A contemporary account of the completion of the additional rail bridge over the River Tyne.
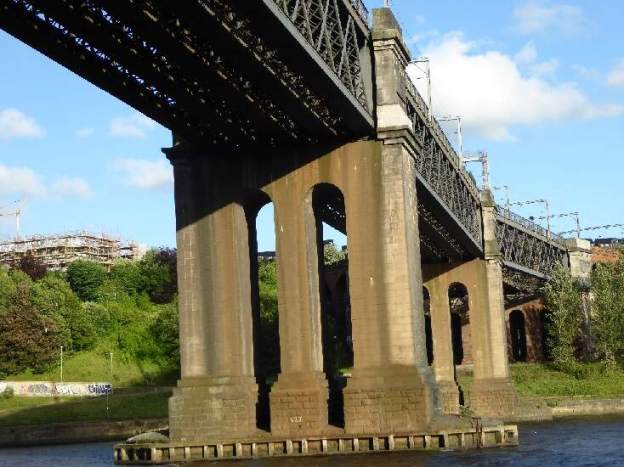
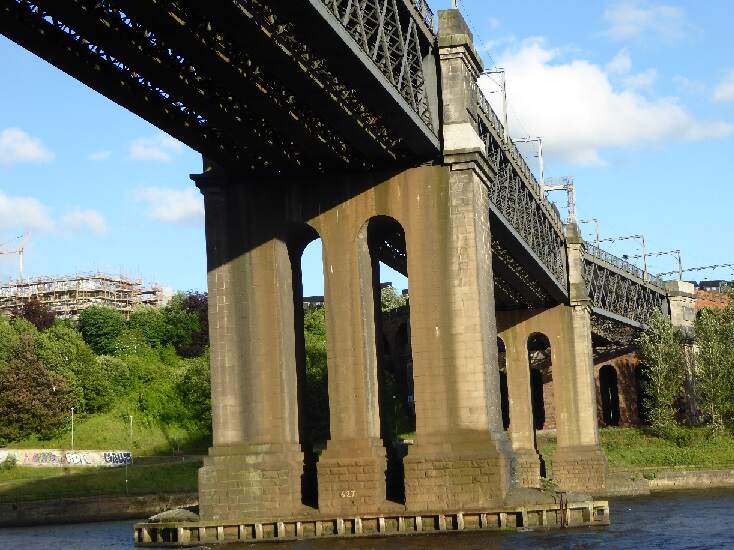
This is the Bridge that became known as the King Edward VII Bridge. It is a Grade II listed structure and has been described as “Britain’s last great railway bridge”. [4]

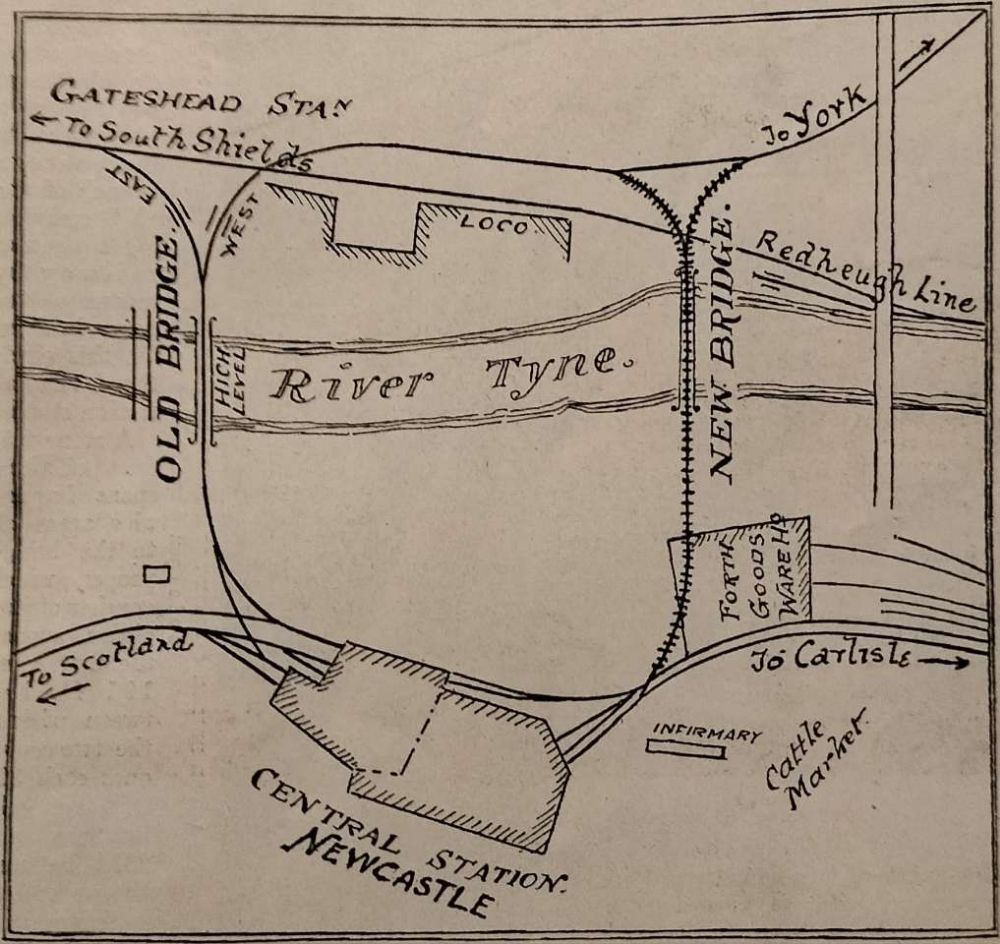
The introduction to the article in the Railway Magazine says:
“Travellers journeying by the East Coast route to and from places north of Newcastle-on- Tyne, have always commented on an anachronism of the twentieth century, that hitherto has required trains to run into a ‘dead end’ station, thus compelling a stop, with consequent delay, whatever might be the stress of competition between the rival routes. Now however, all this is to be altered. Readers of The Railway Magazine are acquainted with the fact that for some years past the North-Eastern Railway has had under construction a duplicate high-level bridge across the Tyne, by means of which trains north to south, and vice versa, will be enabled to pass through the Central Station, without stopping, if necessary, but, at all events, without having the direction in which the train is travelling altered. The plan [above shows] how