The Railway Magazine of February 1952 carried an article by Charles E. Lee about railways in what was German South West Africa. This encouraged me to have a look at the history of Namibia’s railways and their condition and extent in the 21st century. The 1952 article also caught my attention because Manchester Diocese (I was a priest in Manchester Diocese before retirement) is linked with the Diocese of Namibia.
The territory was formally colonized by Germany between 1884-1890. It covered an area of 835,100 sq. km. It was a settler colony and had attracted around 3,000 German settlers by 1903, who primarily settled in the central high grounds. [2]
German South West Africa, now known as Namibia, was a German colony from 1884 to 1915. It was not a province within the German Empire but a separate colonial territory. From 1891, the capital was Windhoek, which also serves as the capital of modern-day Namibia. [2]
The arrival of German settlers disrupted the existing socioeconomic balance and led to conflicts, particularly with the Herero and Nama people.
“In 1883 Franz Adolf Lüderitz, a merchant from Bremen, Germany, established a trading post in southwest Africa at Angra Pequena, which he renamed Lüderitzbucht. He also acquired the adjacent coastal area, which he named Lüderitzland. These areas were constituted the first German colony under German protection on April 24, 1884. The German occupation subsequently extended inland. By the latter 1880s the German Colonial Company for the South realized that it was incapable of administering the territory, and the German government immediately took over the colony’s administration. As a result of the Zanzibar Treaty (1890) between Germany and Great Britain, German South West Africa acquired the Caprivi Strip (named after the German chancellor Graf Leo von Caprivi), a tract of land 280 miles (450 km) long in the extreme northeast of the territory; the colony thus gained access to the Zambezi River.” [3]
German colonial rule was harsh, leading to insurrections and resistance. “Major Theodor Leutwein, governor of the colony in 1894–1904, suppressed insurrections of the Khoekhoe (1894) and of the Hereros (1896). In 1904, however, the Hereros fomented a far more dangerous rebellion. The German force, at first only 750 strong and supported only by one artillery battery, had to face an army of some 8,000 men equipped with modern weapons. Reinforcements increased the German force, ultimately under the command of General Lothar von Trotha, and resulted in a decisive German victory on the Waterberg River. Further Khoekhoe rebellions were put down in 1904–07.” [3]
German South West Africa was occupied by the South African Union Defence Force in 1915 during World War I, and Germany formally ceded the territory under the Treaty of Versailles in 1919. Its administration was taken over by the Union of South Africa (part of the British Empire) and the territory was administered as South West Africa under a League of Nations mandate. It became independent as Namibia on 21st March 1990. [2]
The Railways
The railways in German South West Africa played a crucial role in the colonial administration and the First World War campaign. The German colonial authorities built a railway network between 1897 and 1914 to enable colonial territorialization and facilitate the extraction of resources. [4]
Charles E. Lee tells that “under the German regime, the first railway in South West Africa was the Northern State Railway (NSR), as it was then called, built to a gauge of 60 cm. (1 ft. 11 in.) between Swakopmund and Windhoek, via Jackalswater and Karibib, a distance of 238 miles. This line was begun in 1897 and was built by a German Military Brigade from Europe. It was first intended to be worked by animal power – Argentine mules or Cape donkeys – but steam traction was soon adopted. The first section (15 miles) was opened to traffic from Swakopmund in January 1898. By the end of that year 68 miles were ballasted and 54 open. In July 1900, the line was opened to Karibib, 121 miles, and the whole railway completed to Windhoek, a further 117 miles, in June, 1902. The curves and gradients were very severe, the gradient out of the Khan River gorge, for instance, being 1 in 19 with curves of 180 ft. radius. The rails weighed about 19 lb. a yard and were laid on iron sleepers. There were iron girder bridges at Khan River, Dorst River, and Kubas. The only good and plentiful water supplies were at Swakopmund and Karibib.” [1: p121]
Wikipedia tells us that there was actually an earlier line than the one Lee talks about. It was a small mining rail line at Cape Cross in 1895. [5] “Soon afterwards, the ox-cart transport system totally collapsed, in the wake of a rinderpest epidemic in 1897. As it was necessary to react quickly to the now extremely precarious transport situation, decisions were made: to build a railway line from the German port of Swakopmund to Windhoek (the Staatsbahn); to use existing, 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge military Feldbahn material; and to entrust a railway brigade with the construction work, which began in September 1897.” [5]
Wikipedia continues: “Construction of the railways connecting with the Staatsbahn was aimed partly at military strategic objectives following the uprising of the Herero and Nama, and partly at economic requirements. … By World War I, the following lines had been developed (listed by the first year of full operation):” [5]
- 1902: Swakopmund–Windhoek line, 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge, Karibib–Windhoek section re-gauged in 1911 to 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) gauge. [5]
- 1906: Otavibahn, 600 mm gauge. [5]
- 1905: Onguati–Karibib branch. [5]
- 1908: Otavi–Grootfontein branch. [5]
- 1907: Lüderitzbahn, 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm). [5]
- 1909: Seeheim–Kalkfontein branch. [5]
- ca 1911: Kolmannskuppe–Elisabethbucht–Bogenfels, industrial railway of the diamond fields. This 600mm gauge railway was electrified from 1911 (the only electric railway in Namibia’s history). Diamond mining in the region gradually moved south. The northern part of the line as far as Pomona was abandoned in 1931, and some of its materials were used for the extension of the railway towards Oranjemund. The southern section was operated with diesel traction. This line no longer exists. [5]
- 1912: Windhoek–Keetmanshoop railway, 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) gauge. [5]
- 1912: Rehoboth shuttle, 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge (questionable). [6][7][2][5]
- 1914: Otjiwarongo–Outjo–Okahakana, 600 mm gauge (project started, but not completed due to the war). [5]

Lee talks of the formation, by the Otavi Mining & Railway Company, an Anglo-German syndicate owning the copper mines at Otavi and Tsumeb, of a railway: “This company was formed in Berlin in 1900, in accordance with an arrangement between the South-West Afrika Company, the Disconto-Gesellschaft of Berlin, and the Exploration Company. The first intention was to build a 3 ft. 6 in. gauge railway from Port Alexander in Portuguese West Africa to run in a south-easterly direction up the Muende River Valley and via Etosha Pan to the Tsumeb Copper Mines, and later to extend this line to Rhodesia to form a trans-African railway. Eventually it was decided to form a 60 cm. gauge line entirely in German territory connecting Swakopmund with Tsumeb, a distance of 351 miles. Construction was undertaken by Arthur Koppel & Co. and was begun in November 1903, but was delayed by the Herero War, and the work completed on 25th August 1906. This undertaking, called the Otavi Railway, had the distinction of being the longest narrow-gauge railway in the world. Branches were laid subsequently from Otavi to Grootfontein (56 miles) and from Onguati to Karibib on the State Railway (9 miles). The cost is stated to have been about £2,400 a mile, or roundly £1,000,000 in total. The railway was bought by the German Imperial Government in 1910 for £1,250,000, but the management was left in the hands of the company under a 30-year lease, terminable after 10 years.” [1: p121]
This line was well constructed, and well ballasted. It had a ruling gradient of 1 in 66 and minimum curvature of 150 metres. The permanent way consisted of steel rails in 30-ft. lengths, 30 lb. a yard, laid on steel sleepers weighing about 26 lb. each. “From Swakopmund, for a distance of 68 miles, the line rises steadily on a grade of 1 in 66 to Ebony Station, where it reaches an altitude of 3,500 ft. (On the down journey, the last 40 miles into Swakop-mund can be run by gravity.) From Ebony there is a regular fall to Usakos, which is 2,640 ft. above sea level. From Usakos it climbs 690 ft. in 13 miles to Onguati, and continues to rise until it attains its greatest elevation near Kalk-feld, where the summit is 5,200 ft.” [1: p121]
“The Otavi Railway, like the State Railway, was built to the 2 ft-gauge, though a difference of 1 centimetre in the wheel gauges is stated to have prevented the free interchange of rolling-stock. The widening to 3 ft. 6 in. of the gauge between Swakopmund and Omaruru had been voted by the German Railway Board, but the work had not been put in hand by the outbreak of the 1914 war. A new branch projected at the same period was the Ovamboland Line, the first aim of which was to provide Ovambo labour for the South. The Landesrat in November 1913, approved a line of 2 ft-gauge, but on earthworks and bridges wide enough for a 3ft. 6in. gauge track, to run from Otjiwarongo (on the Otavi Railways) to Outjo and Okahakana.” [1: p121]

