nine third-class compartments in one vehicle, seating 108 passengers, while the composite carriage has two first-class and four third-class compartments seating 64 passengers, together with luggage and driver’s compartments. There is thus total accommodation for 172 passengers for each unit pair of vehicles. The length over buffers of each coach is 57 ft. 7 in. and the width over the body is 9 ft. The engine is a 2-4-2 radial tank, the diameter of the coupled wheels being 5 ft. 8 in. and of the radial wheels 3 ft. 7 in. Cylinders are 17.5 in. diam. and 26 in. stroke: boiler pressure is 180 lb. per square inch; length over buffers, 37 ft. 2 in. When the train is made up to six coaches the total length over buffers is 382 ft. 8 in. In one direction the engine is operated as with an ordinary steam train, but in the other direction the driver operates the engine from the driver’s compartment at the rear end of the train.” [1: p128]

The locomotives used on the push-pull services in the old Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway area of the then very new combined company were Webb’s 2-4-2T locos. [4]
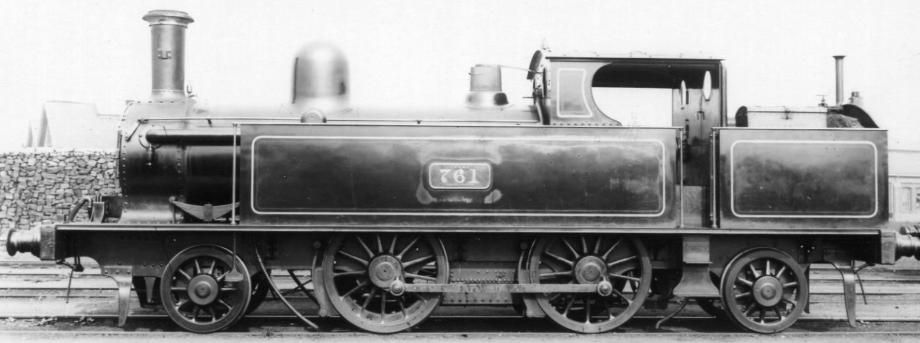
The LNWR 4ft 6in Tank was a class of 220 passenger 2-4-2T locomotives manufactured by the London and North Western Railway in their Crewe Works between 1879 and 1898. The ‘4ft 6in’ refers to the diameter of the driving wheels. “The design was an extension of the earlier 2234 2-4-0T built from 1876 which became known as ‘Chopper Tanks’. They had been designed for working local passenger trains. From 1909 many locomotives of the class were fitted for Push-Pull working, giving the nickname of ‘Motor Tanks’. … Withdrawals started in 1905: 118 were scrapped in the years up to 1923 grouping, leaving 90 to be passed to the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. They were allocated power class 1P, and assigned the numbers 6515–6600 and 6758–6761; although only 37 survived long enough to receive them: withdrawals restarted in 1924, and when the last was withdrawn in June 1936, the class became extinct. None were preserved.” [5]
The 2-4-2T engines were not the only locos adapted by the LNWR for push-pull working. From 1914 onwards some of the LNWR Webb ‘Coal Tanks’ “were fitted with push-pull ‘motor train’ equipment with the first so equipped being 576 and 597 which were then deployed on the Brynmawr to Ebbw Vale service. The system used by the LNWR involved the use of mechanical rods and linkages which ran beneath the axles of the locomotives. By 1921, the company was operating 30 branches by this method with many being worked by ‘Coal Tanks’. As a result, 55 locomotives had been equipped with the necessary equipment.” [2]
Webb built his class of 500 0-6-0 coal locomotives between 1873 and 1892 for slow freight work. Between 1881 and 1897 he built 300 0-6-2Ts which were tank engine versions of his of the 58320 class. These tank engines became known as ‘Coal Tanks’. “They had the same cheaply produced cast iron wheels and H-section spokes as the tender engines. A trailing radial truck supporting the bunker was added also with two similarly cast iron wheels. … They were almost entirely built of Crewe standard parts, including the radial rear axle. … Most were relieved of freight duties when the extent of their appalling brakes (initially made of wood) were uncovered, and some were fitted for motor train working.” [3]
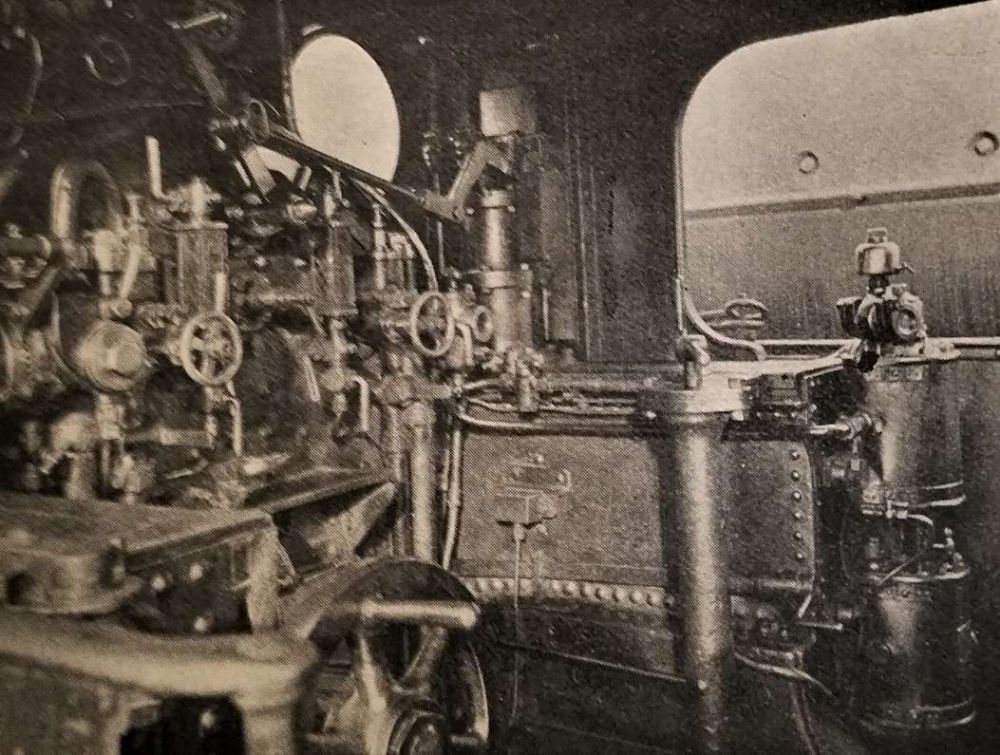
The Railway Magazine article continues:
“The engine and train are fitted with the automatic vacuum brake. A compressed-air apparatus is installed to operate the regulator handle on the engine, when the driver is controlling from the driver’s compartment.