this improvement is effected by means of the new bridge and connecting lines. His Majesty the King has consented to open the new bridge, and thus inaugurate the improvement, on Tuesday, 10th July, after which date it will be possible to work the North-Eastern Railway trains that pass through Newcastle-on-Tyne in a manner showing a considerable improvement in the system now [pertaining]” [1: p9-10]
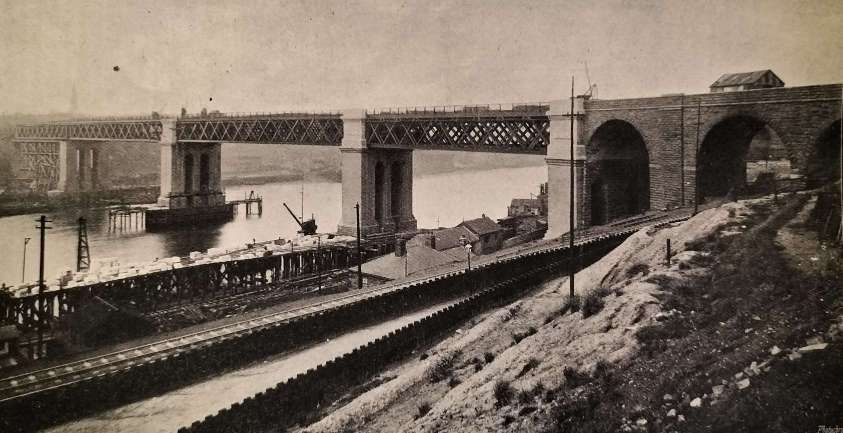

From the South side of the River Tyne a triangular junction gives access to the bridge, which is described by The Railway Magazine::
“A stone viaduct of three spans forms the approach to the bridge proper, which consists of four girder spans; the first being 191 ft. between piers, the two centre ones each 300 ft., and the northern span 231 ft. between the piers; this is followed by a stone viaduct of 10 spans each 25 ft. wide. The height of the ten piers of this viaduct, from road level to the spring of the arch, is 18 ft., and the arches are semi-circular, the arch stones being 18 in. in depth. The distance from road level to rail level is 33 ft., the foundations being on clay and averaging about 7 ft. in depth. This arching rests on ashlar piers 4 ft. thick and 51 ft. transversely, each pier being relieved by three 7 ft. arches.