A sum of £450,000 was allowed for the line from Otjiwarongo to Outjo and Okahakana “in the German Loan Estimates for 1914-15. The first section, including the 55 miles from Otjiwarongo to Amiab Poort, was to cost £250,000. Construction was begun, and the line was laid for 22 miles before the outbreak of hostilities in the first world war.” [1: p123]
“Railway developments south of Windhoek, on the 3 ft. 6 in. gauge, made it desirable to convert the earlier 2ft. lines. During 1911, the section from Karibib to Windhoek was converted to 3 ft. 6 in. gauge at a cost of £550,000, with the Bechstein-Koppel Gesellschaft as contractor. The ruling gradient [was] 1 in 66 with a minimum curvature of 656 ft. This work was completed during 1913. The Swakop River at Okahandja [was] spanned by a bridge 350 ft. long, and there [was] a smaller bridge at Otjihavera. About the same time, the coastward section from Karibib to Swakopmund was practically abandoned in favour of the alternative route provided by the Otavi Railway. In fact, the settlers in the Swakop Valley, who asked for a short railway to link them with Swakopmund, were promised in November 1913, that the material from the disused 92 miles of the State line between Swakopmund and Kubas would be used for this purpose, but it was not done.” [1: p123]
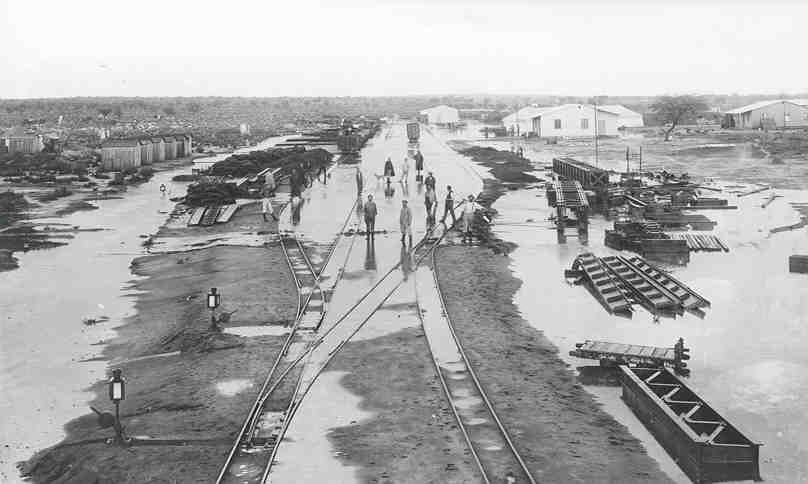
An image showing an armoured train in South West Africa during World War I, 1914-1918, can be found here [29] The South African army invaded the German colony of South West Africa in March 1915 overrunning the much smaller German forces.
Wikipedia tells us that, “With the outbreak of World War I, the German Schutztruppe military unit retreated from the coast, and withdrew into the inland. In the process, the Schutztruppe destroyed the Otavibahn, and the old Staatsbahn towards Karibib, as far as Rössing.” [5]
The Staatsbahn was abandoned but this was not the case with the Otavibahn. In 1914, “British troops … moved forward from the British enclave of Walvis Bay, and by the end of 1914 they had built a 37 km (23 mi) long 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) railway to Swakopmund. The Otavibahn was also reconstructed in 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) as far as Usakos, and the section between Usakos and Karibib was realigned. The network north of Usakos remained in 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge; the workshop for both gauges was consolidated in Usakos, and the one in Karibib was closed.” [5]
Lee tells us that by 1917 the Staatsbahn line from Karibib to the coast had ceased to exist. “the line between Karibib and Rossing (95 miles), the 10-mile branch from Jakalswater (built to carry water from the Swakop River at Riet), and the Kubas military line (4.5 miles), were lifted and removed to provide material for Tanganyika and the Union of South Africa.” [1: p123]
Lee goes on to confirm that the Union forces, in the course of their invasion of German South West Africa, “laid a 3 ft. 6 in. line for 100 miles inland from Swakopmund to Kranzberg along the original track of the Otavi line, which the Germans had wrecked in their retreat. This was completed in August, 1915. The construction of a new 12.5-mile section, of the same gauge, from Kranzberg to Karibib, was completed in July 1915, and again connected the Otavi Railway with the [NSR]. Thus, in August 1915, there was continuous communication of uniform gauge for the first time from Swakopmund to points south of Windhoek. As strategic railways had meanwhile linked the Union Railways with those of South-West Africa on 25th June 1915, a through railway of 1,635 miles was provided between Walvis Bay and Cape Town.” [1: p123]
Also during the first world war, a new railway from South Africa was constructed – “as an extension of the De Aar-Prieska Railway – to achieve a secure supply route for … South African troops. In 1916, the line was connected to the German network at Kalkfontein (now Karasburg).” [5]
“With the linking of the Kranzberg-Tsumeb 2ft-gauge line to the workshops at Usakos by means of a third rail between Usakos and Kranzberg on the 3-ft. 6-in. gauge track of improved location, the 9-mile section from Karibib to Onguati was no longer of value, and it was uplifted in 1924.” [1: p123]
“The former Otavi Railway system [was] therefore represented [in 1952] by about 100 miles of 3 ft. 6 in. line on the coastward section, part of the main railway system of South-West Africa, and 307 miles of 2ft-gauge farther inland. [In 1952, there were] also various private branch lines (some disused) connected with the 2ft section. [In 1952], the present main line of this gauge [was] from Kranzberg to Tsumeb, some 251 miles, on which one train in each direction [was] run two days a week.” [1: p123]
Wikipedia continues: Under South African/British occupation, the following lines were established (listed by first year of full operation): [5][10]
- 1914: Walvis Bay–Swakopmund in 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm). [5]
- 1915: Swakopmund–Karibib: Reconstruction in 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm). [5]
- 1915/1916: (De Aar)–Nakop (border)–Kalkfontein in 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm). [5]
- 1921: Otjiwaronge–Outjo 600mm gauge (based on German preparations). [5]
- 1929: Windhoek–Gobabis railway in 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm). [5]
- From 1958: the Otavibahn north of Usakos was gradually regauged to 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm), with the new line being laid parallel to the existing line, but largely on new foundations; the new line was in operation from 1961. [5]
“From August 1915 the Namibian railway network was operated de facto by South African Railways, and this arrangement became official in 1922. … From 1959, steam locomotives were gradually replaced by diesel locomotives, for which an engine-house was built in Windhoek. This made operations very much easier, because water is in short supply in Namibia, and the coal needed to heat the water in the steam locomotives also had to be procured from the Transvaal.” [5]
The Namibian Network in the 21st century
In the 21st century, the rail network of Namibia is operated by TransNamib. As of 2017, the Namibian rail network consisted of 2,687 km of tracks. [11]
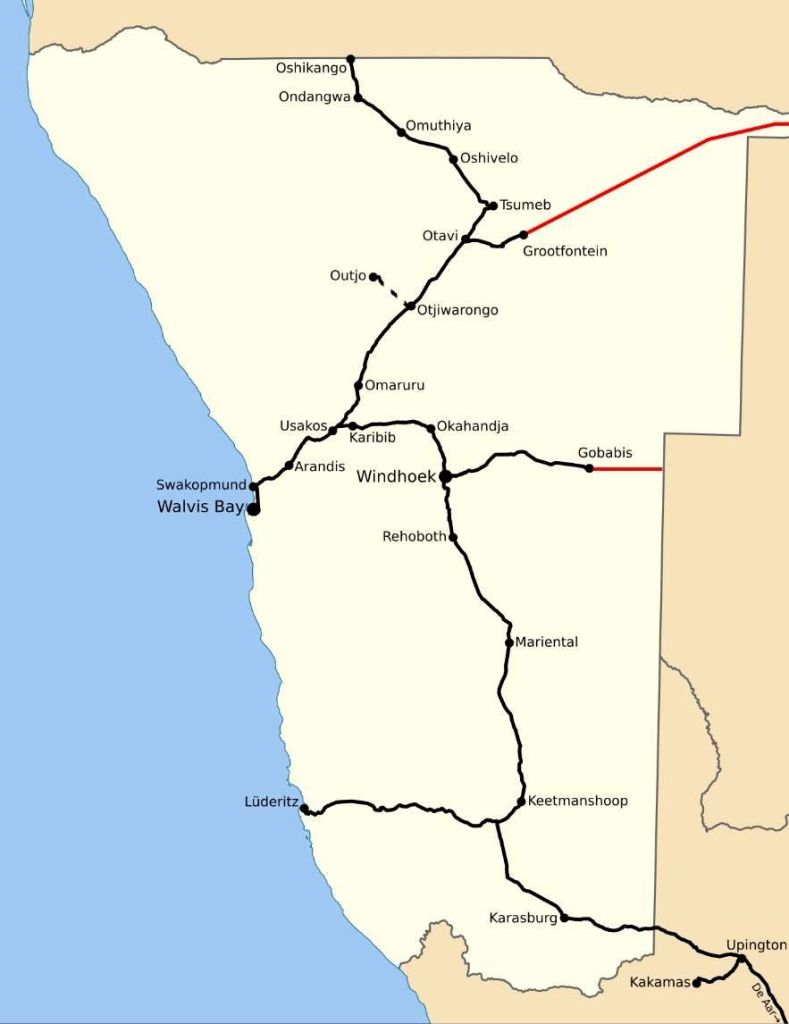
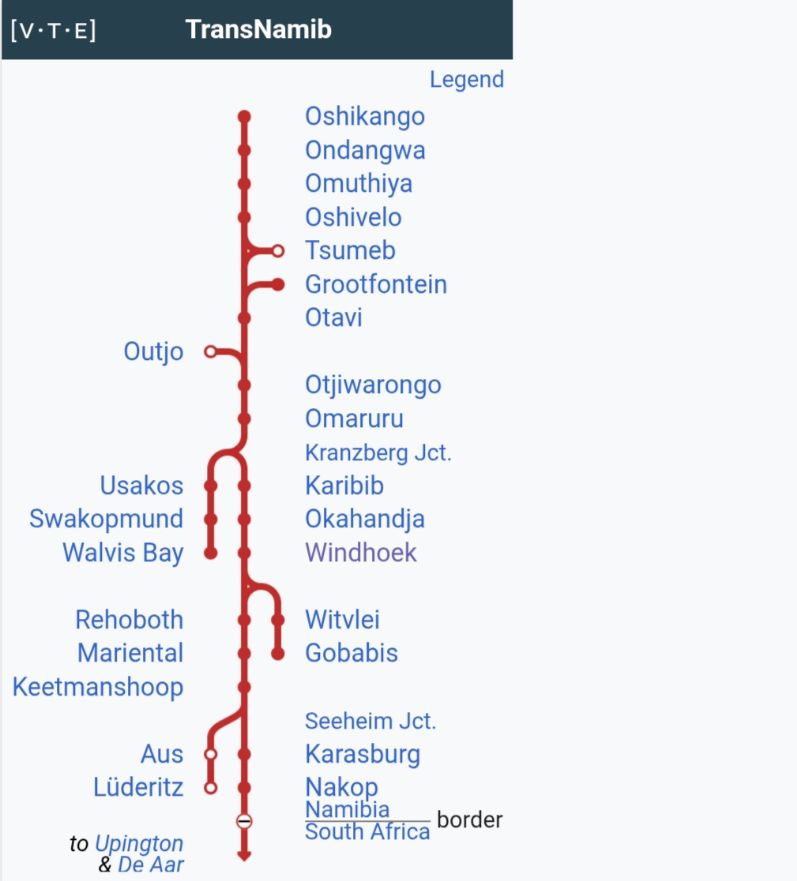
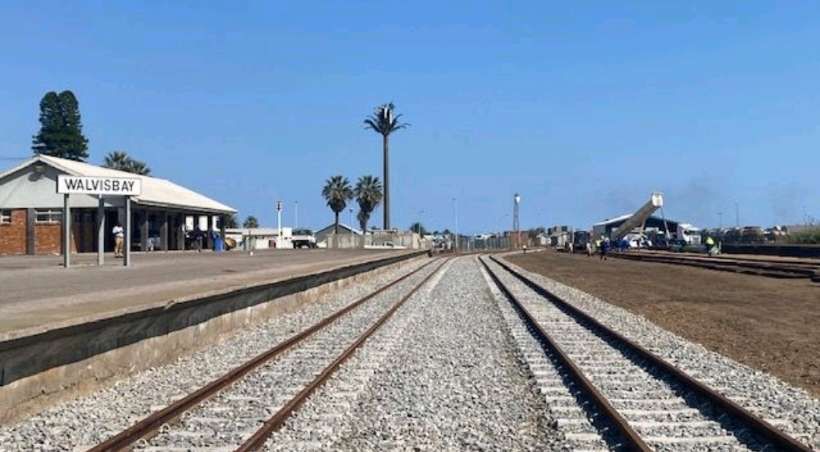
Windhoek-Kranzberg
The railway line from Windhoek to Kranzberg is 210 kilometres (130 miles) long and was completed in 1902. [10]
- Windhoek (capital – junction)
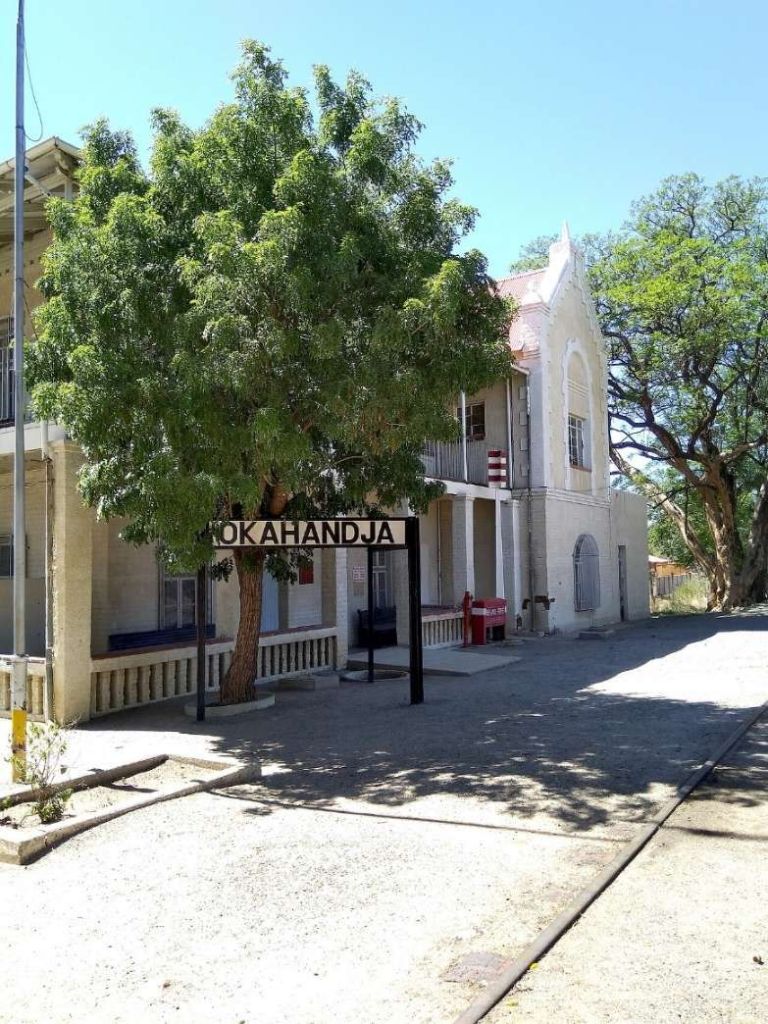
- Okahandja
- Karibib (proposed cement works)
- Kranzberg (junction Tsumeb v Windhoek)
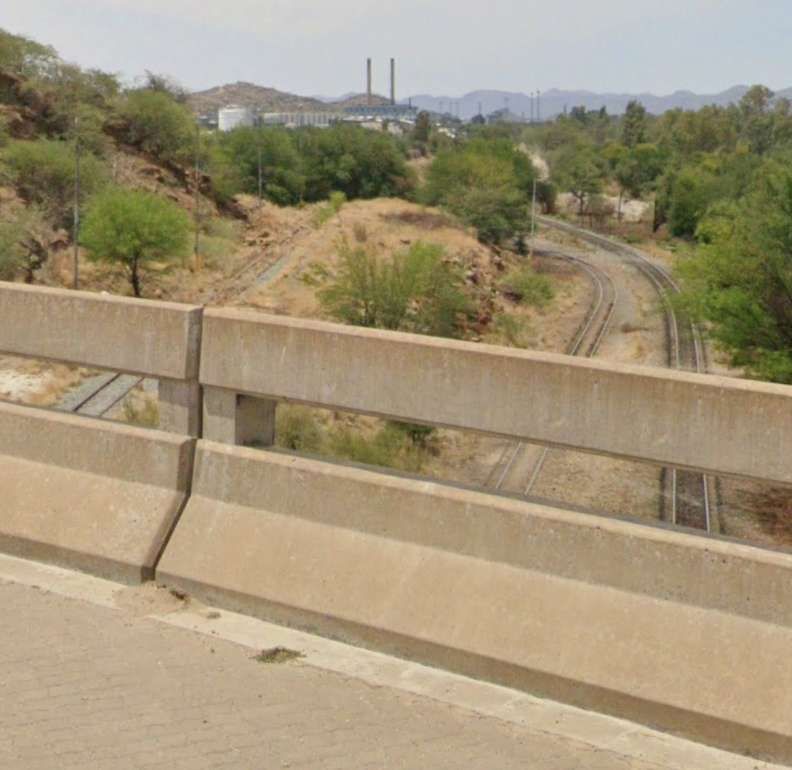
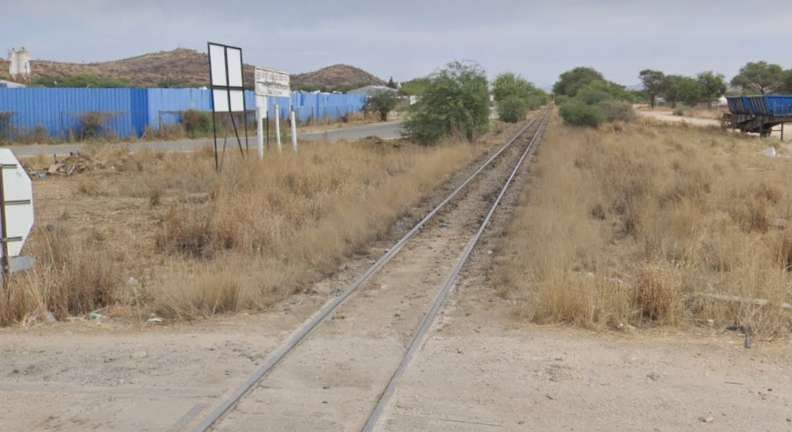
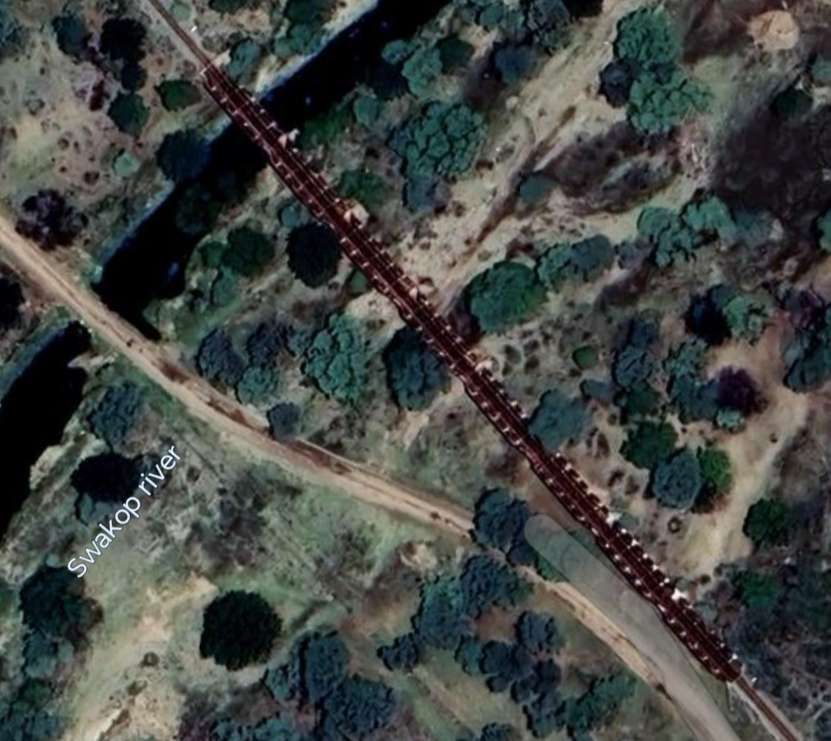
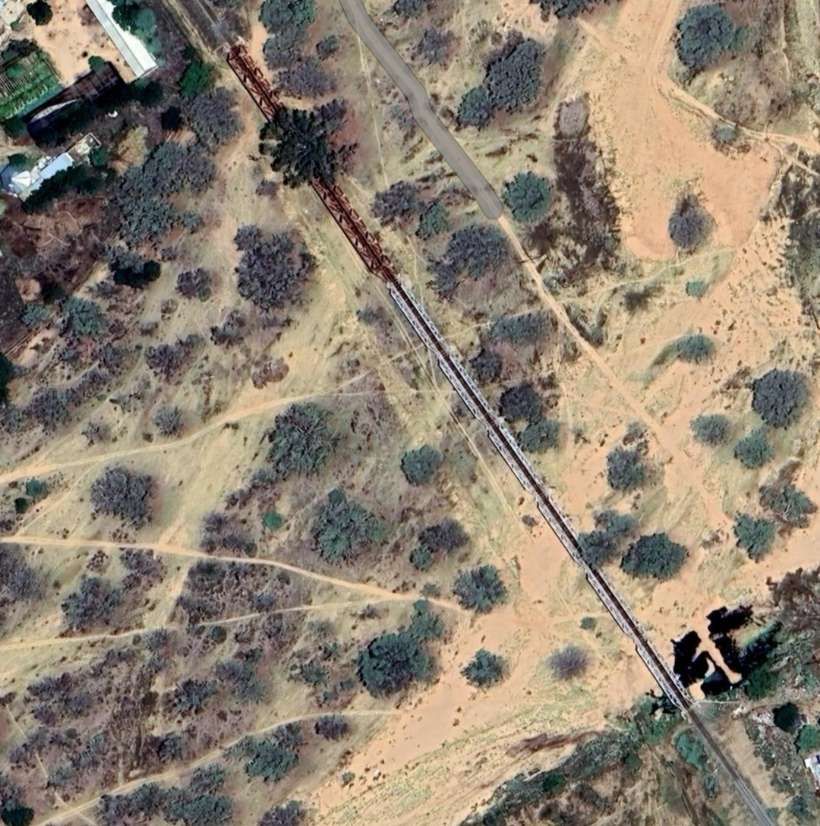
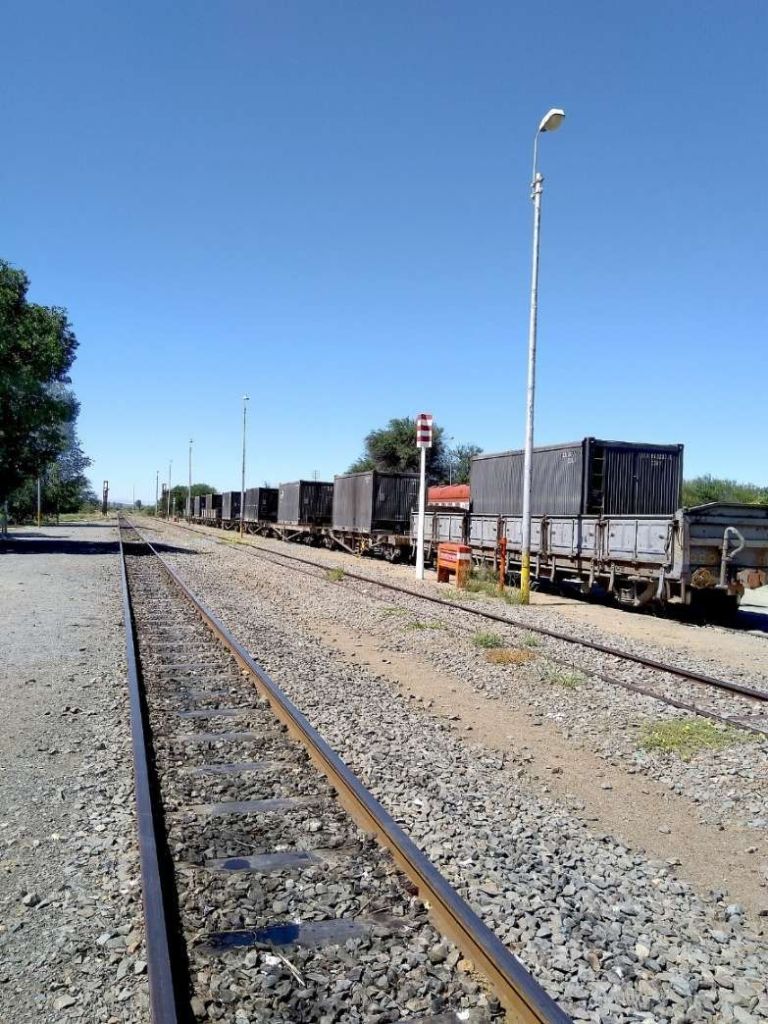
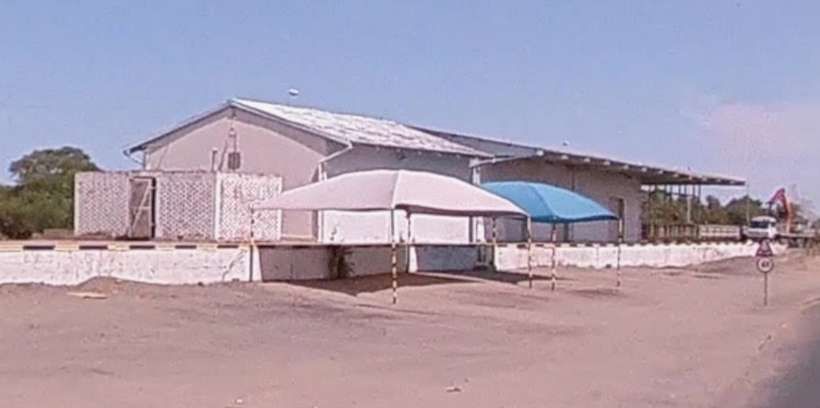
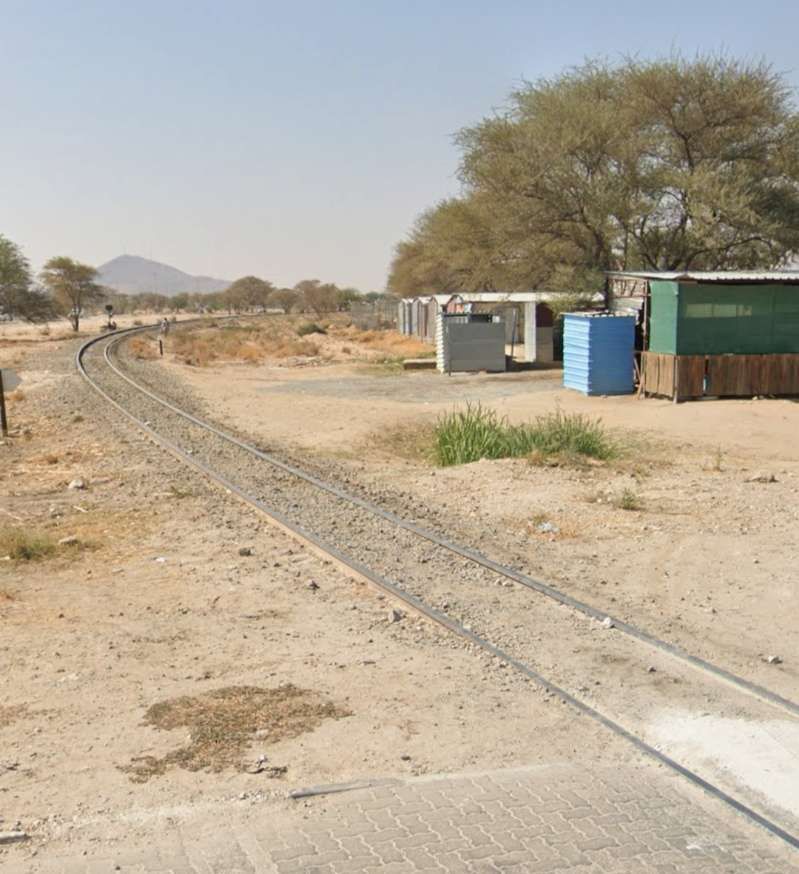
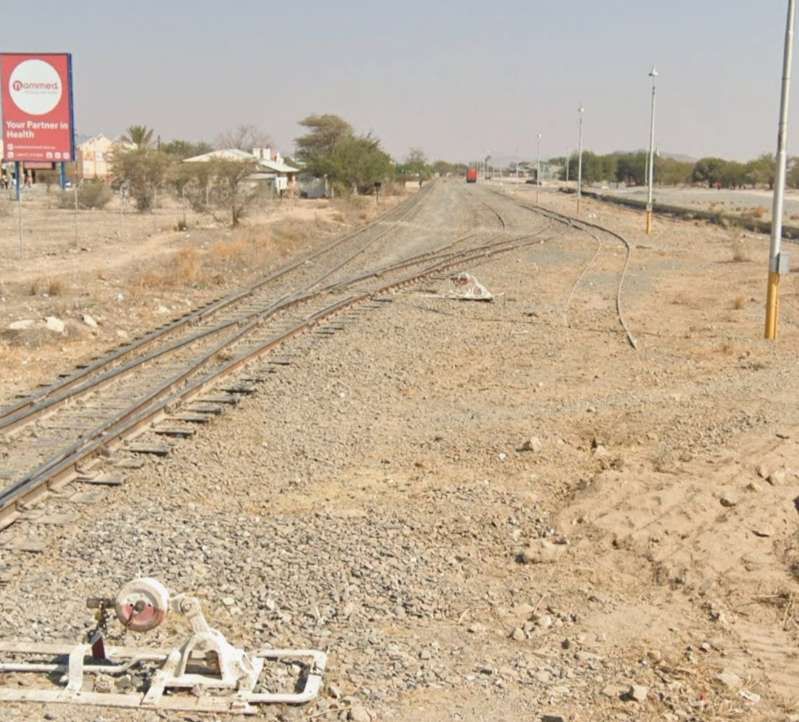
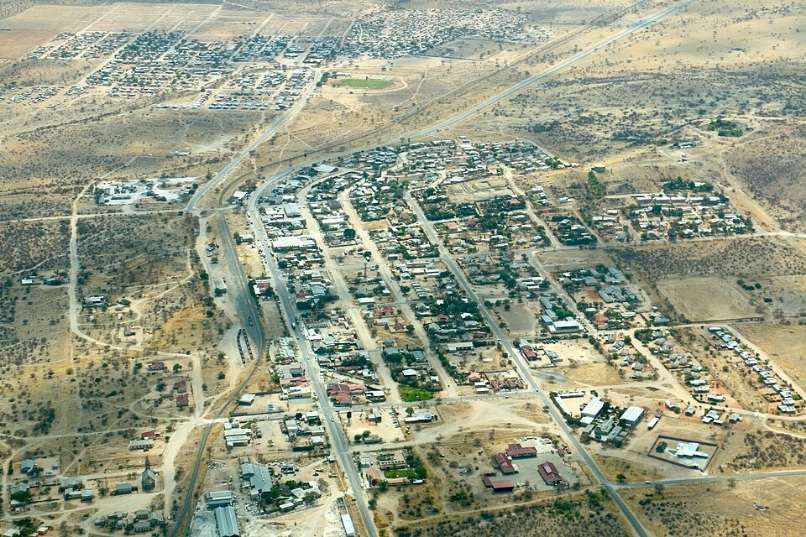
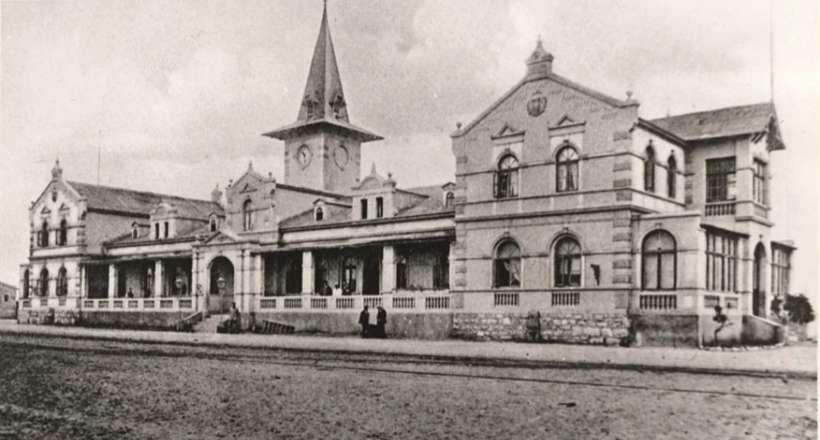
After the aerial image immediately below, the next three images form a kind of ‘tryptic’ which shows the TransNamib train yard and station at Windhoek. Taken together they show the full site. …
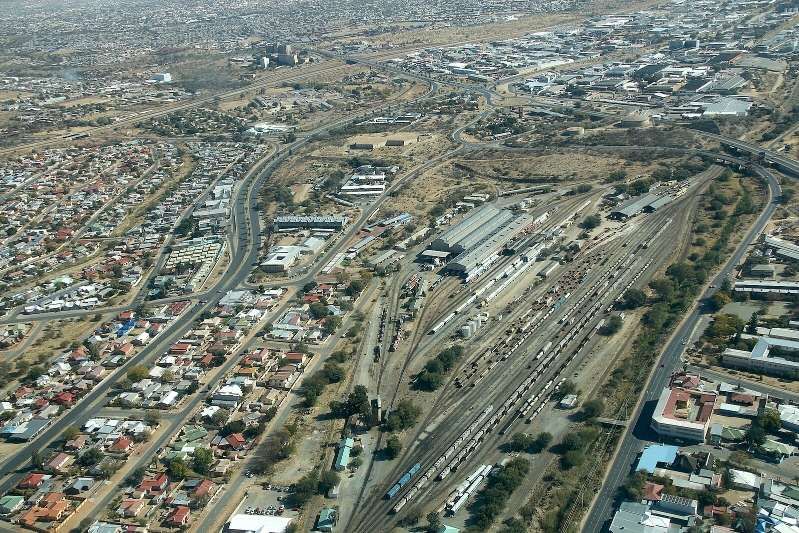
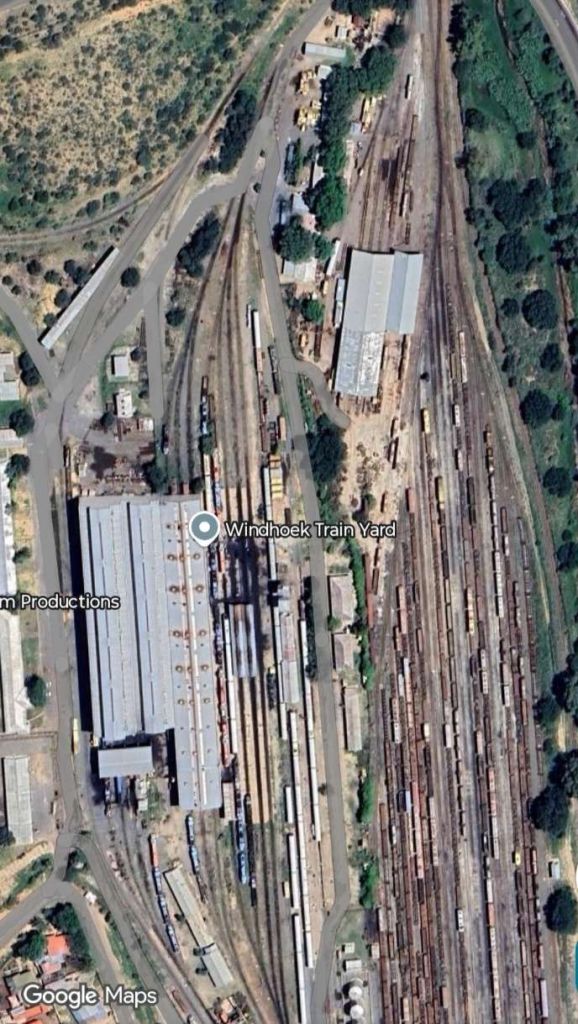