The regulator handle is shown connected to a rod by means of a French pin; the other end is coupled to an operating air cylinder by means of a bell crank lever. The operating cylinder contains two pistons, one larger than the other; both are mounted on the same piston rod. The chamber between the two pistons is directly connected to an auxiliary reservoir, to which air pressure is supplied through a back pressure valve, so that a sufficient air pressure is always available. The underside of the large piston can be put in communication with the main reservoir or the atmosphere under the control of the driver’s compressed air valve. When air pressure is supplied to the underside of the large piston it is placed in equilibrium, and the air pressure from the auxiliary reservoir then forces up the small piston, and opens the regulator. When the air pressure on the underside of the large piston is destroyed, by opening the driver’s compressed-air valve to atmosphere and closing the air supply from the main reservoir, the air pressure from the auxiliary reservoir forces down the large piston and shuts the regulator. By manipulating the driver’s compressed air valve any desired opening of the regulator may be obtained. … Movement of the regulator on the engine is repeated to the driver by an electrical indicator fixed over the look-out window in the driver’s compartment. The vacuum and pressure gauges are placed on each side of the electrical indicator in the driver’s compartment, above the observation window. A pneumatic whistle is provided to give warning on the road.
A special feature of this train is the driver’s ‘safeguard’ in the event of the driver becoming incapacitated when driving alone from the rear. If he releases his hold of the brake handle in this condition it will act as an ’emergency handle’, immediately shutting the regulator and applying the brake.” [1: p129]
Following the 1923 grouping, the London Midland & Scottish Railway (LMS) became responsible for this fleet of push-pull fitted 2-4-2T and 0-6-2T Locomotives. The LMS took the decision to adopt the Midland Railway’s vacuum-worked push-pull equipment instead of the LNWR system.
As we have already noted, withdrawals of the 2-4-2T locos started as early as 1905: 118 had gone before the 1923 grouping, 90 were passed to the LMS. “They were allocated power class 1P, and assigned the numbers 6515–6600 and 6758–6761; although only 37 survived long enough to receive them: withdrawals restarted in 1924, and when the last was withdrawn in June 1936, the class became extinct. None were preserved.” [5]
In all, 65 of the ‘Coal Tanks’ (0-6-2Ts) received the LMS vacuum-worked push-pull fittings, “12 of them formerly having had the mechanical type. … The use of push-pull equipped ‘Coal Tanks’ was long-lived with the last one running on the Bangor to Bethesda branch as late as 1951.” [2]
References
- ‘Reversible’ Steam Train, London & North Western Railway; in The Railway Magazine, London, August 1922, p128-129.
- https://www.keymodelworld.com/article/lnwr-webb-coal-tanks-0-6-2t-history, accessed on 25th October 2024.
- https://preservedbritishsteamlocomotives.com/2f-58880-58937-0-6-2t-lnwr-webb-coal-tank, accessed on 25th October 2024.
- https://www.discountmags.com/magazine/the-railway-march-1-2022-digital/in-this-issue/38, accessed on 25th October 2024.
- https://www.hattons.co.uk/directory/vehicledetails/3144969/2_4_2t_class_4_6_chopper_lnwr, accessed on 25th October 2024.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/LNWR_4ft_6in_Tank_Class, accessed on 25th October 2024.