The new line is next carried by a bridge across Pottery Lane, and then enters the well-known Forth goods warehouse of the North-Eastern Railway at the first storey level by steel girders resting on brick piers. The spans through the warehouse are 40 ft., and the foundations for the piers are taken down to good clay beneath the cellar floor. The distance from rail to the bottom of the foundation is 40 ft. The roof of the warehouse is held up by a wind screen, resting on the piers outside the parapet girders, and the corner of the building, cut off by the railway, is now being used as offices for the goods staff.
Beyond the goods warehouse the new line continues to a junction with the Newcastle and Carlisle Railway, a short distance west of the Central station at Newcastle.
The new bridge carries four pairs of metals.
The total length of the main bridge, measuring from the first abutment on the north side to the abutment on the south side is 1,150 ft. The girders measure 48 ft. 6 in. from centre to centre of parapets, and the breadth of steel work overall is 50 ft., so that there is thus provided a space of 6 ft. between the tracks, and room for a pathway for the use of platelayers on either side. The girders are built of double lattice work, with top and bottom booms 3 ft. deep, and are braced together at the top and bottom by transoms, of which the lower are of lattice work and the upper of plate work 164 in. deep, the latter carrying the timberway on which the rails run. Each girder has panels of 23 ft., of which the struts or ties are lattice girders 4 ft. 1 1/2 in. wide.
The girders for the centre spans have a camber of 7 1/2 in. and the north span of 6 in. The parapets, which are 5 ft. high are bracketed to the outside of the girders and are of lattice work, and, in order to carry the railway over the piers, the opposite top booms are bracketed out towards each other leaving a space of 6 in. between the ends of the top booms of the girders. To provide for expansion these girders rest on roller bearings at one end of cast steel, with a base of 38 sq. ft. each. The total weight of steel for each of the spans is: North span, 950 tons; two central spans, 3,482 tons; southern span, 1,350 tons. As the rails begin to diverge on the pier in the southern side of the river they are some distance apart at the next pier, there being then 132 ft. between the parapets. For this span of 191 ft. there are also five girders, but they spread out towards the south like a fan instead of being parallel.
The river piers are of Norway granite, and the foundations have all been taken down to the same depth, namely, 69 ft. below high water, and they have been built in caissons. The adoption of the caisson method of constructing the foundations marks a difference between the new high-level and the old bridge, as the latter was built on piled foundations. It should, however, be remembered that in 1845, when Stephenson’s great work was undertaken, the Tyne could almost be forded at low water, whilst there is now a deep-water channel beneath both bridges.The total length of the new railway is 4 furlongs 2 chains, whilst the loop to the south-east is 1 furlong 2 chains in length. Of this length of railway 19 chains is straight, including the crossing of the river, but the rails are on a 10-chain curve on leaving the west end of the Central station, and again, on a similar curve on reaching the south side of the river, the south-east curve having a radius of 7 chains. The line is level from the commencement on the north side as far as the pier on the south side of the river, when the main curve falls to the south-west on a gradient of 1 in 132, and the loop falls at 1 in 226. The new high-level bridge has been constructed from the designs of Mr. C. A. Harrison, the chief engineer of the Northern Division of the North-Eastern Railway, and this gentleman laid the foundation stone on 29th July 1902, so that less than four years have been occupied in constructing the bridge and new approach railway to Newcastle Central station.” [1: p10-11]

The original ‘High Level Bridge’ – designed by Robert Stephenson
The first High Level Bridge across the Tyne at Newcastle was opened in 1849. It was designed by Robert Stephenson, that bridge carried rail and road traffic and was the first in the world to do so.