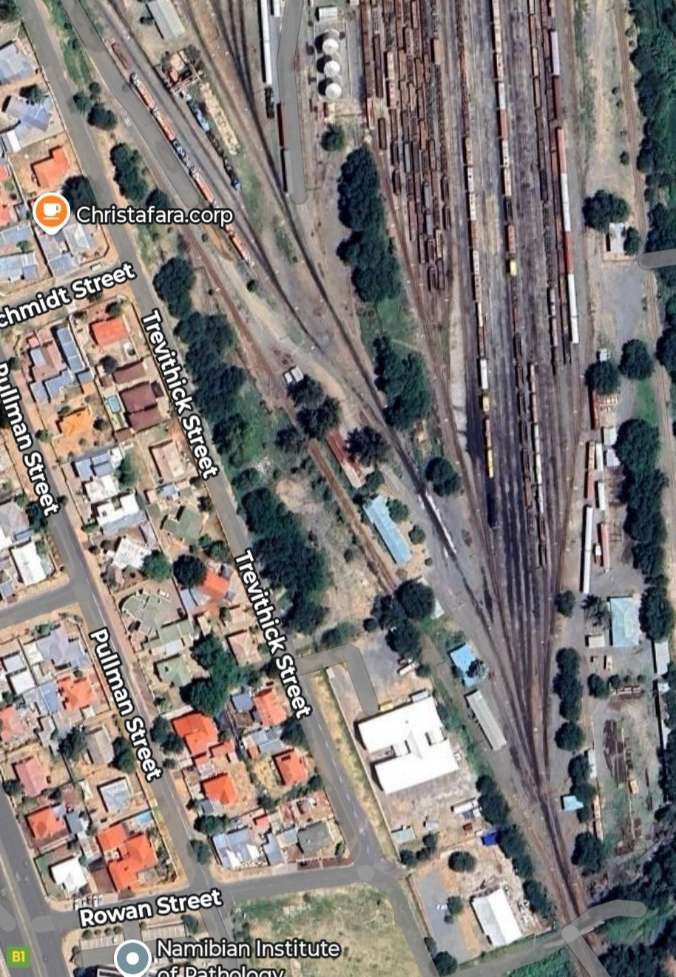

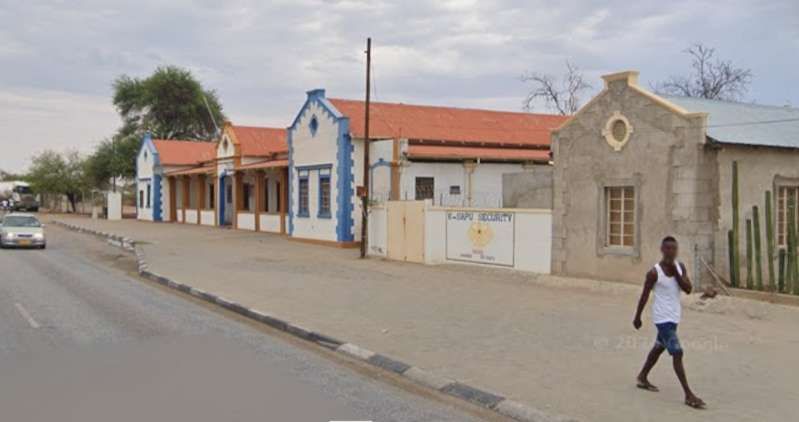
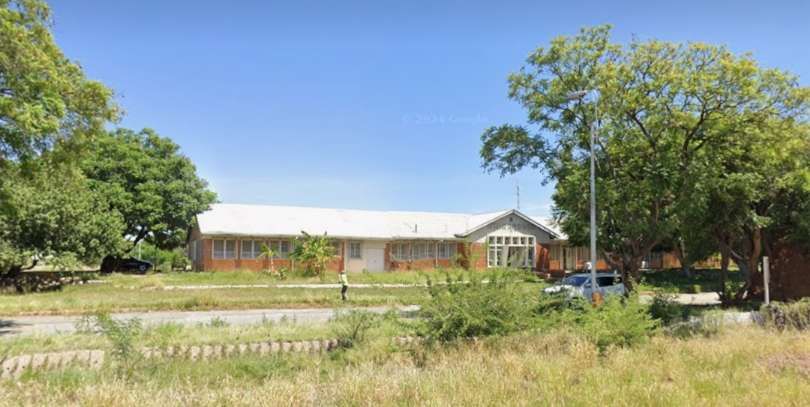
The main station building and the TransNamib Museum are located at the Southeast corner of the whole site.
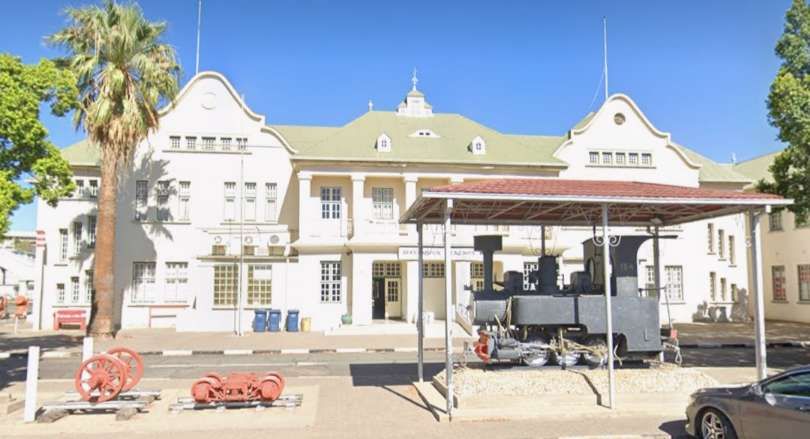
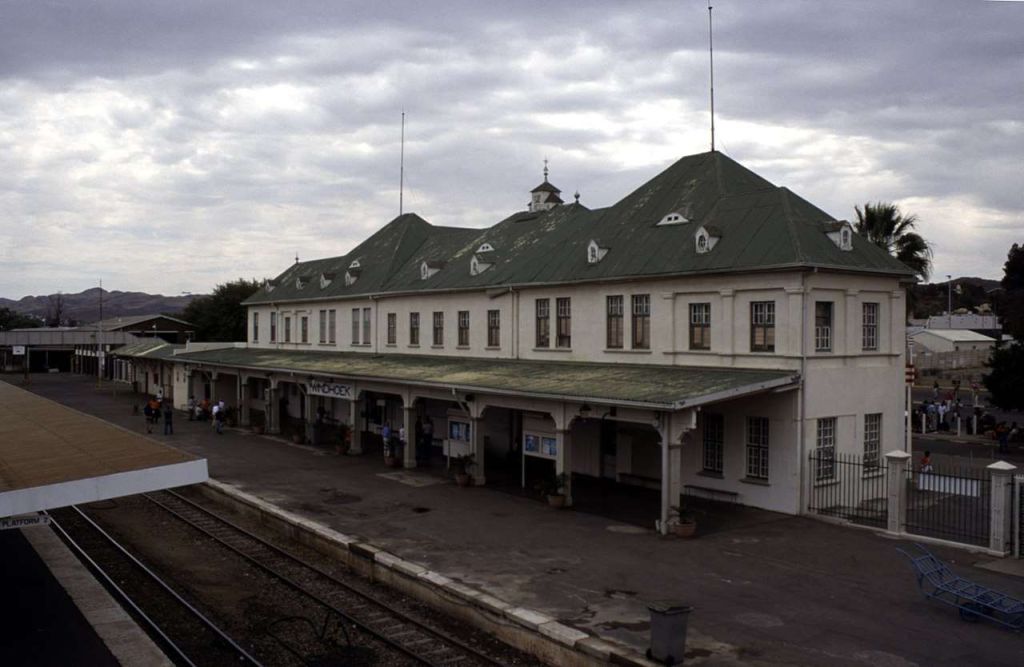


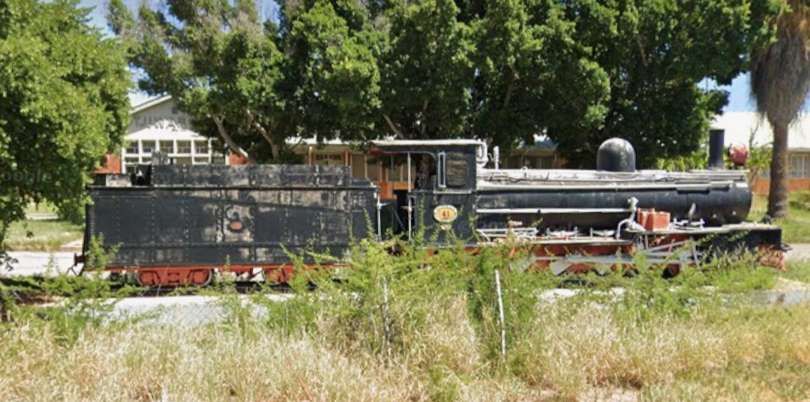
Wikipedia tells us that “the station was built in a Cape Dutch-style and is located on Bahnhof Street. An additional northern wing was constructed by South African Railways in 1929 to match the existing style of the building. … The station also houses the small Trans-Namib Railroad Museum which outlines Namibian transport history, particularly that of the railway. Opened on 1st July 1993, the exhibition consists of a wide range of railway equipment, maps and related items which date back to German colonial times. Another part of the exhibition is dedicated to Namibian Airways history and Namibian Maritime history. … Across from the entrance [to the station] stands the German locomotive ‘Poor Ole Joe’, one half of a South West African Zwillinge, No 154A, the sole surviving specimen of this type of steam locomotive. It was originally shipped to Swakopmund in 1899 and reassembled for the run to Windhoek” [23][24]

Namibia Scientific Society posted the following on Facebook on 9th June 2020: Poor Ole Joe is a 600mm-gauge steam locomotive “and was manufactured in 1900 by Henschel & Sohn GmbH, Kassel, Germany, under the serial number 5376. It was put into operation in 1904 and operated on the Swakopmund – Windhoek route. The steam locomotive was taken out of service in 1939 after traveling approximately 371,000 miles.” [25]
There is some uncertainty over the date of fabrication of the locomotive. Perhaps the two years mentioned relate to a date when the locomotive was shipped from the factory and the date of completion of the reassembly in Swakopmund?
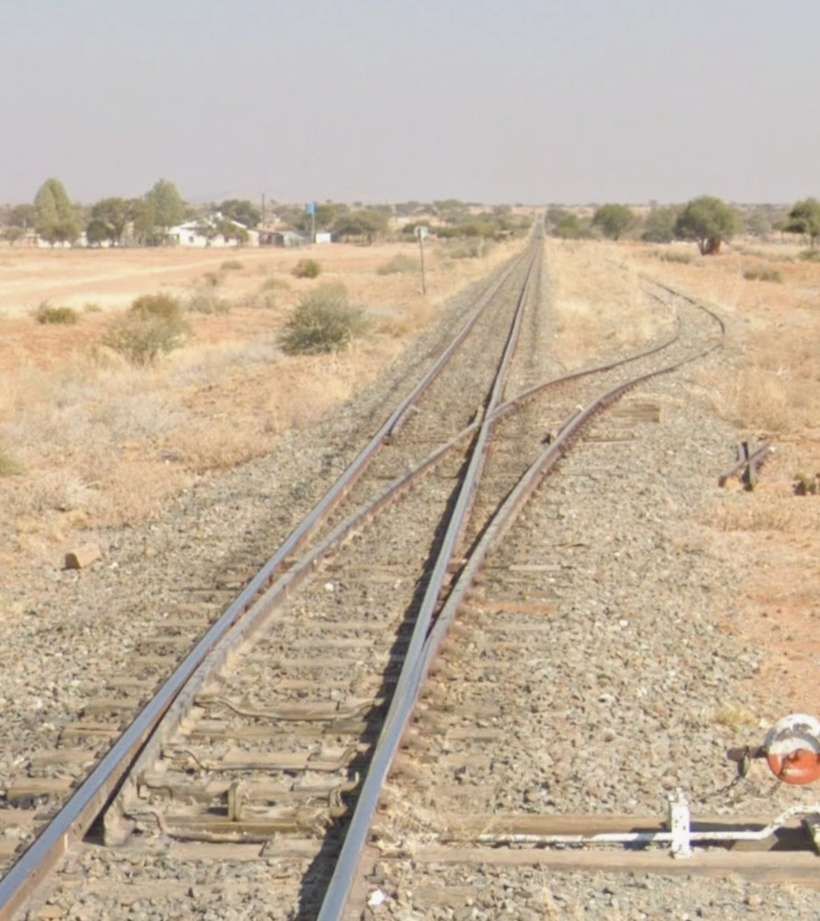
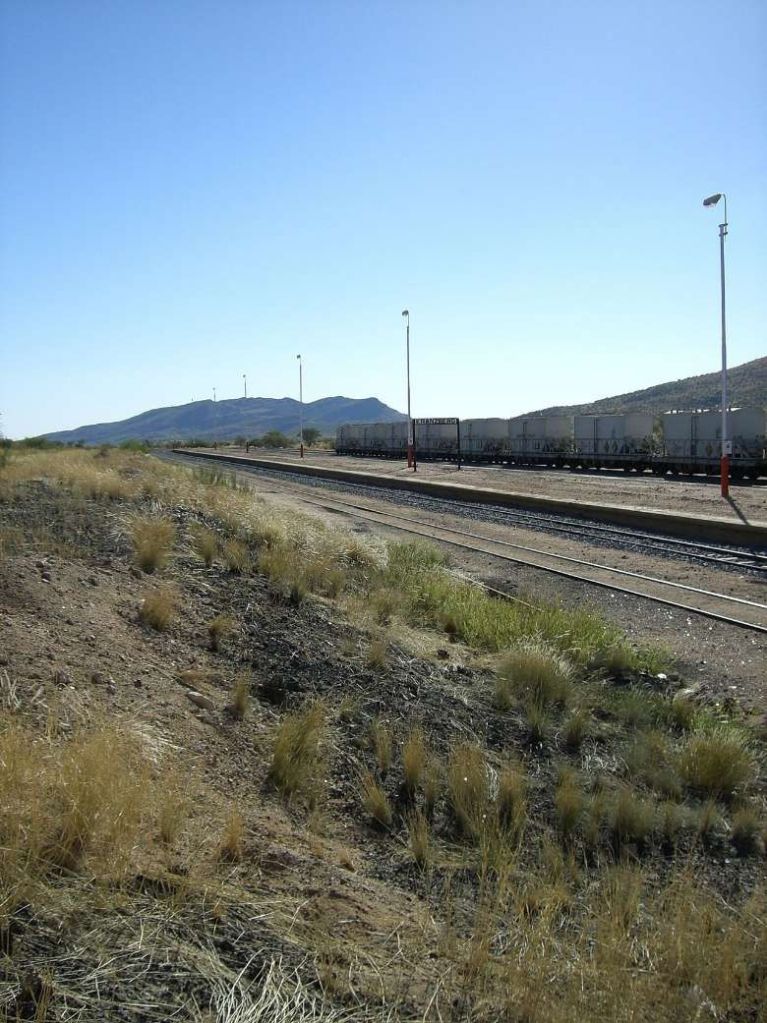




































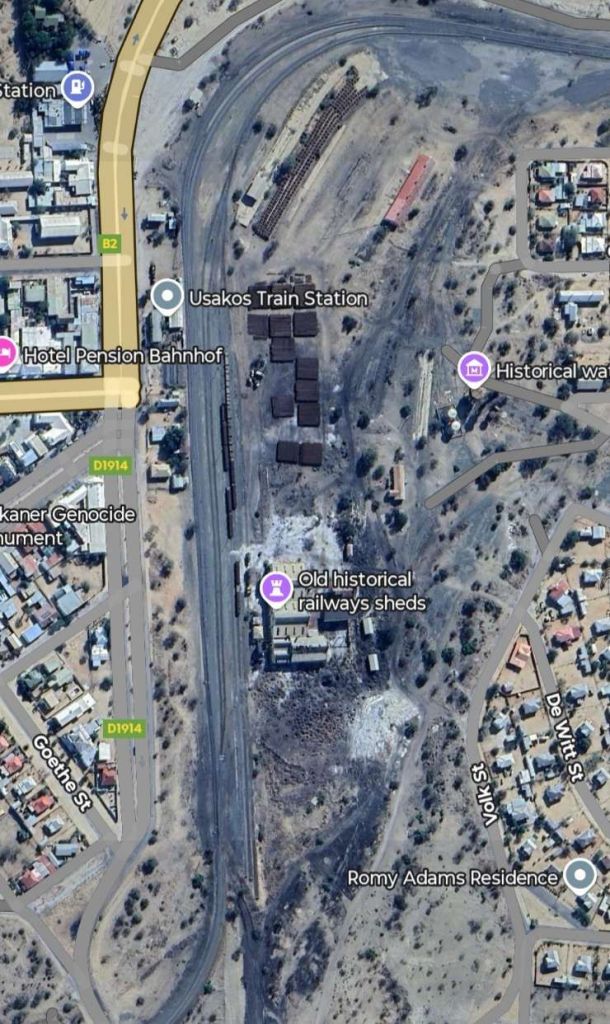
Kranzberg-Walvis Bay
The railway line from Kranzberg to Walvis Bay is 201 kilometres (125 miles) long. The section between Kranzberg and Swakopmund was completed in 1902. In 1914, an extension to Walvis Bay was commissioned; the rails were laid close to the shore of the Atlantic Ocean. In 1980, this extension was replaced by an alternative route behind the dunes that allowed for higher axle load. [10]
- Kranzberg (junction Tsumeb v Windhoek)
- Usakos
- Arandis (crossing loop)
- Swakopmund
- Walvis Bay (port)
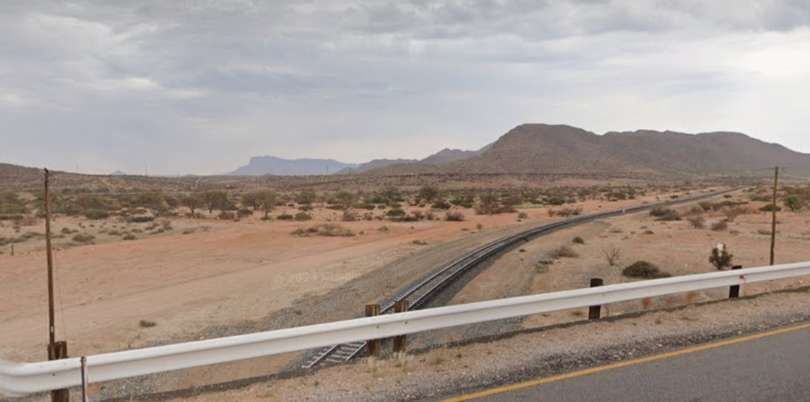


Key locations along the line to Swakopmund are illustrated below: …
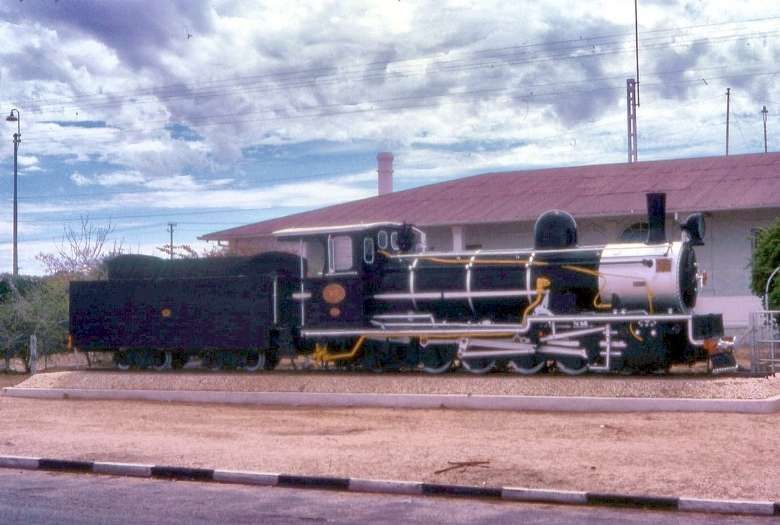
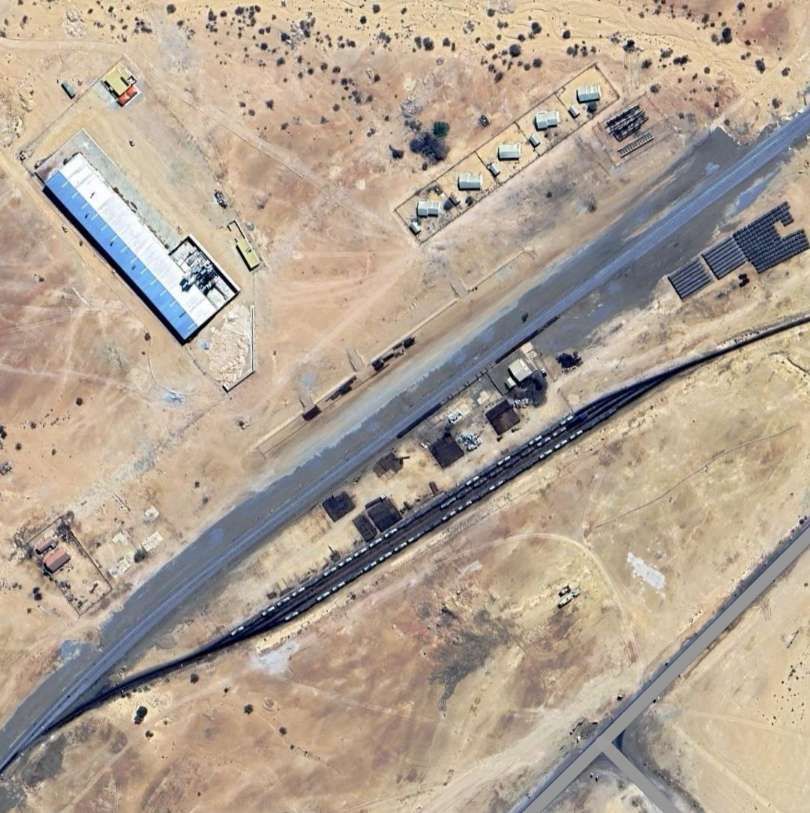









Before having a look at the Rossing Uranium Mine, it is worth a quick diversion Northwest of the station and marshalling yard shown above. The Namibia Institute of Mining & Technology is host to a plinthed display of a locomotive and carriages from the old 2ft-gauge railways of Namibia.

This train was once on display in Windhoek. It was moved to the Namibia Institute of Mining Technology (NIMT) outside Arandis. and restored with the help of Wesbank Transport and AWH Engineering, Rigging and Rentals. The locomotive, is a Henschel Hb 56. The locomotive and its wagons were in use between Usakos and Tsumeb between 1906 and 1959. The South African Railways then donated it to the National Museum in Windhoek and in 1964 it was placed in front of the Alte Feste, but it was too close to the Reiterdenkmal and was moved in 1974 to the southern side. The train consists of the locomotive, a coal wagon, a closed goods wagon, a passenger coach for first and second class and a wagon in which the conductor travelled with the mailbags, milk and cream cans that were picked up along the route. The passenger coach could transport 16 passengers. The first-class passengers could sit on upholstered seats while the second-class passengers sat on plain wooden benches. The two classes were divided by a small washroom. The conductor’s wagon was destroyed in 2007 when it was set alight by a homeless person who slept in the train and made a fire. The boilermaker and carpentry students at NIMT renovated the train. [35]
“The locomotive is from the class Hb 0-6-2T. Of the 15 locomotives built by Henschel for the Otavi line between 1905 and 1908, six were absorbed into the SAR. The engines had Allan valve gear and often ran with an auxiliary tender attached which contained both coal and water.” [36]









(22°47′17″S 014°35′20″E), © Olga Ernst & Hp.Baumeler and Iicenced for reuse under a Creative Commons Licence, (CC BY-SA 4.0). [11]

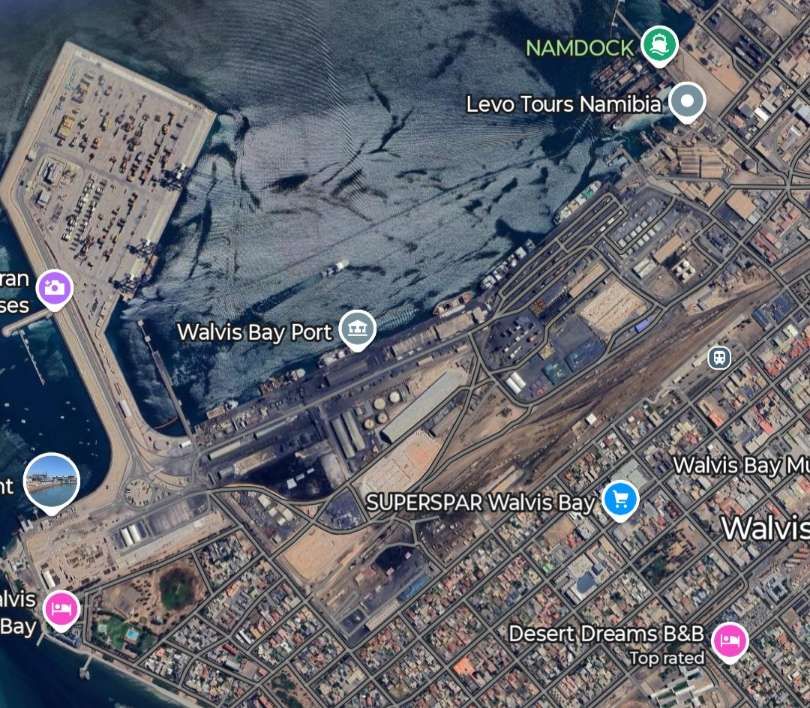
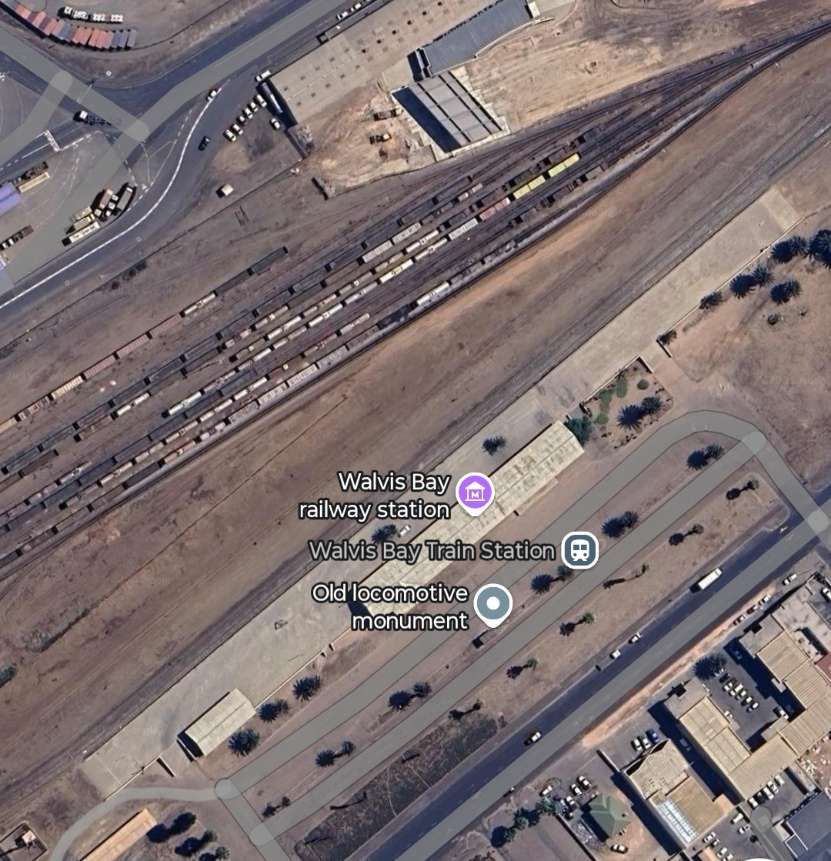



Walvis Bay was a British enclave in German South West Africa. The first narrow gauge railway in the British ruled Cape Colony was in Walvis Bay. Initially projected merely to connect the jetty with the town, the Walvis Bay Railway was opened in 1899 and ran for twelve miles up north to the German border at Plum. [17]
“On 6th March 1899 the Agent General for the Cape of Good Hope ordered a “Sirdar” class locomotive named ‘Hope’ which was almost as long in transit to Walvis Bay – where it arrived on 22nd August 1899 on board the British barque Primera – as it had been in the building. Because of the extremely light nature of the track (12 lb. rail with sleepers spaced three feet apart) HOPE was provided with an additional pair of carrying wheels at both ends. Thus the standard 0-4-0T type was converted to a 2-4-2T type. Even so the maximum axle load of ‘Hope’ in working order would be about 1¾ tons, which is considerably more than today’s suggested figure for this category of track of 1 ton 4 cwt. Within six years the railway was virtually moribund and by 1915, ‘Hope’ had been laid aside and forgotten. That was because the Germans preferred to use their own harbour in Swakopmund.” [17][18]

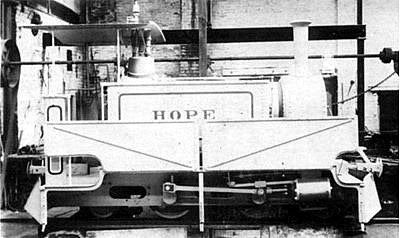
Two works photographs of ‘Hope’: in the one with the valance (wheel cover) raised, one of the smaller carrying wheels can just be made out on the left of the picture. [17][18]
Kranzberg-Otavi
The railway line from Kranzberg to Otavi is 328 kilometres (204 miles) long and was completed in 1906. [10]
- Kranzberg (junction Tsumeb v Windhoek)
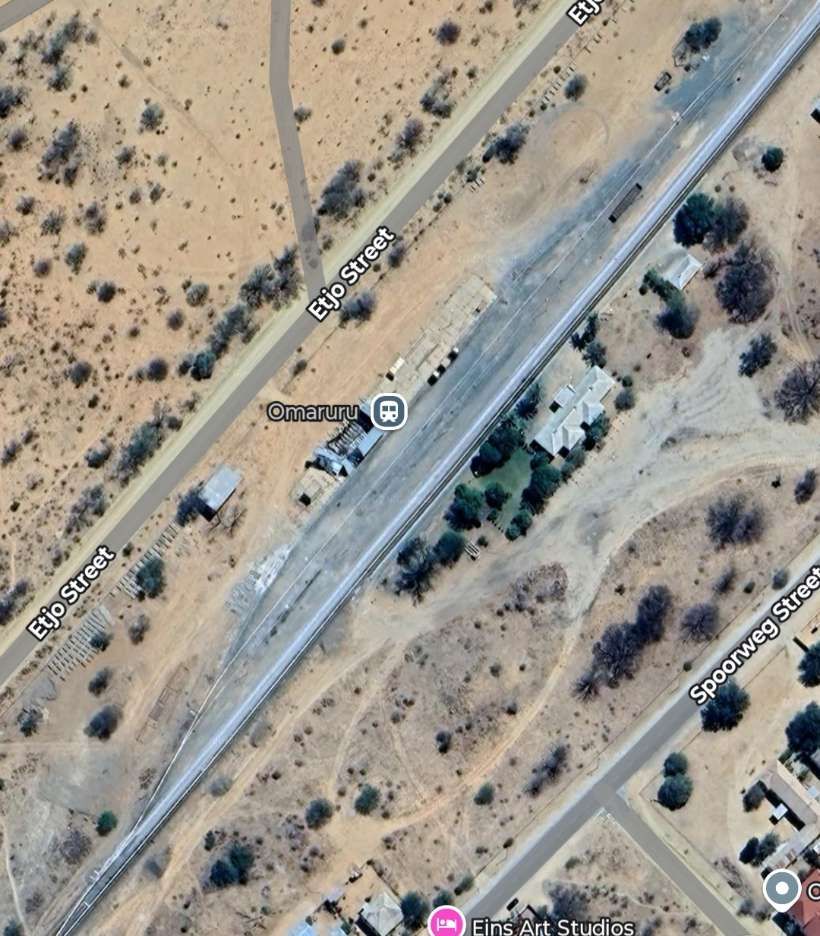
- Omaruru
- Kalkfeld (short siding)
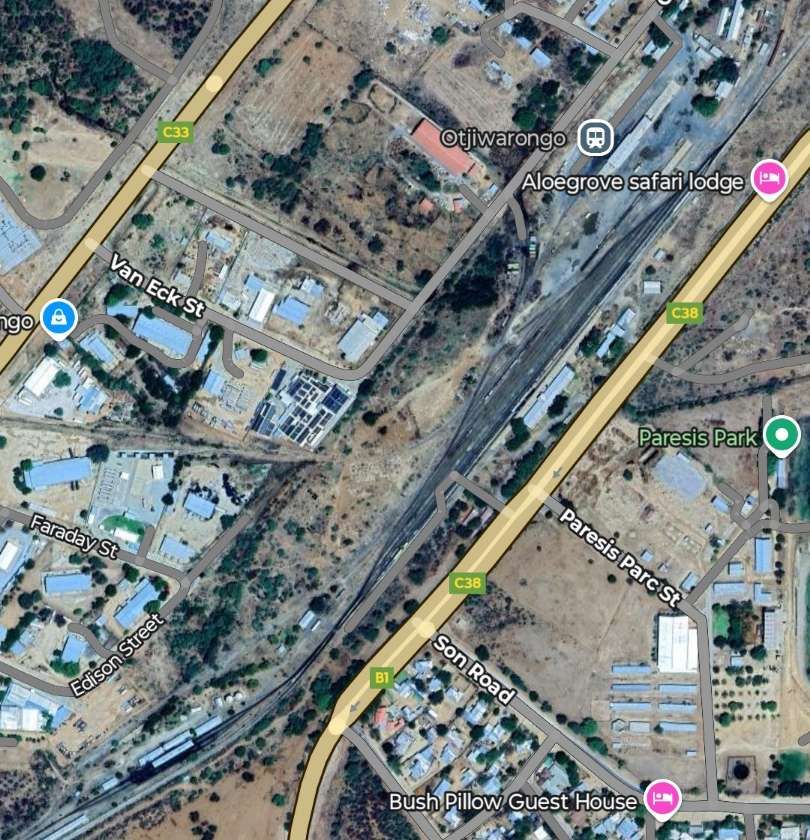
- Otjiwarongo (junction for Outjo)
- Otavi
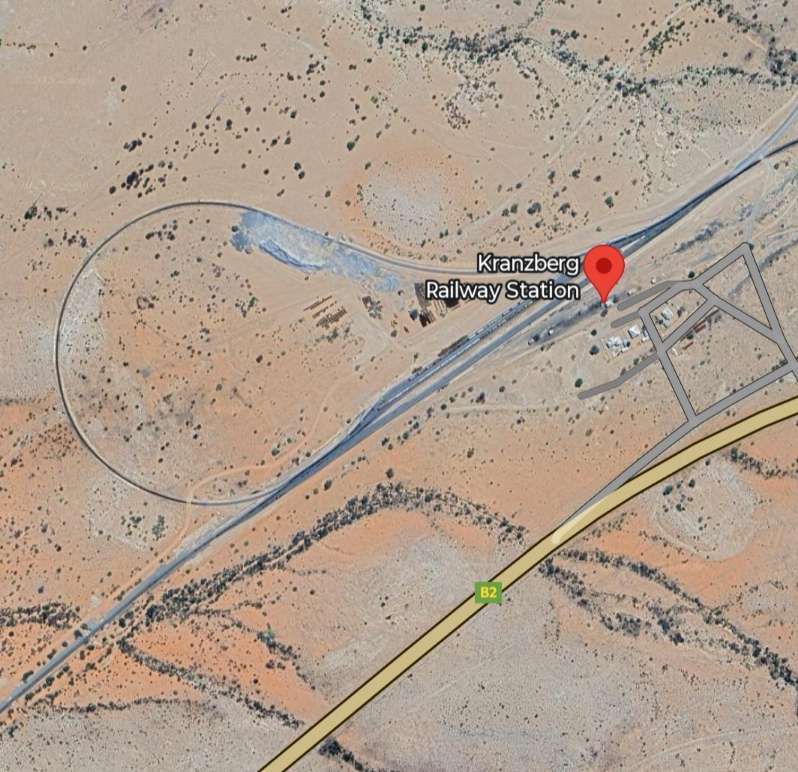
Kranzberg Railway Station has already been featured above. The next images show the line from there to Otavi. …

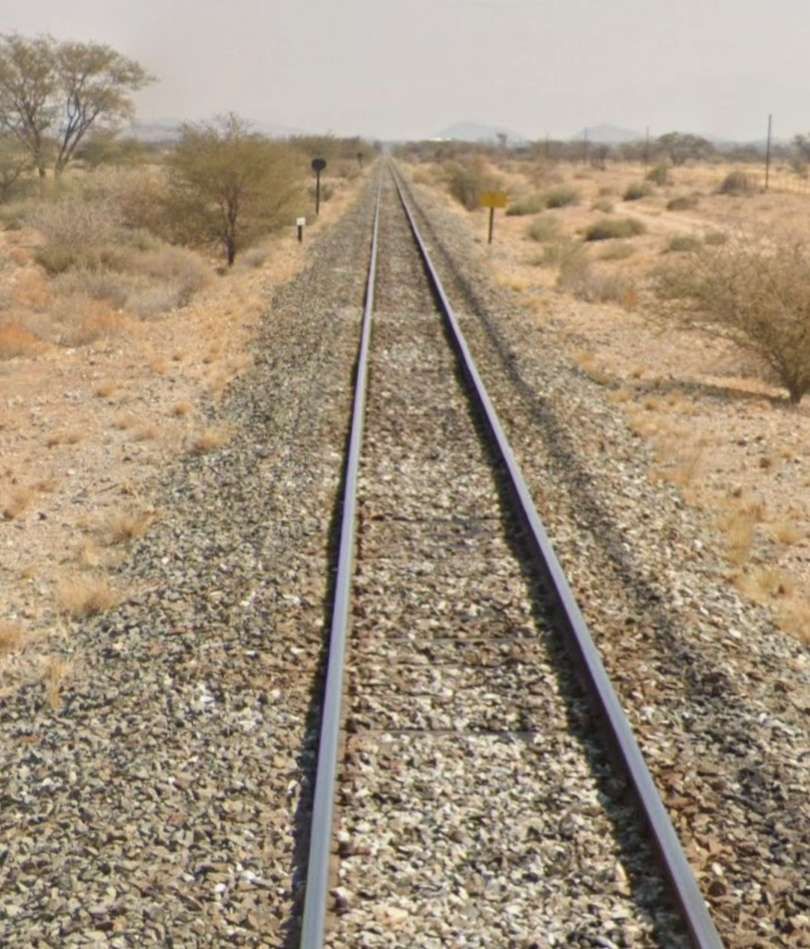
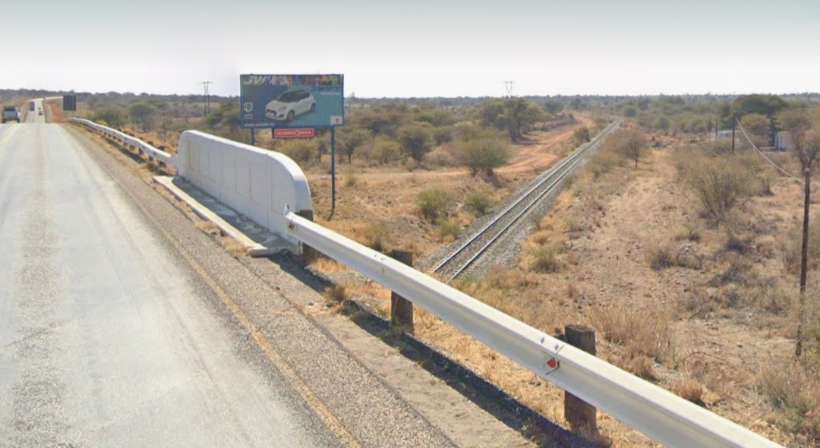
The loop allows trains from Windhoek to access the route to Otavi without reversing. That line running towards Otavi sets off from Kranzberg in a Northeasterly direction crossing a series of dry watercourses and gradually taking a more northerly course before encountering the D2315 (a dirt road).
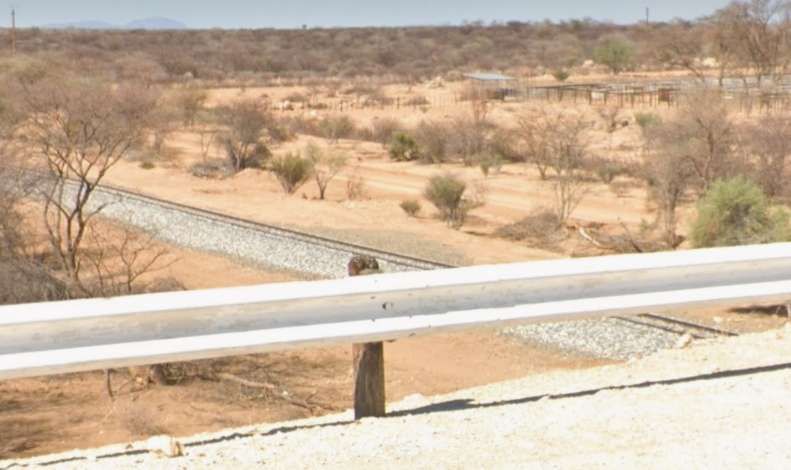
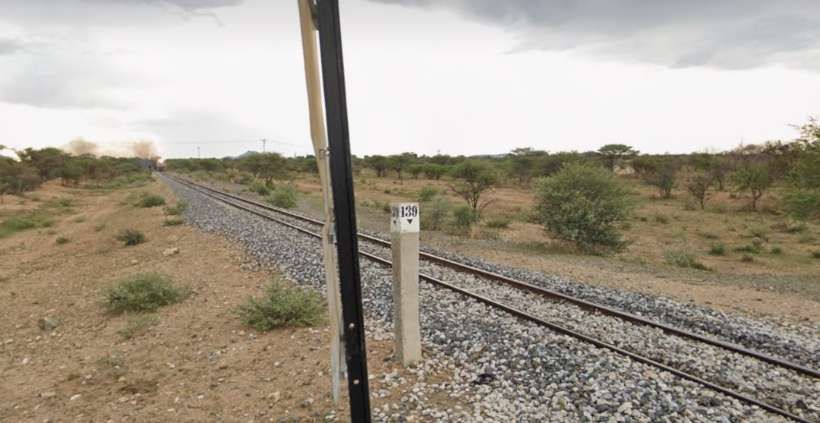

















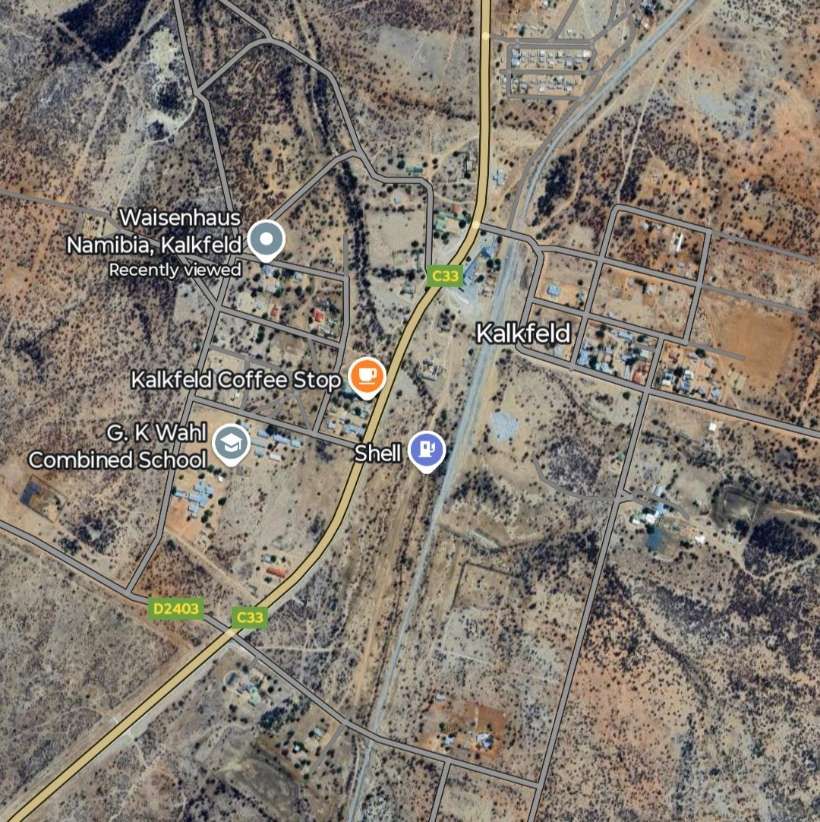


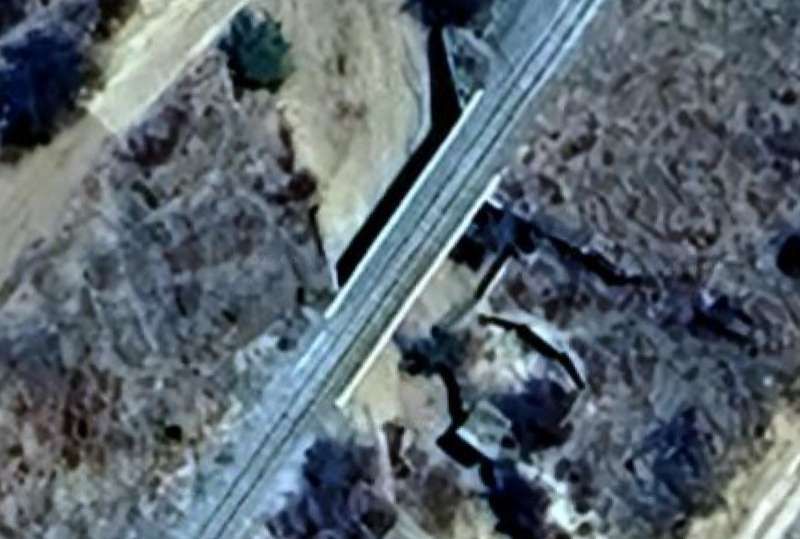
From Kalkfeld the line heads in a generally Northeasterly direction towards Otjiwarongo.