Network Rail tells us that “the Newcastle & Berwick Railway secured the Act to build its line in 1845. It stipulated that the company should construct a combined road and rail bridge across the River Tyne between Newcastle and Gateshead, to be completed within four years. … The bridge was designed by Robert Stephenson and detailed drawings were made under the supervision of Thomas E Harrison. To avoid excessive width, and thereby expense, it was decided to carry the railway above, rather than beside, the roadway. The roadway itself was designed to be 20ft (6m) wide with a 6 1/2ft (2m) footway on either side. The combined width allowed three standard gauge tracks to run across the top rail level of the bridge. The overall length of the bridge was to be 1338ft (408m).” [2]
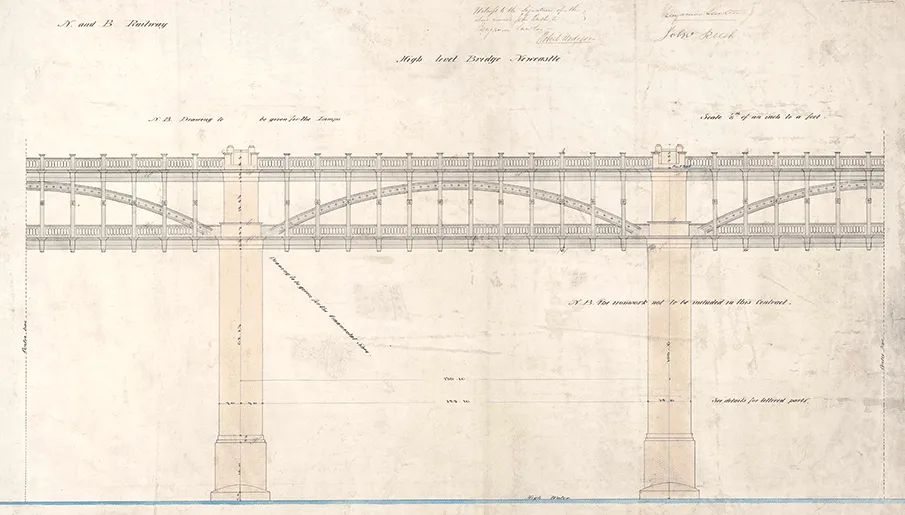
Network Rail goes on to describe the construction of the bridge:
“The bridge was a tied arch (or bow-string) bridge with the main structural elements made of either cast or wrought iron. It had in total six spans each 125ft (38m) in length, the cast iron bows supporting the railway while wrought iron ties supported the road deck below. To enable a level line for the railway across the deep and wide Tyne valley, the roadway was built at 96ft (29m) and the railway 120ft (37m) above high water on the river. Contracts for the production of the ironwork were let to local firm Hawkes, Crawshay & Co. of Newcastle.
The bridge sits on five masonry piers, 50ft (15m) thick and 16ft (5m) wide. Although the River Tyne at the point the bridge is constructed was no more than 3ft (1m) deep at low water, its bed consisted of some 30ft (9m) of silt before underlying bedrock could be reached.
A recent invention, the ‘Nasmyth Steam Pile Driver’, was used for the first time in bridge building, enabling the piles for the bridge foundations to be driven down to the bedrock quickly and efficiently. Rush & Lawton of York were contracted to build the five main masonry piers and the land arches on each side carrying the approaches; 50,000 tons of stone was quarried near Newcastle, mainly at Heddon on the Wall.