The next five images are a sequence which shows a long passing loop, perhaps halfway towards Otjiwarongo.
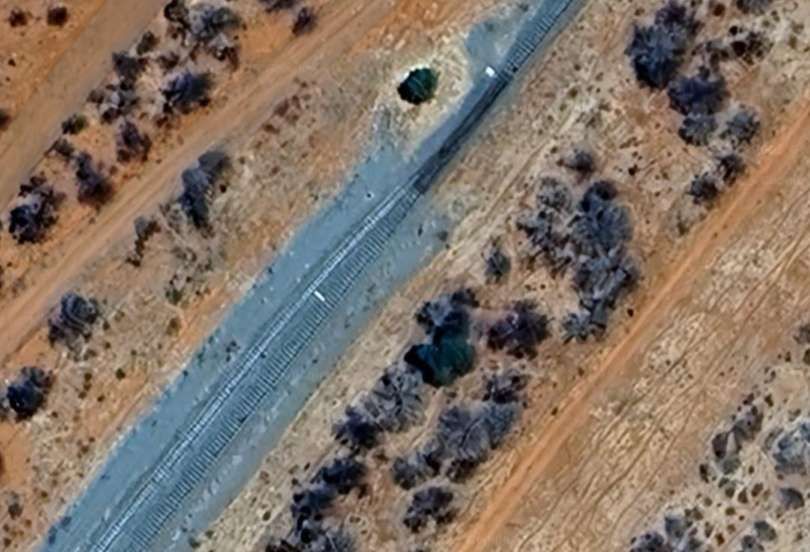
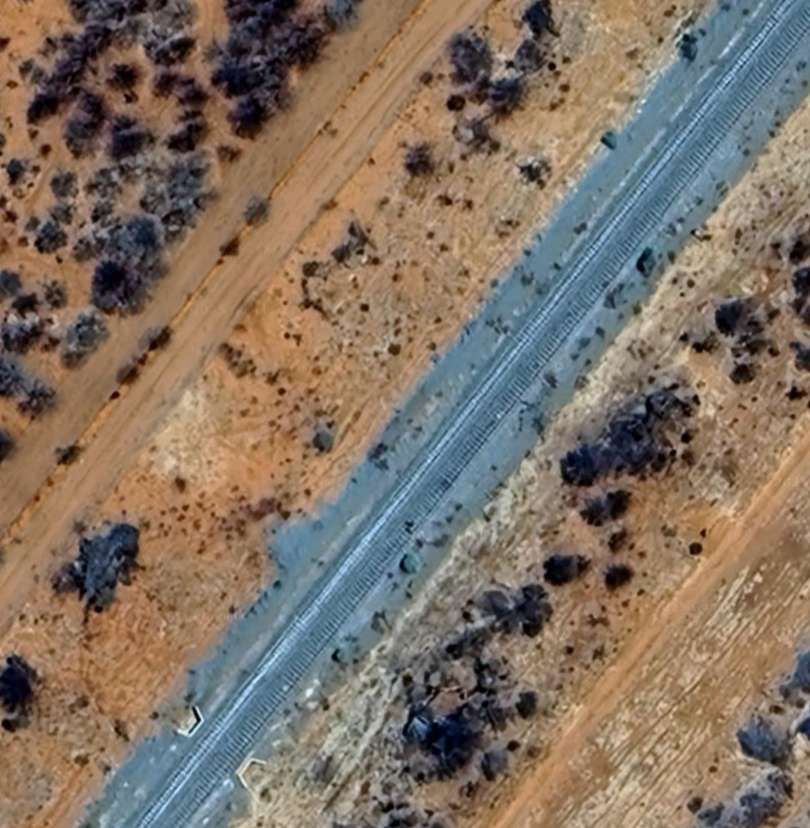
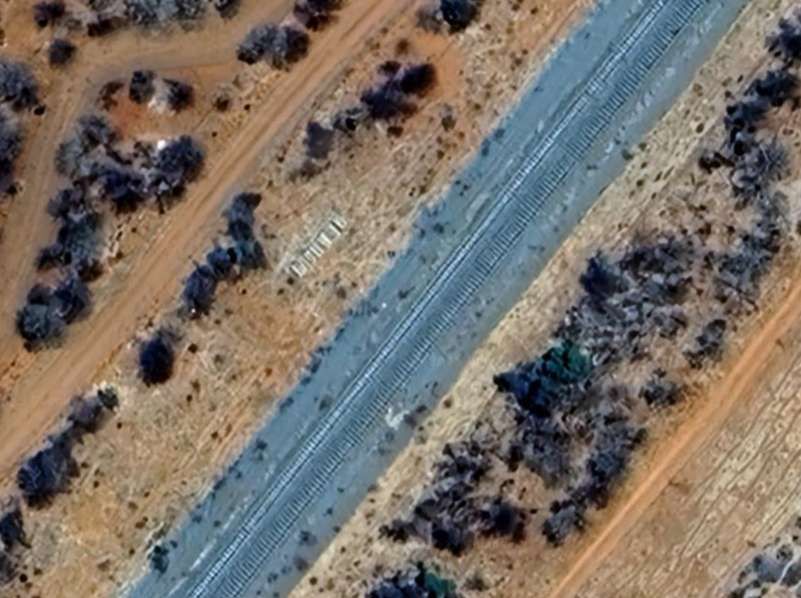
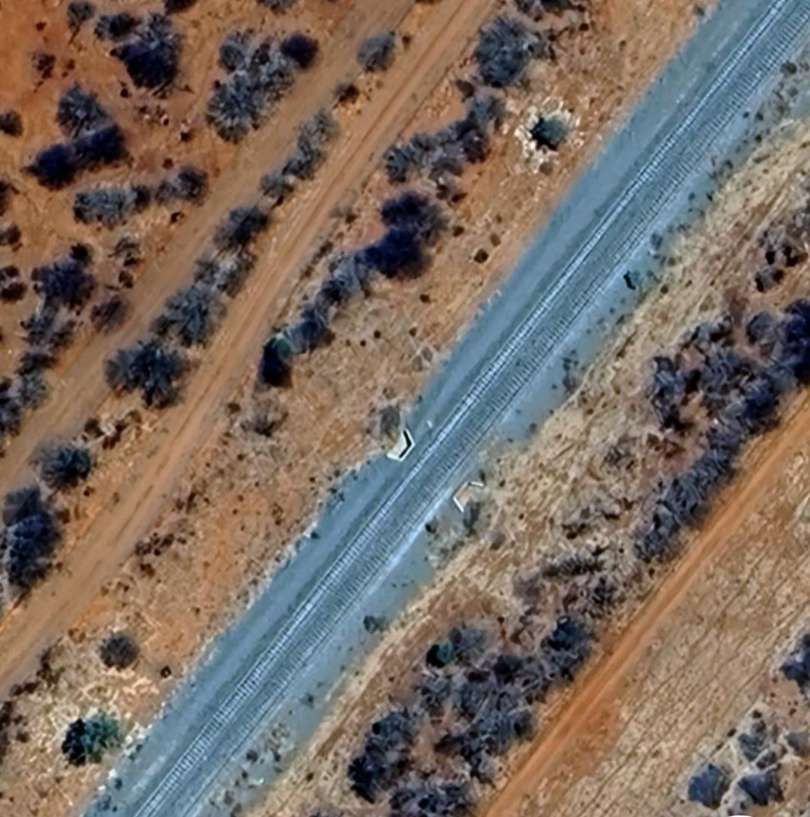
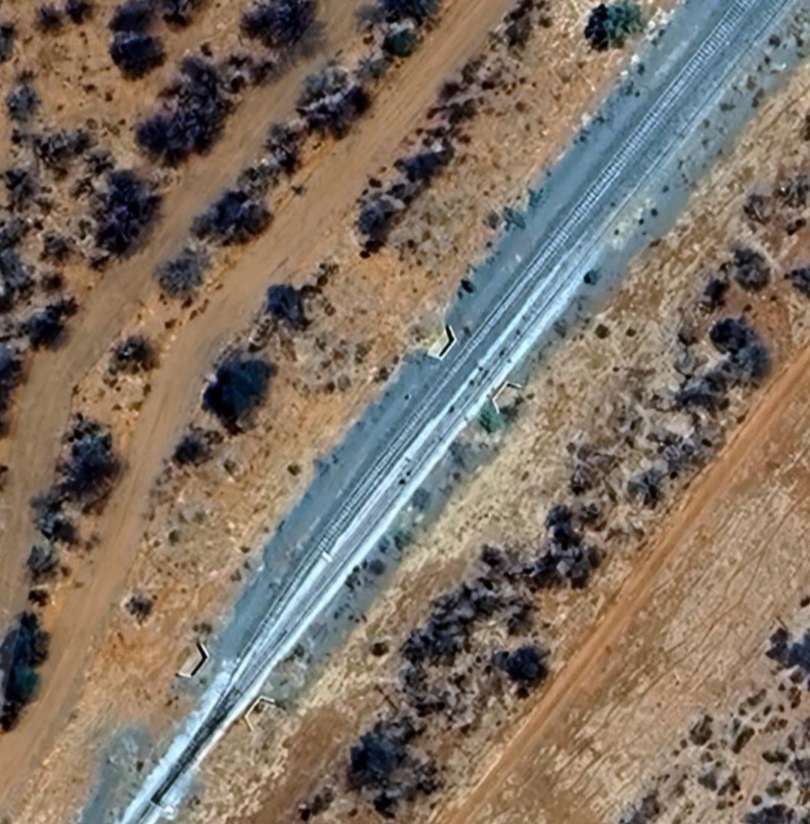





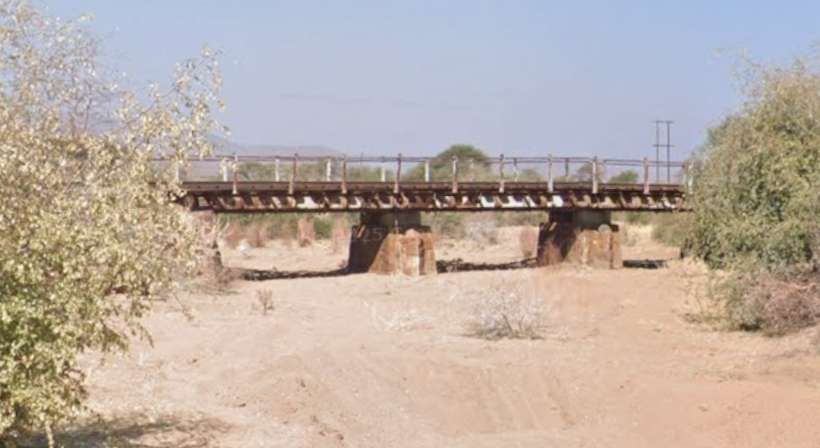
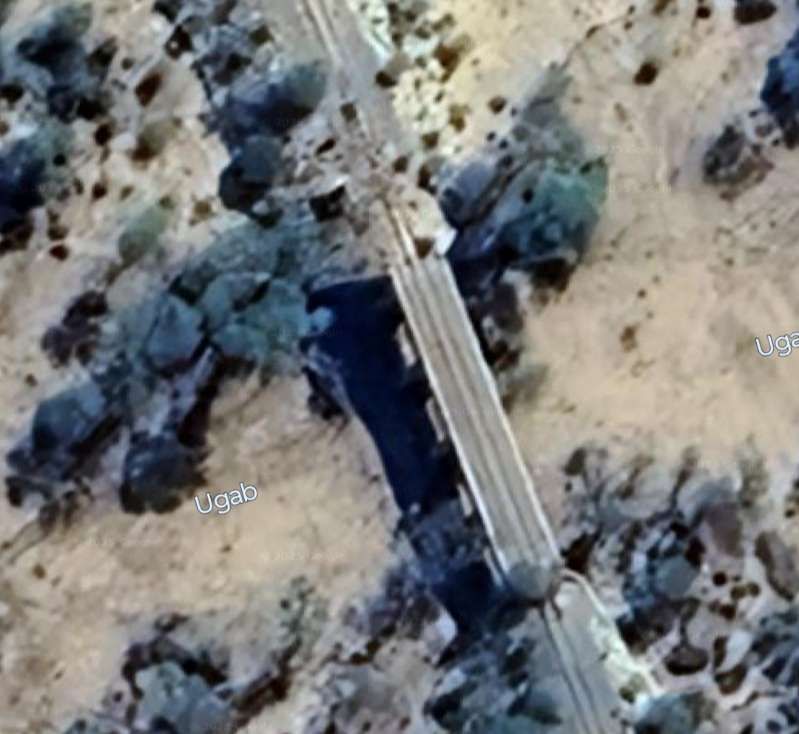
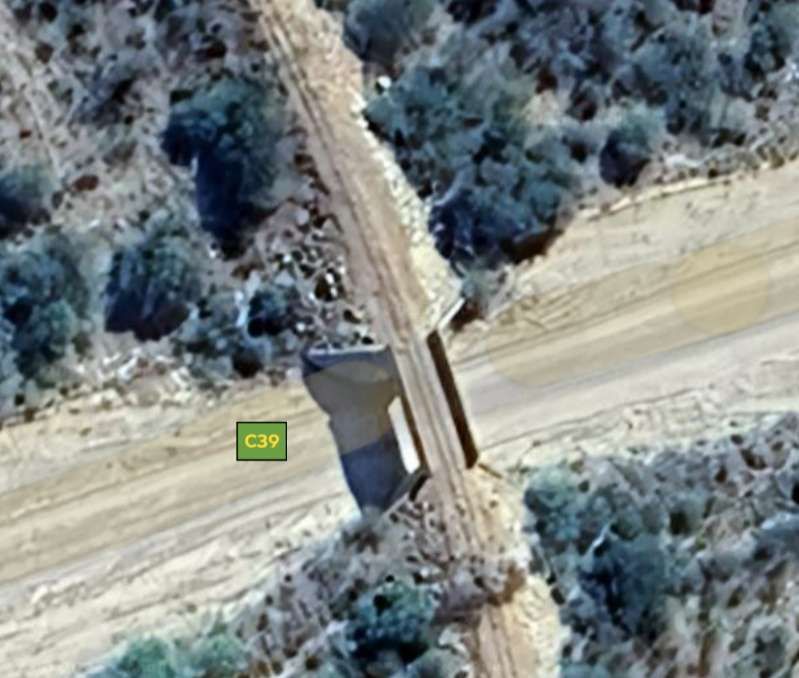
The next five images show a sequence of structures over dry river beds
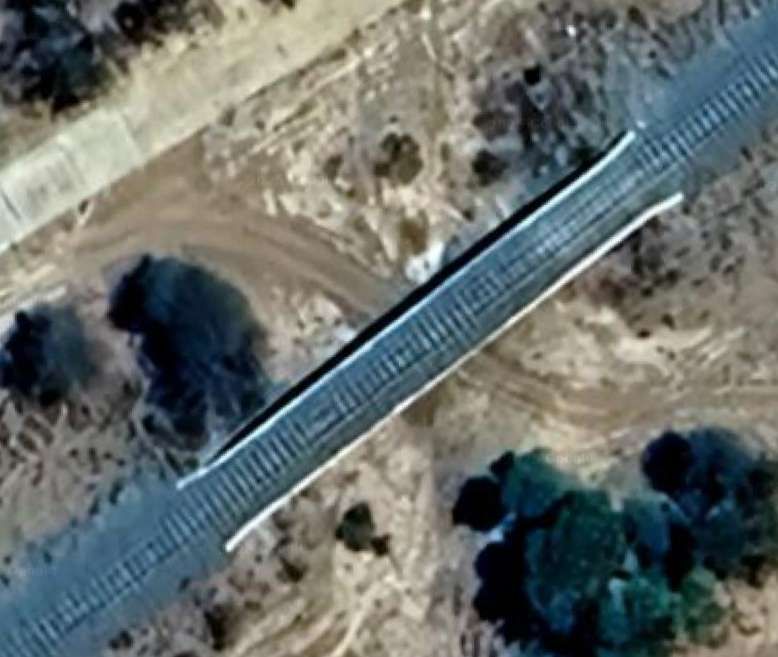
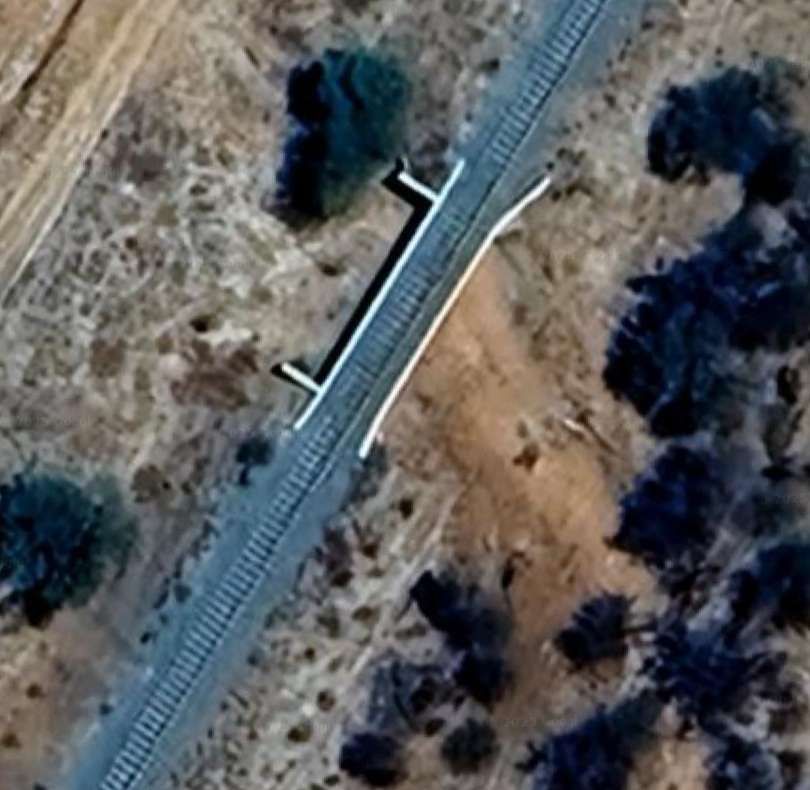
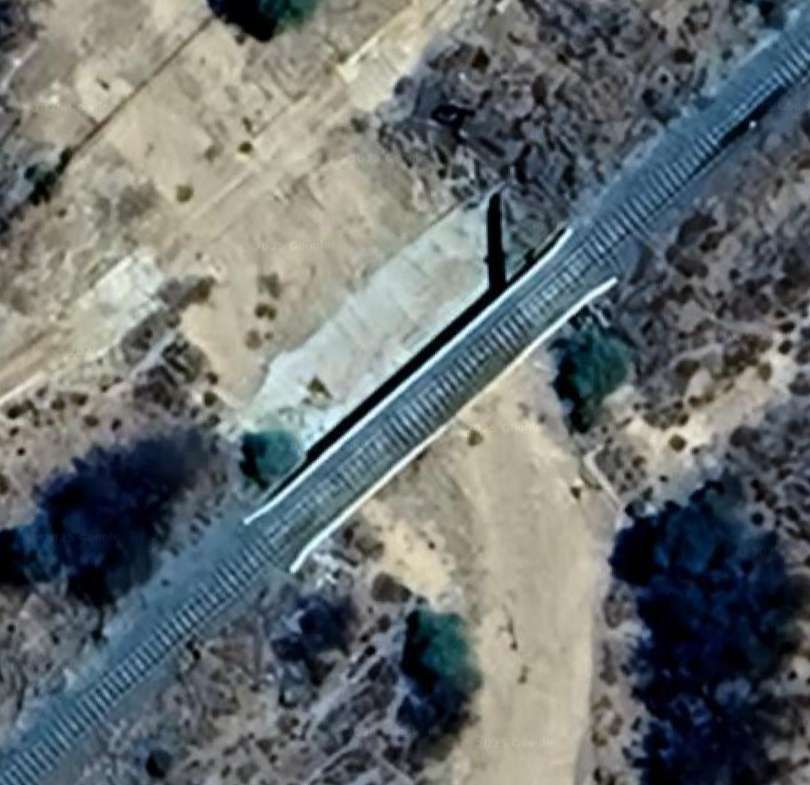
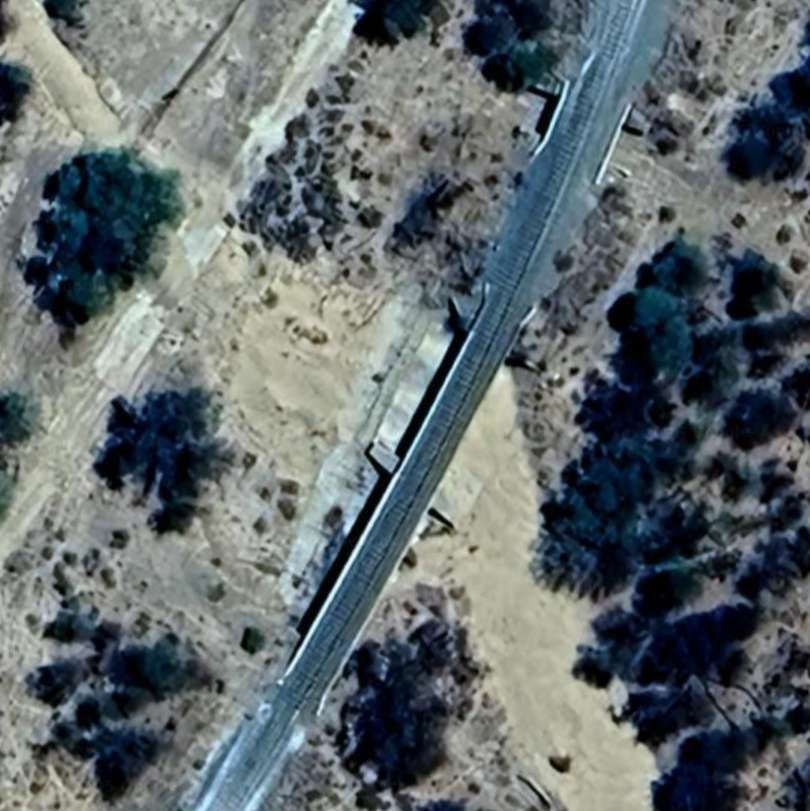
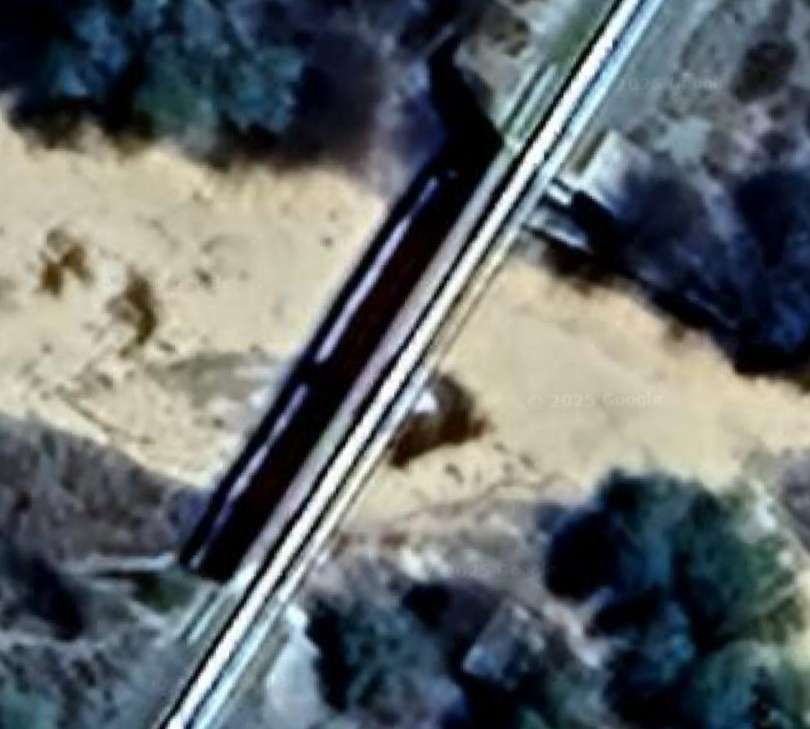
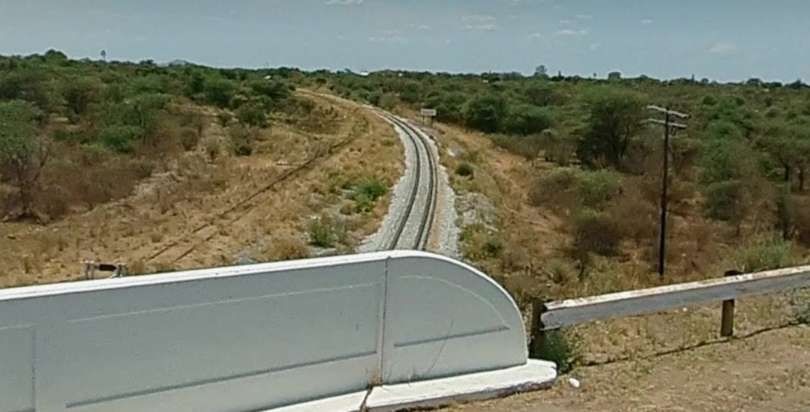