To assist in the construction work a wooden viaduct was built immediately to the east of the permanent one. This temporary structure was opened to railway traffic on 29 August 1848, just a year before the High Level Bridge itself was opened by Queen Victoria on 28 September 1849. The public roadway over the bridge was not completed and opened until some six months later.” [2]
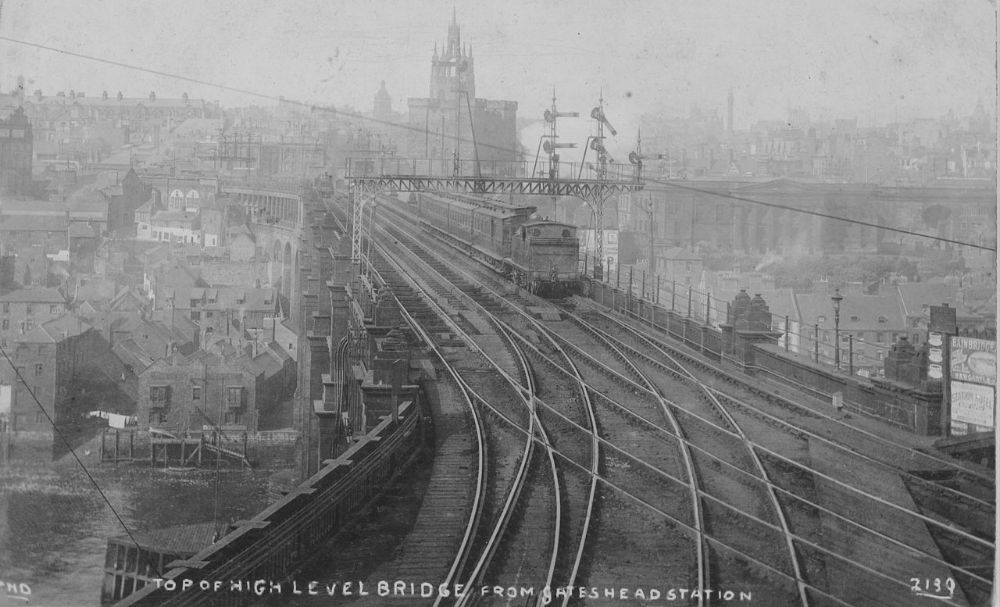
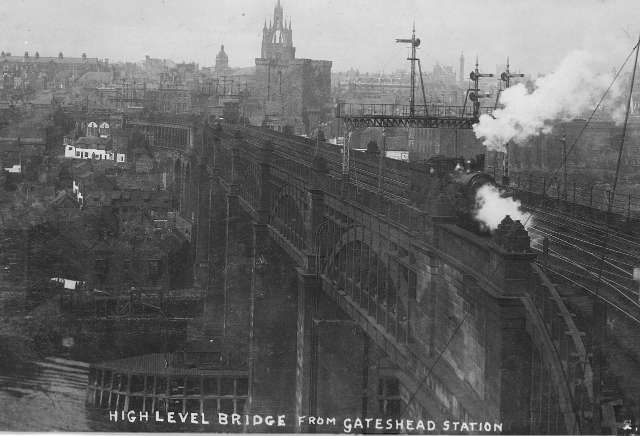
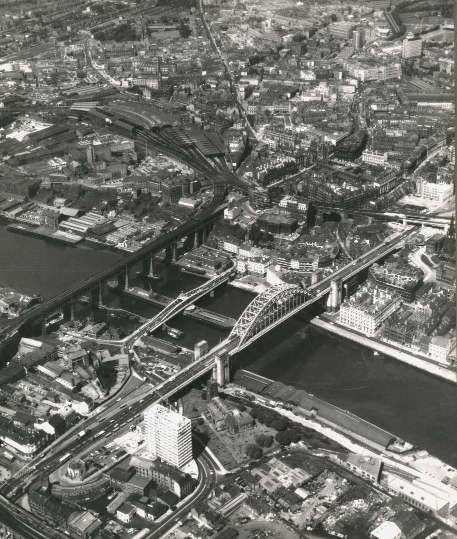
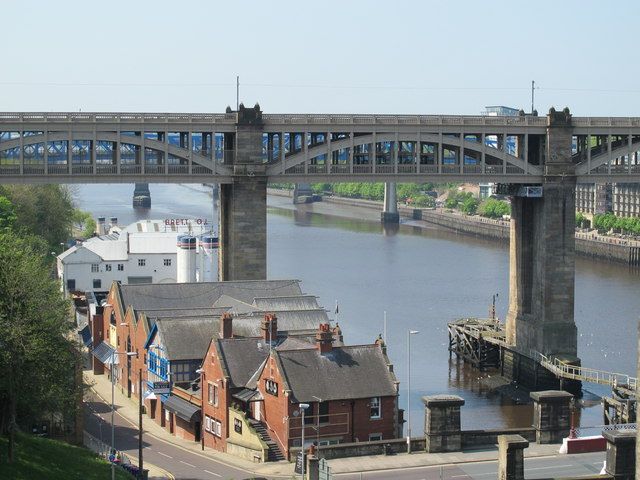
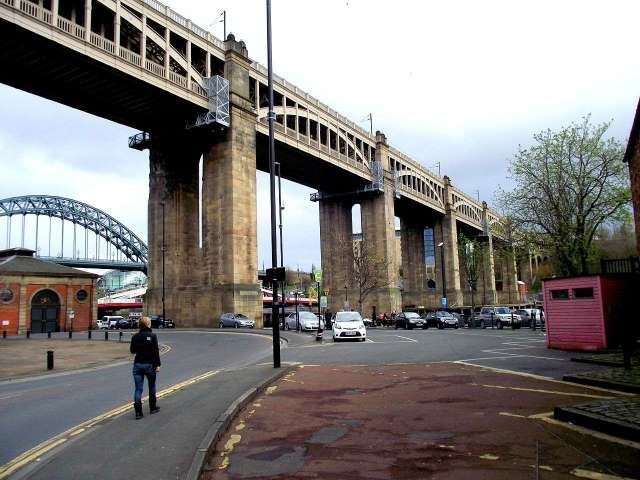
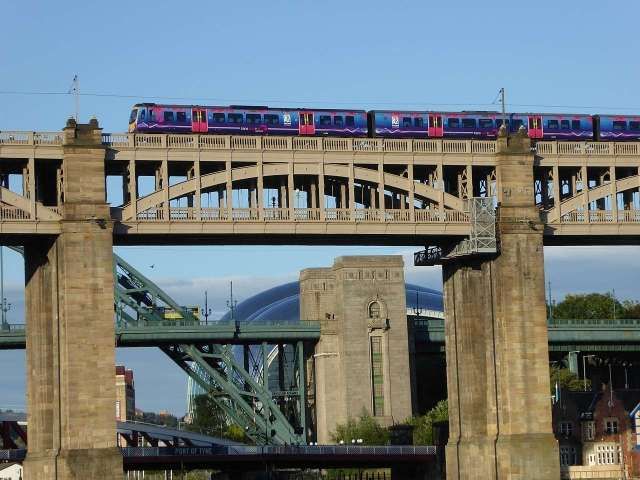
A Gallery of photos, drawings and engravings of Stephenson’s High Level Bridge. …..
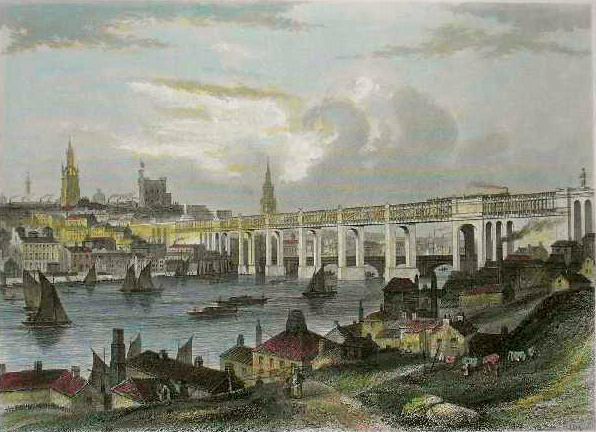








References
- The New High Level Bridge at Newcastle-on-Tyne; in The Railway Magazine, London, July 1906, p9-11.
- https://www.networkrail.co.uk/who-we-are/our-history/iconic-infrastructure/the-history-of-the-high-level-bridge-newcastle, accessed on 25th October 2024.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_Level_Bridge,_River_Tyne#/media/File:Newcastle_high_level_bridge,_12_September_2010.jpg, accessed on 26th October 2024.
- David Morton; The Tyne’s King Edward VII railway bridge at 110: A brief history in 14 historic facts; in The Evening Chronicle, Trinity Mirror, Newcastle upon Tyne, 7th July 2016, accessed via https://web.archive.org/web/20120429085232/http://www.twmuseums.org.uk/discovery/buildingbridges/the-king-edward-vii-railway-bridge/ on 27th October 2024.
- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:King_Edward_VII_Bridge,_Newcastle_upon_Tyne,_July_2015_(05).JPG, accessed on 27th October 2024.
- https://historicbridges.org/bridges/browser/?bridgebrowser=unitedkingdom/kingedward7bridge, accessed on 27th October 2024.