The line to Otavi continues heading Northeast. …












It is worth noting here that the original gauge of the line from the coast to Otavi and Tsumeb was originally built to 2ft-gauge. Later it was converted to 3ft 6in gauge. The line was built for the Otavi Mining and Railway Company (Otavi Minen- und Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft or OMEG). The company was founded was a railway and mining company in German Son 6th April 1900 in Berlin with the Disconto-Gesellschaft and the South West Africa Company as major shareholders. [41]
The first locomotives designed for regular service were fifteen 22-tonne 0-6-2T locos built by Arn. Jung. [41][42: p45] Henschel & Sohn built twelve locomotives similar to the Jung design and three 0-6-0T locos. [41][42: p45] Twenty 8-wheel auxiliary tenders carrying 8 cubic metres of water and 3.5 tonnes of coal were built to enable these tank locomotives to complete longer runs. [41][42: p45][43: p65] Henschel & Sohn built three HD class 2-8-2 in 1912 with separate 8-wheel tenders for long-distance running. [42: p47] These locomotives weighed 59 tonnes (including the 26-tonne tender) and remained in service for 50 years as the 2-8-2 type became standard for the railway. [41]
By 1913, train service included 4 express trains, 14 mixed trains, and 29 freight trains each week. [42: p39] Express and mixed trains included a baggage car, a car for African passengers, and a coach for first and second class passengers. [42: p39] The passenger coaches carried concrete ballast in a depressed center section to minimize the possibility of wind tipping a lightly loaded car off the rails. [43] Express trains stopped only at designated stations, but other trains would stop at intermediate points when transport was required. [42: p39] Equipment included: 96 low-side ore gondolas; 55 high-side gondolas; 20 limestone gondolas; 20 boxcars; 12 tank cars; 4 stock cars; 3 passenger coaches; and an executive business car with a kitchen, a bathroom, and an office convertible to a bedroom at night. [41][42: p42][43: p65]
There were also some self-powered steam rail cars with a coal bunker, a mail compartment, 2 compartments for Europeans, and 4 for Africans. [41][42: p36]
Otavi-Grootfontein
The railway line from Otavi to Grootfontein is 91 kilometres (57 miles) long and was completed in 1908. [10]
- Otavi (junction for Grootfontein)
- Grootfontein (branch terminus)
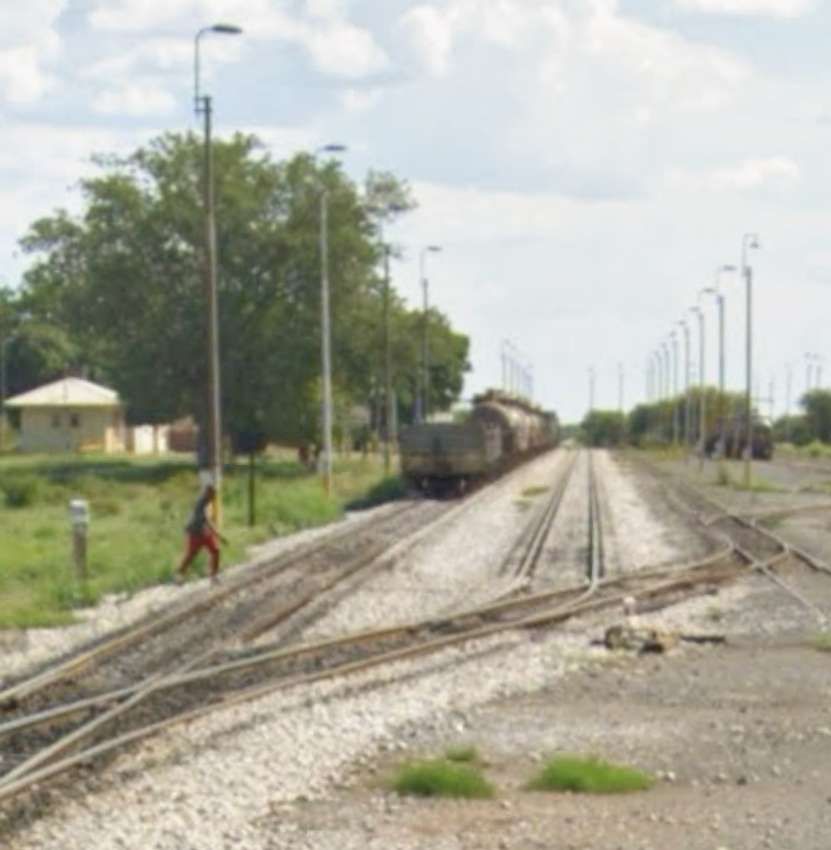
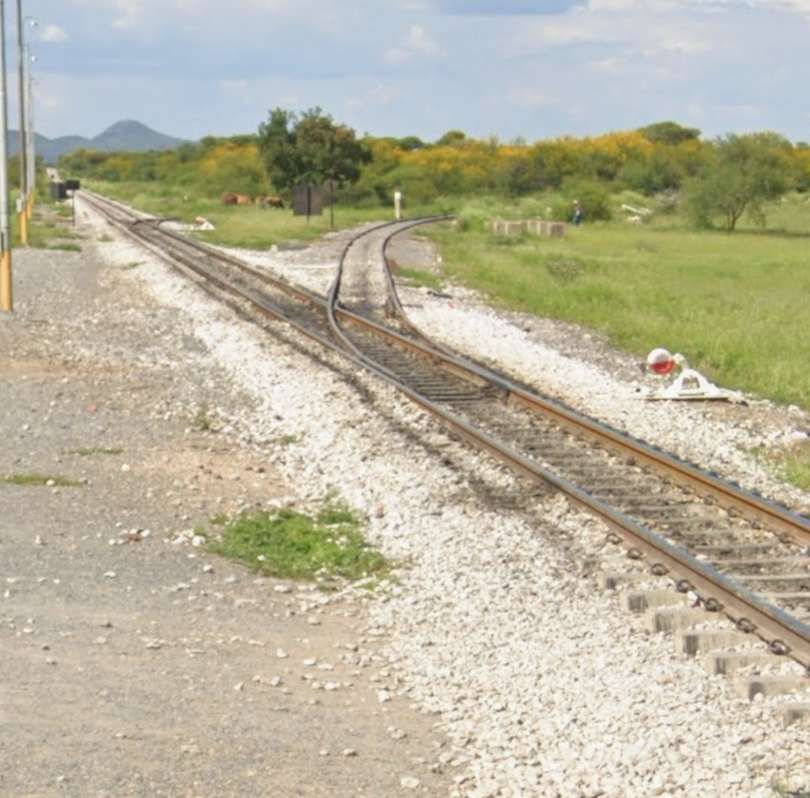
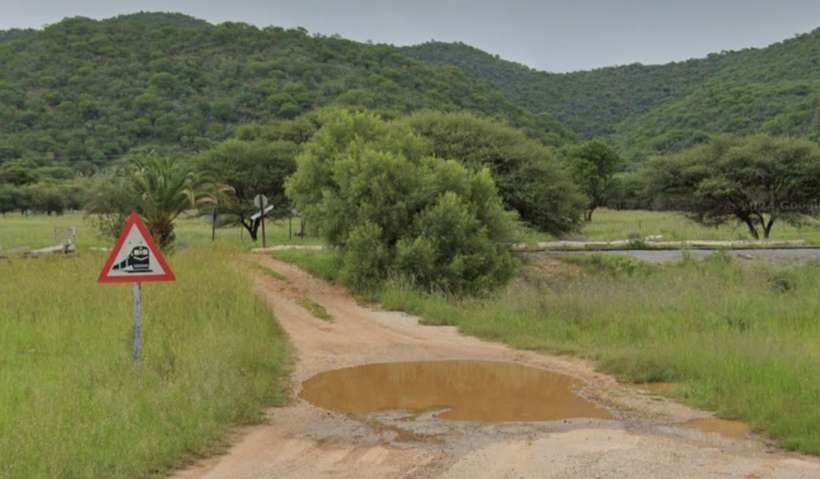
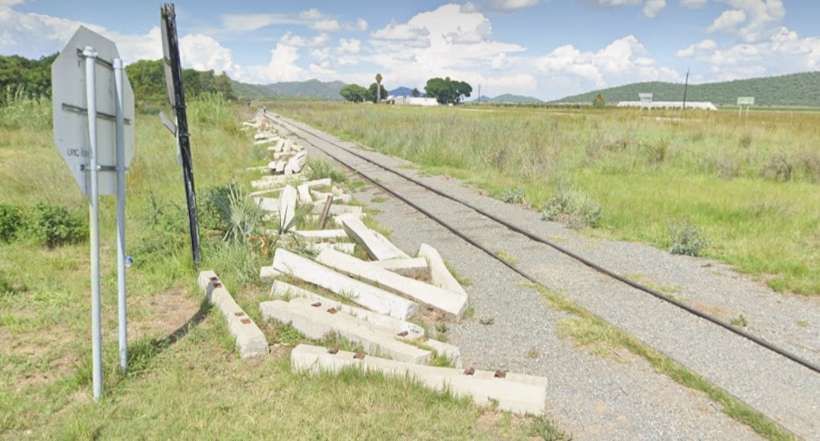








The line turns away from the B8, to the North. As it does so it crosses the D2860 at an ungated crossing.
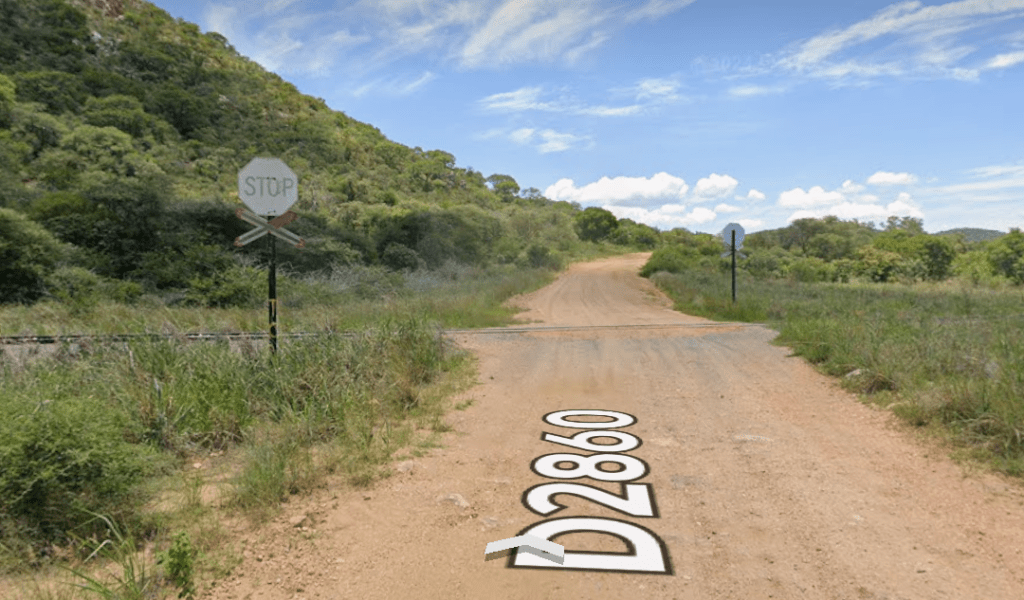

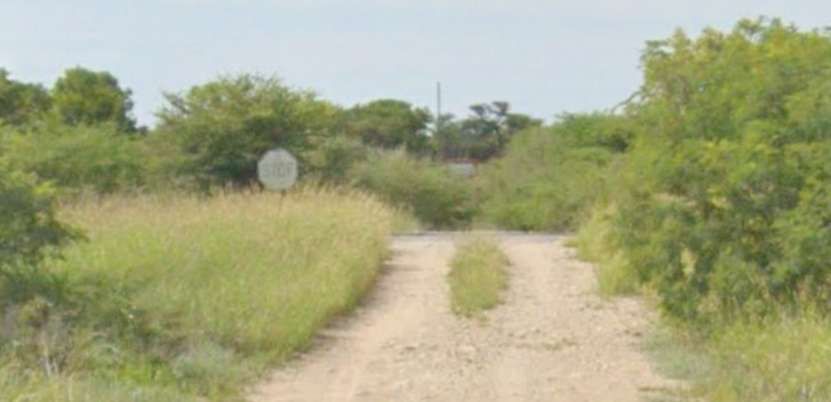
The line follows the D2860 and then the D2905 before passing under the B8, as it heads for Grootfontein.
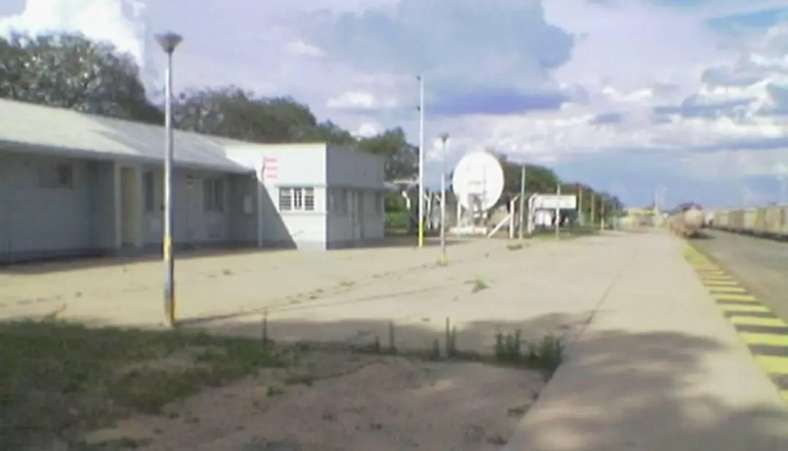
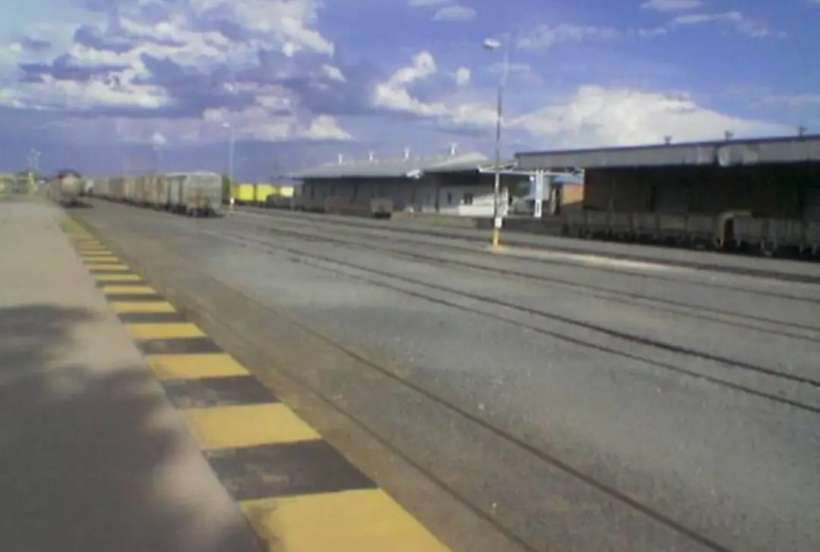




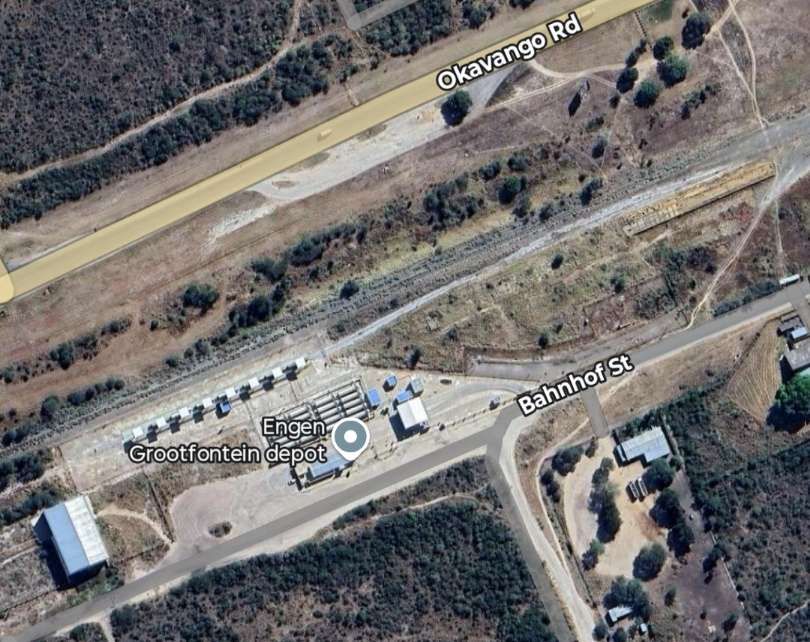



Grootfontein railway station is being converted into a logistics hub for business with the DRC and Zambia.
At the moment, trucks from the DRC, Zambia or Namibia travel about 2,500 kilometres from Walvis Bay harbour to Lubumbashi. With the introduction of the Grootfontein hub, these trucks will travel a distance of about 1,400 kilometres. TransNamib is prepared to dedicate four trains a week for this business idea. [44]
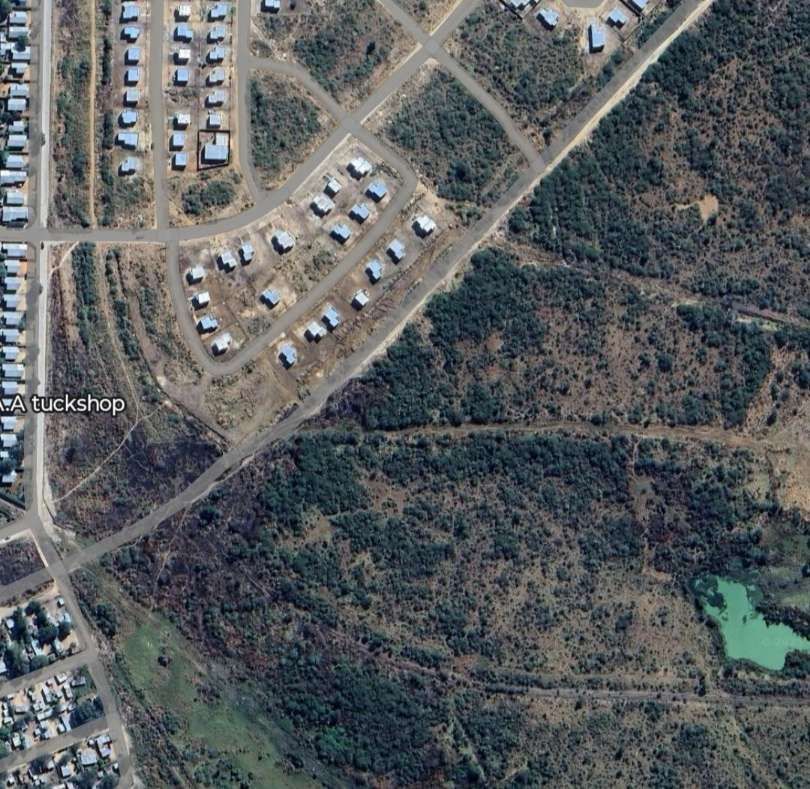







Otjiwarongo-Outjo
- Otjiwarongo (junction for Outjo)
- Outjo (railhead)
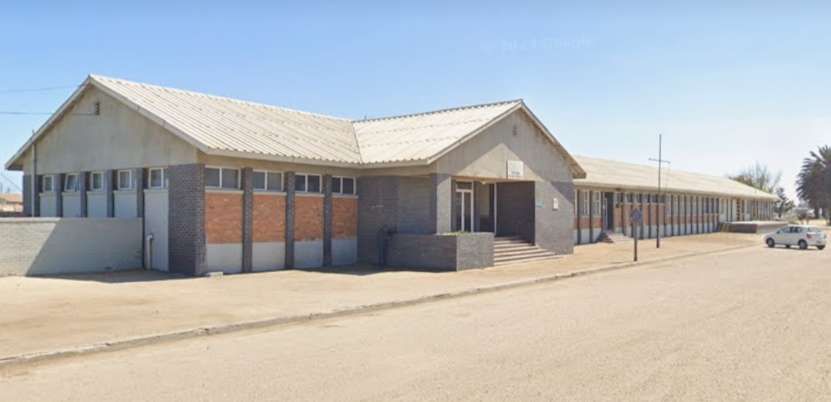
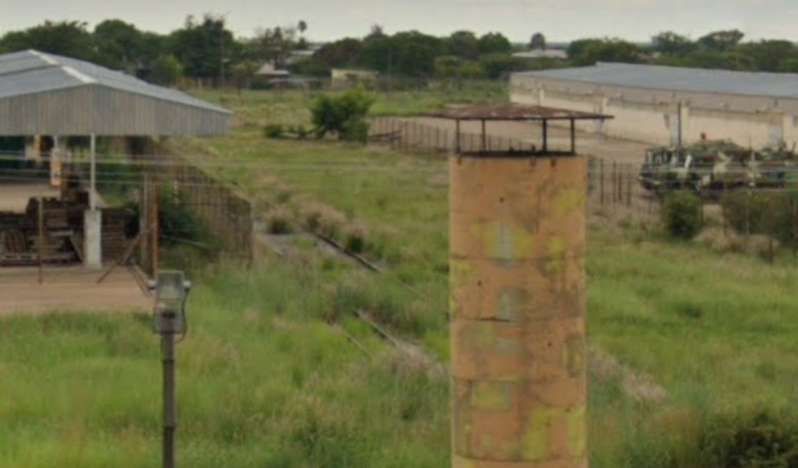
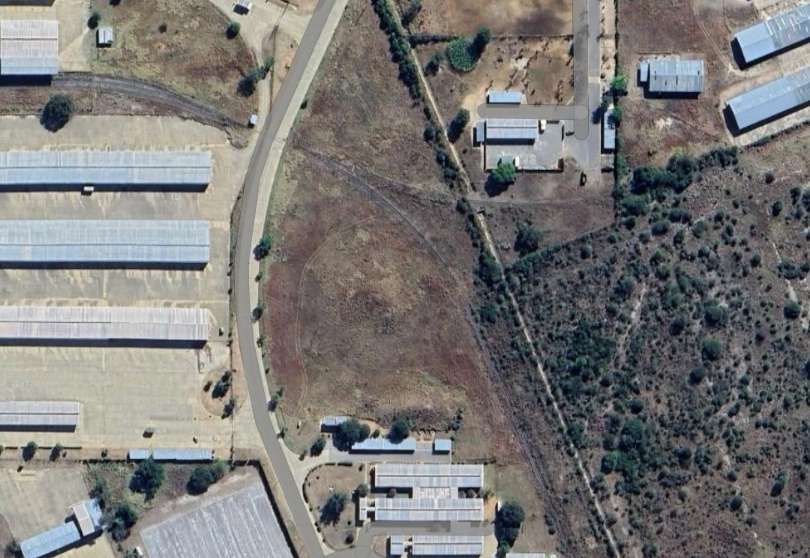
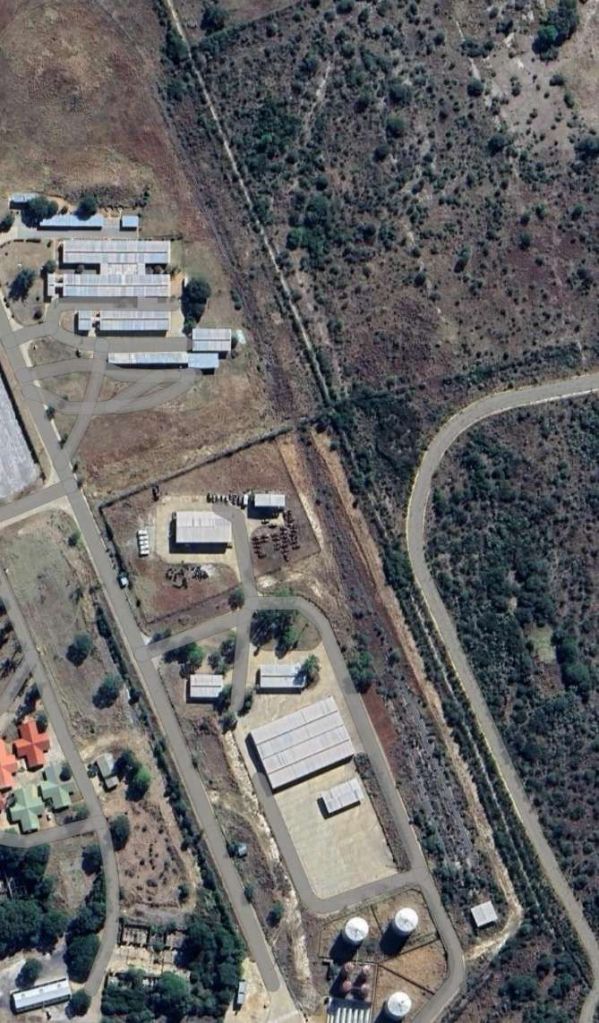
Otjiwarongo Railway Station is illustrated above. The railway line from Otjiwarongo to Outjo is 69 kilometres (43 mi) long. The first 26 kilometres (16 mi) were completed under the German colonial administration in 1914/1915; the railway line was named Amboland Railway in reference to the territory of the Ovambo people. The link to Outjo was completed in 1921 under South African rule. [10]













The next series of six photographs show sidings parallel to the running line. This location is more than just a passing loop but I have not been able to establish whether a specific local industry was the reason for the sidings. The photographs run in sequence Southeast to Northwest. …






The next sequence of four photographs shows a passing loop on the line. In sequence, these photographs run from the Southeast to the Northwest. …












Otavi-Oshikango
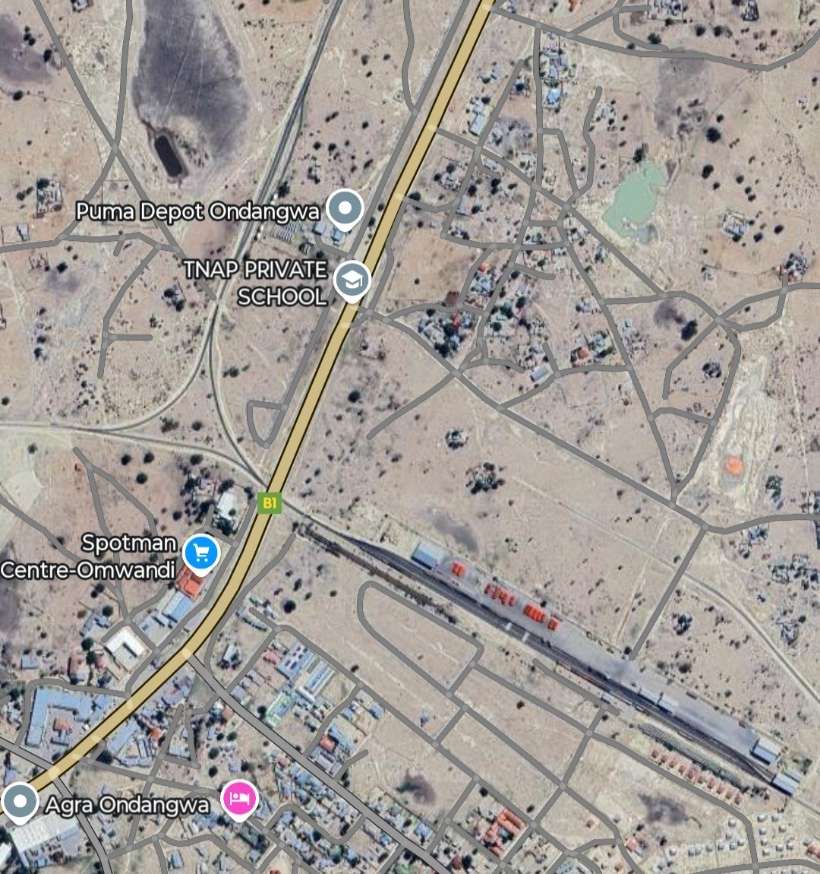
In 2005, a new 89 km section of Northern Railway from Tsumeb to Oshivelo was opened by President Sam Nujoma, as part of the “Northern Extension” of the railway link from Kranzberg to Otavi. Construction on the project’s second phase, a 59 km stretch from Ondangwa to Oshikango on the Angolan border at a cost of about N$329m, was scheduled to be completed by December 2007. Ondangwa Station opened in 2006 for freight.
In phase 3, a 58 km branch from Ondangwa to Oshakati was constructed at an estimated cost of N$220m, for completion in December 2008. For the future a connection from Oshikango to a point near Cassinga is planned on Angola’s southern railway system. [11][13][14]
The Ondangwa-Oshikango line was officially opened by President Hifikepunye Pohamba in July 2012. In order to keep the system operational and safe, provincial governor Usko Nghaamwa implored local residents to stop stealing railroad ties and sections of the wire fence. [11][15]
- Otavi (junction for Grootfontein)
- Tsumeb
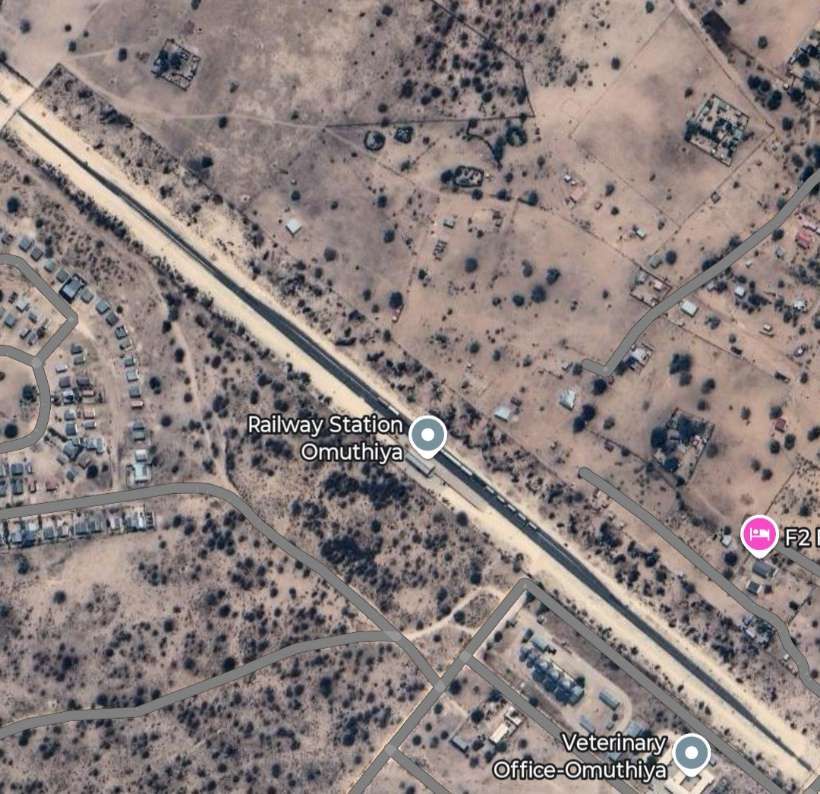
- Ondangwa (junction)
- Oniipa (road bridge)
- Onjdiva [11][14]
- Namacunde [11][16]
- Oshakati
- Oshikango (Angolan border)

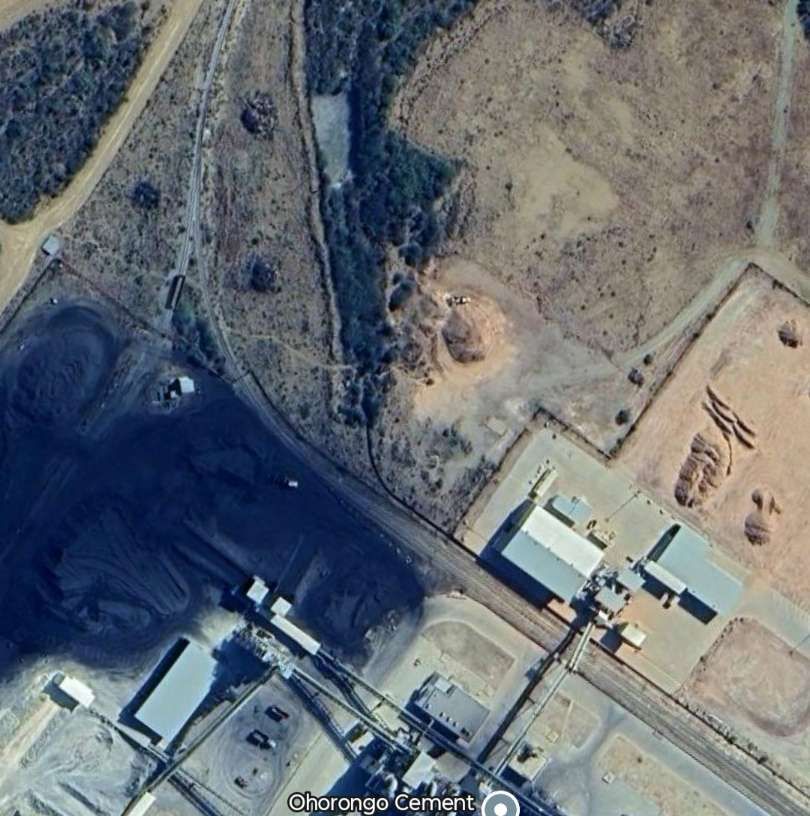
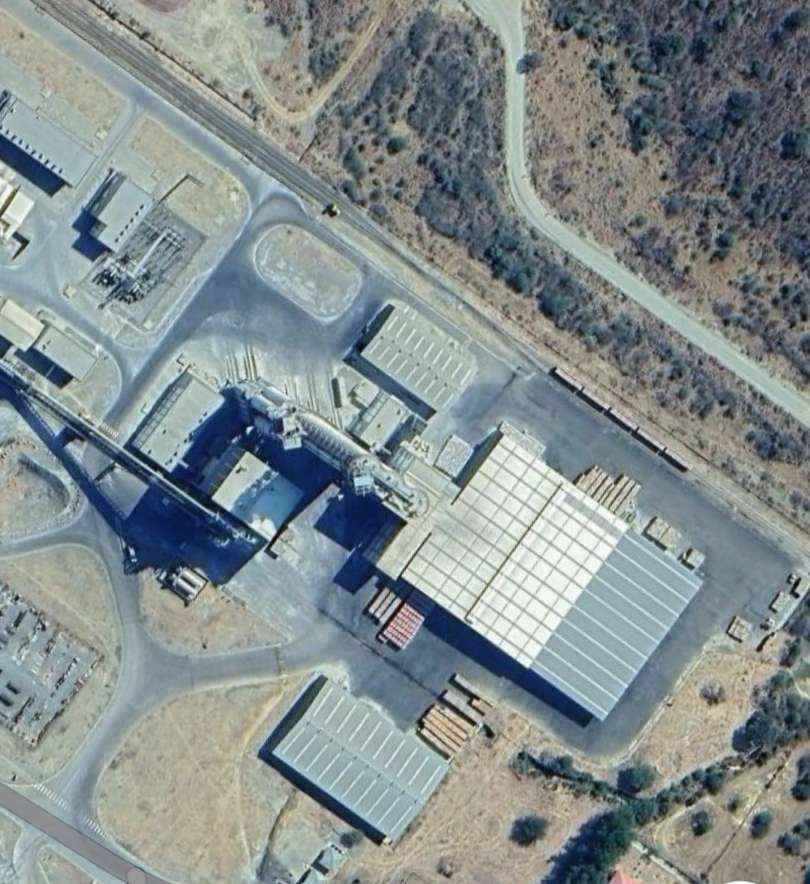
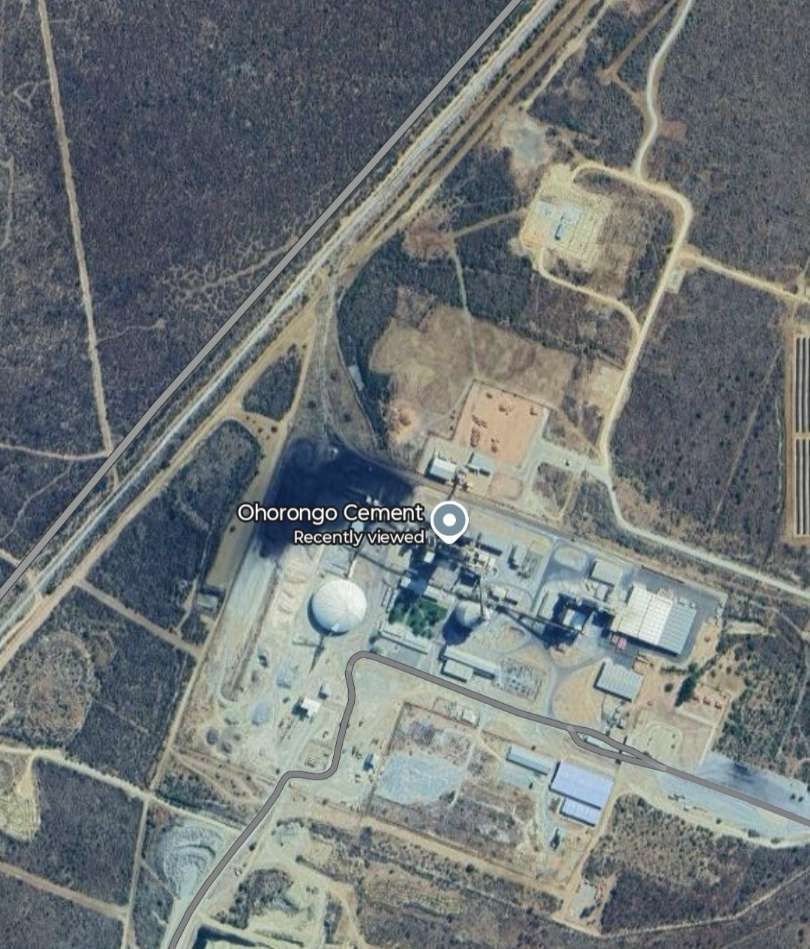
The journey towards Tsumeb runs uneventfully over flat ground surrounded by shrub and small trees, heading North-northeast, until it reaches Ohorongo Cement Works.
An aerial view of the works can be found here. [48] That view looks North across the Works and shows the railway and a dedicated branch to the Works in the background.




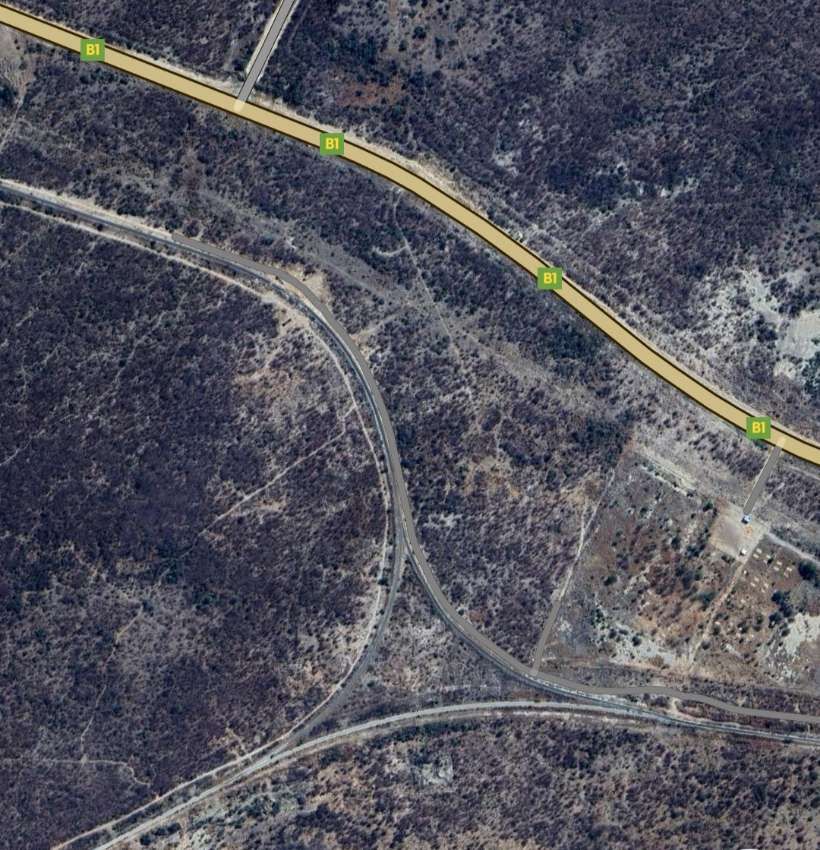
The railway continues Northeast over largely unremarkable flat terrain, before turning East, encountering one arm of the B1 and then a triangular junction.
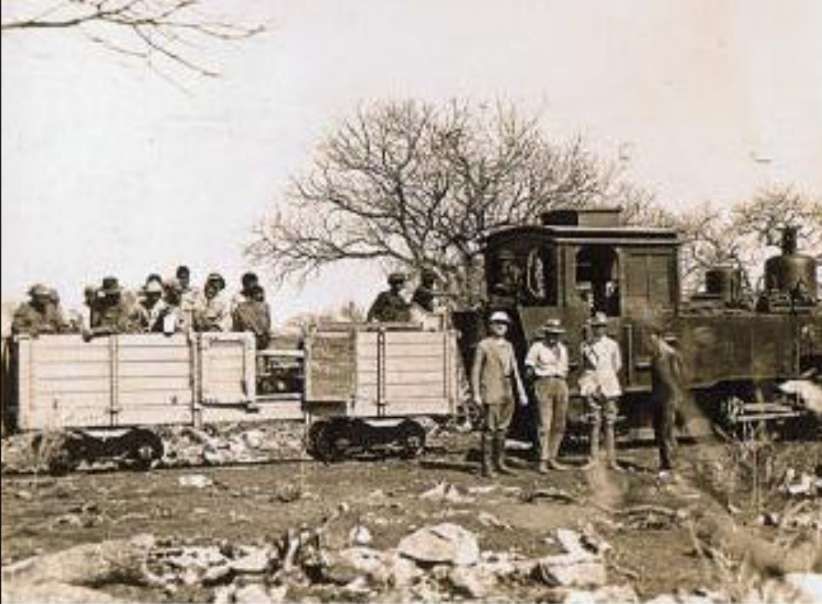
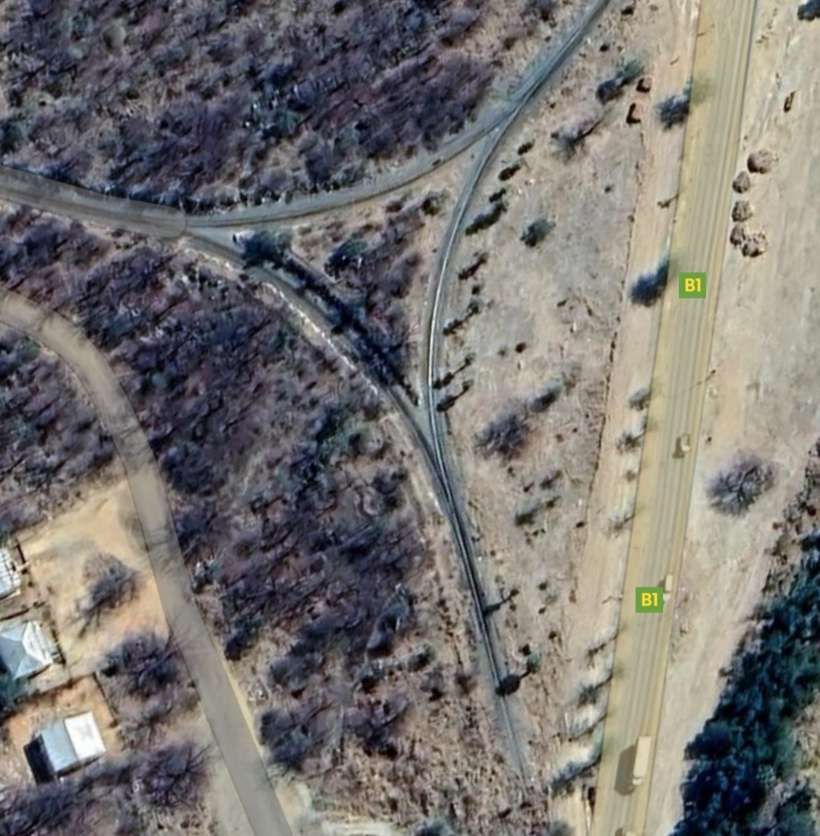
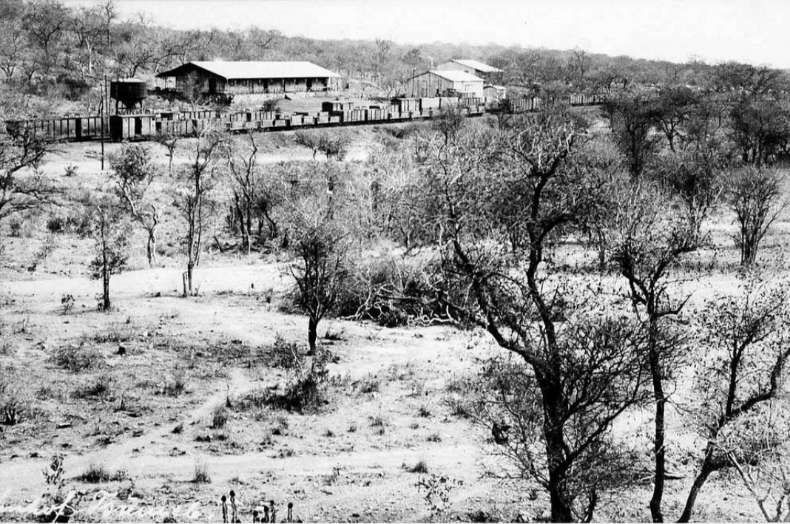







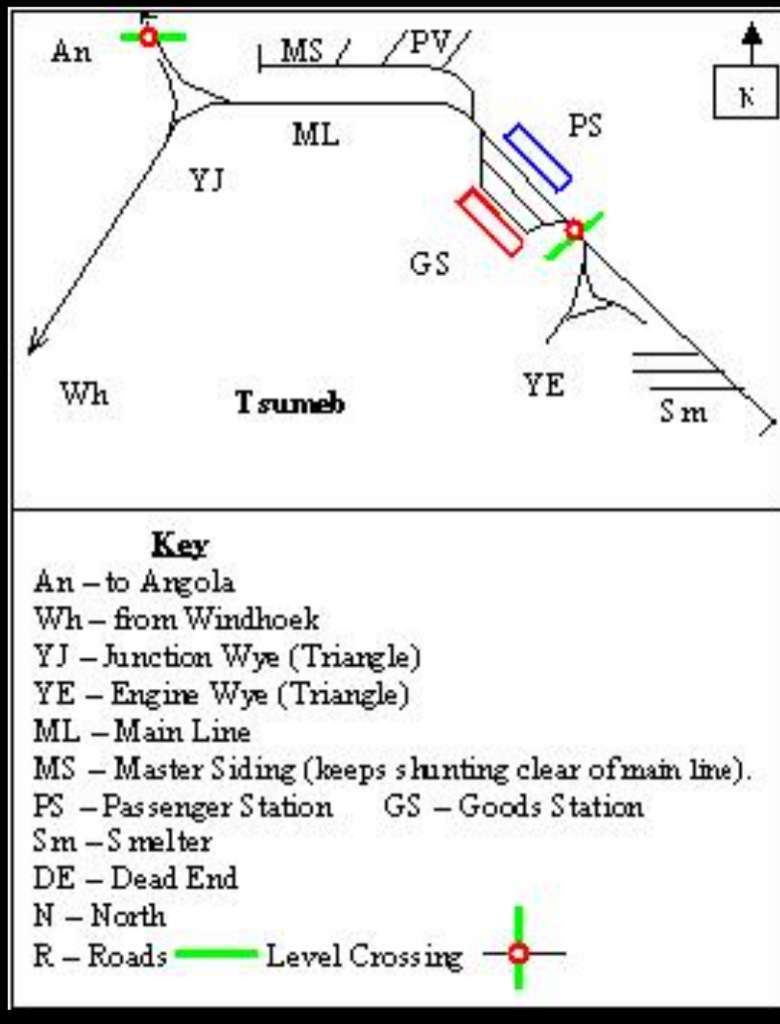

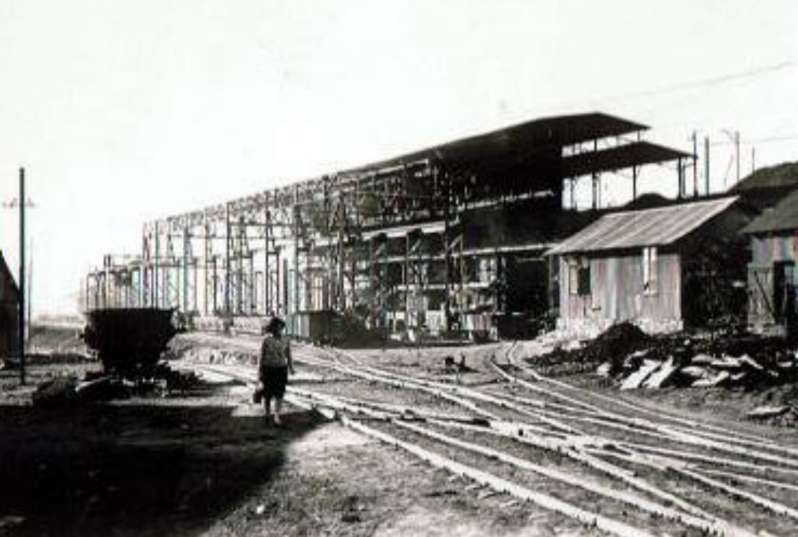
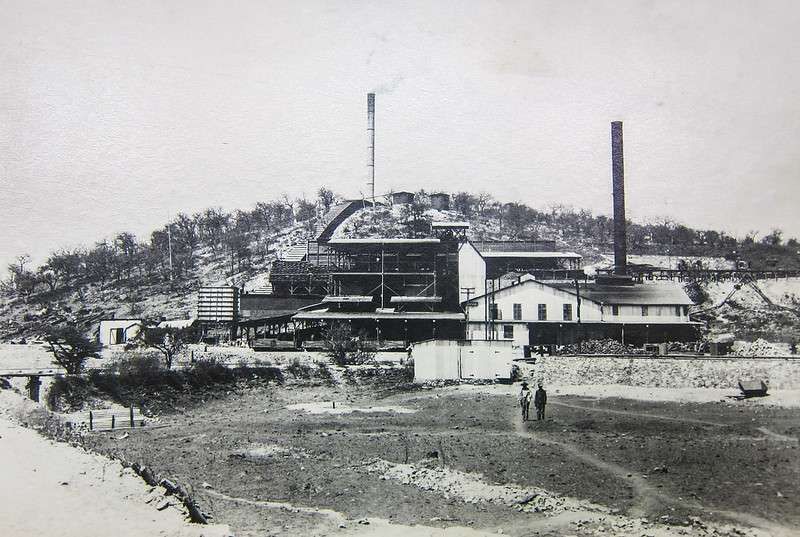
Encyclopedia Britannica tells us that “In 1851 Sir Francis Galton, a British explorer, made note of copper ore deposits in the vicinity of what later became the town of Tsumeb. An Anglo-German company acquired mining rights for the Tsumeb area in 1903. Southwest of Tsumeb is the site of the final German troop surrender to South African forces in World War I. The town remained a small copper-mining centre until the Tsumeb mine was purchased in 1947 by a largely U.S.-based corporation. It has since been developed as a planned company town (although ownership of the mine has changed hands several times), exploiting mineral deposits that include significant amounts of lead and copper as well as zinc, cadmium, silver, and germanium (a metalloid element used as a semiconductor). An integrated copper and lead smelter treats concentrates from Tsumeb and other mines. Owambo labourers are the chief contract workers.” [50]
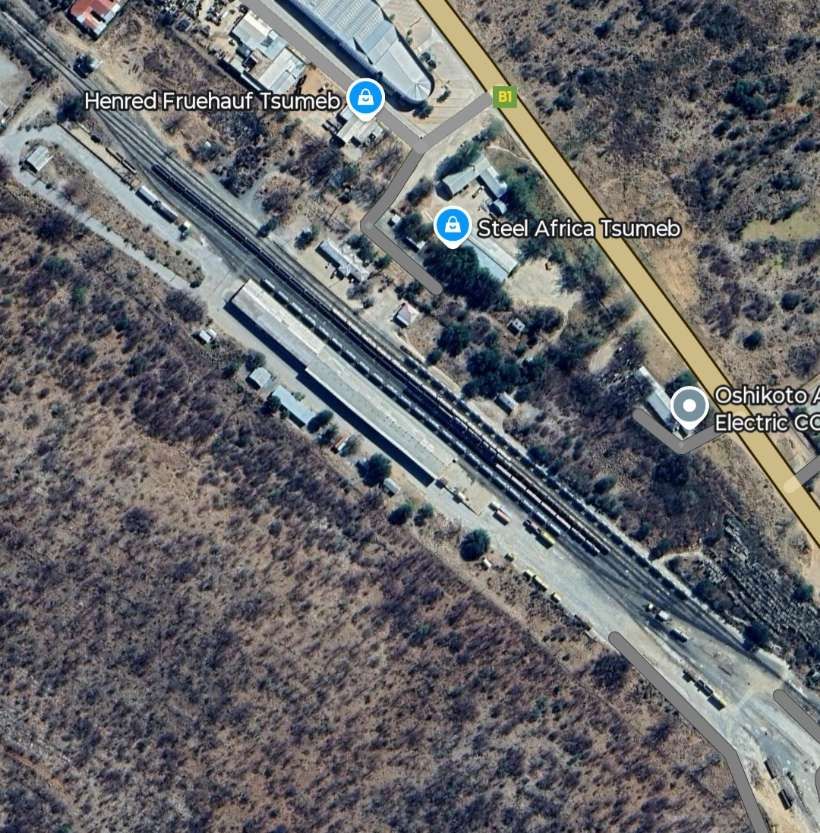
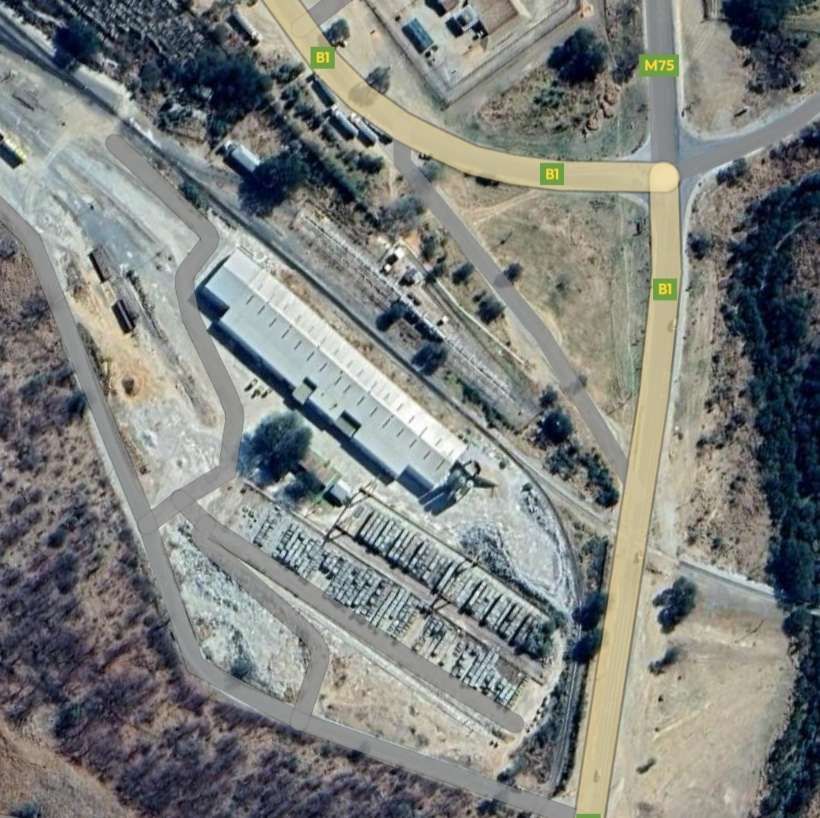
The mine, owned by Dundee Precious Metals sits to the East of the B1.



The line to the North of Tsumeb left the triangular junction to the West of the town heading first to the West and then to the Northwest and then directly North alongside the D3007, before turning West-northwest again.
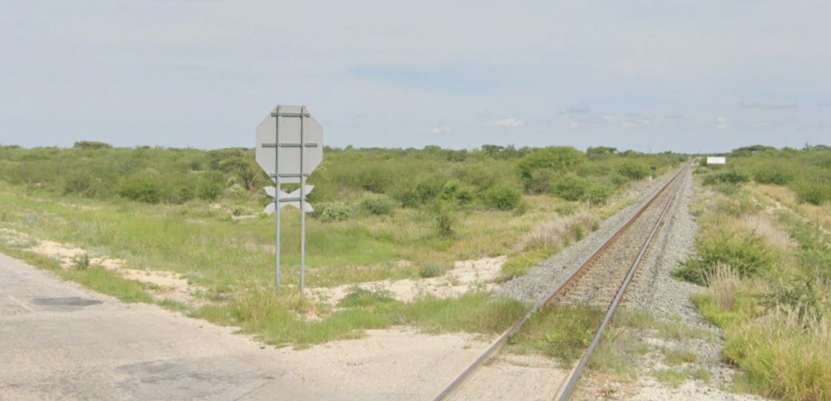
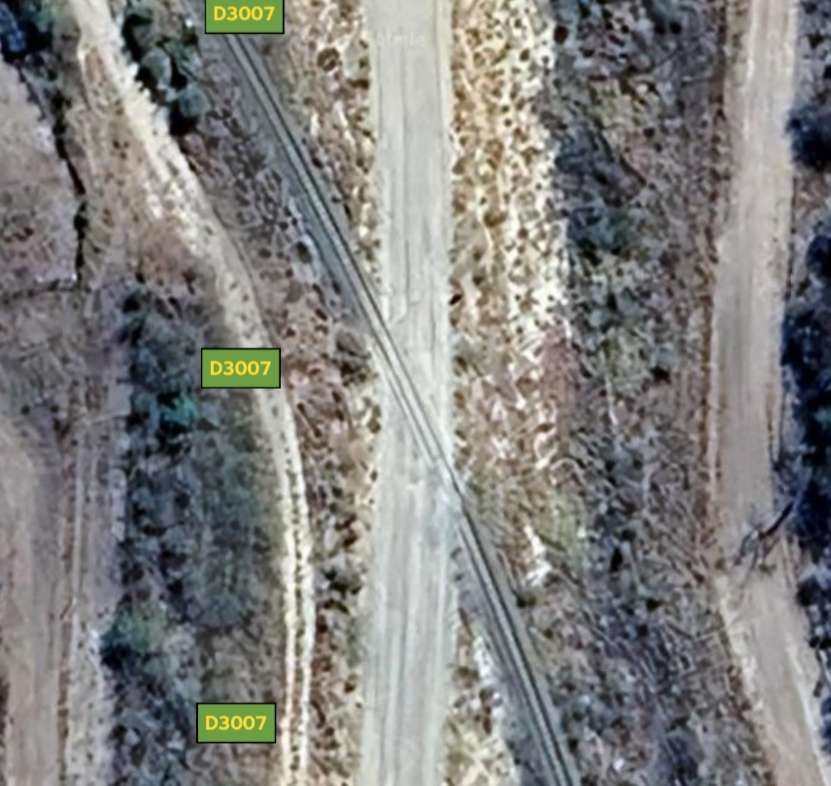



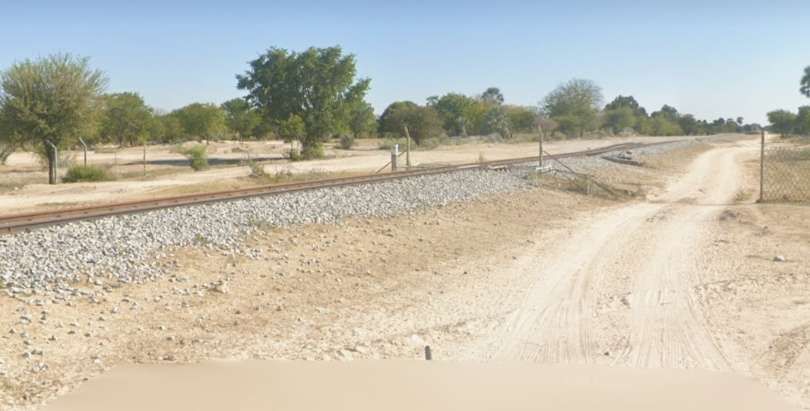
After a few kilometres on a West-northwest heading, the line then turns to the North-northwest and runs parallel to the B1 for some considerable distance.
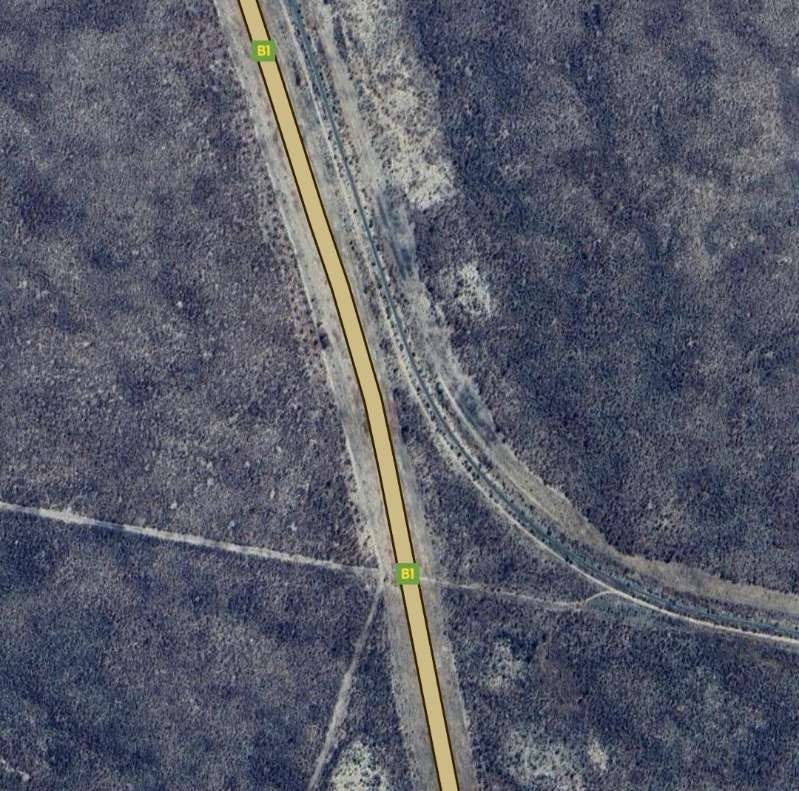
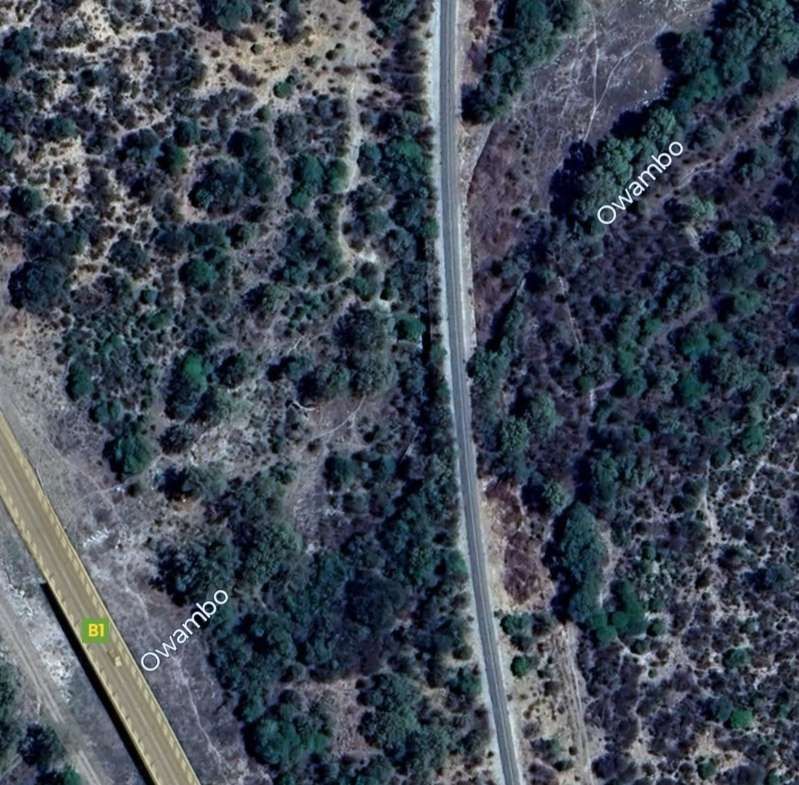
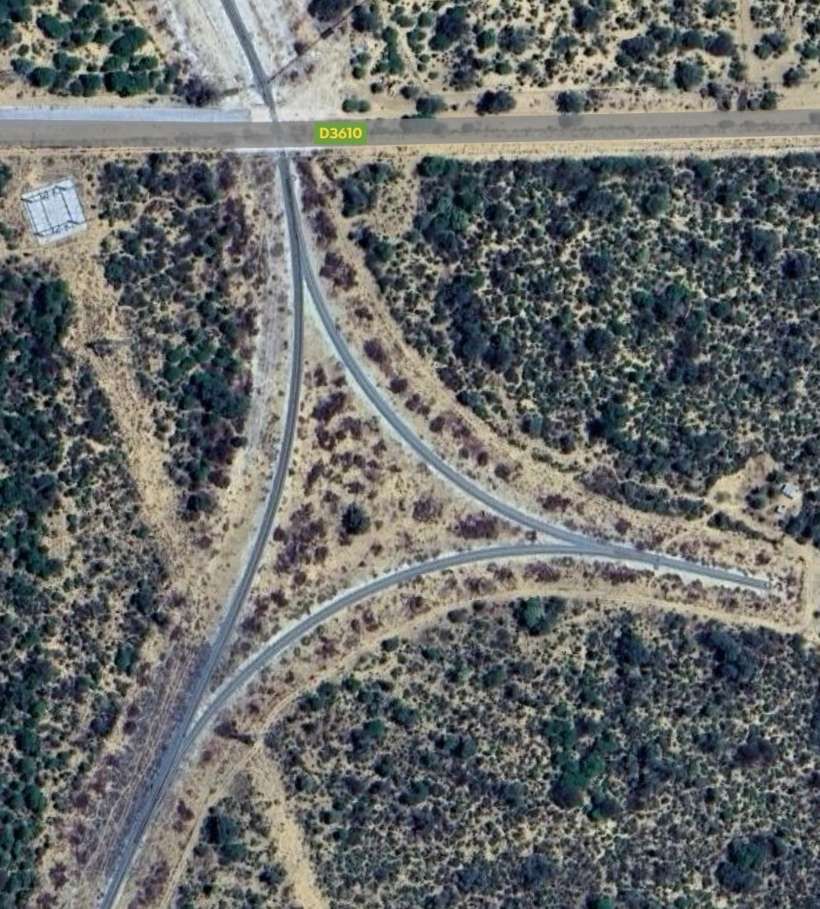
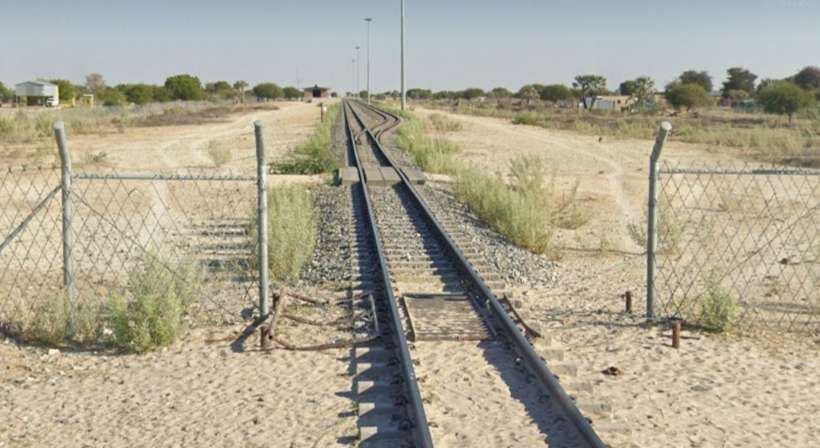
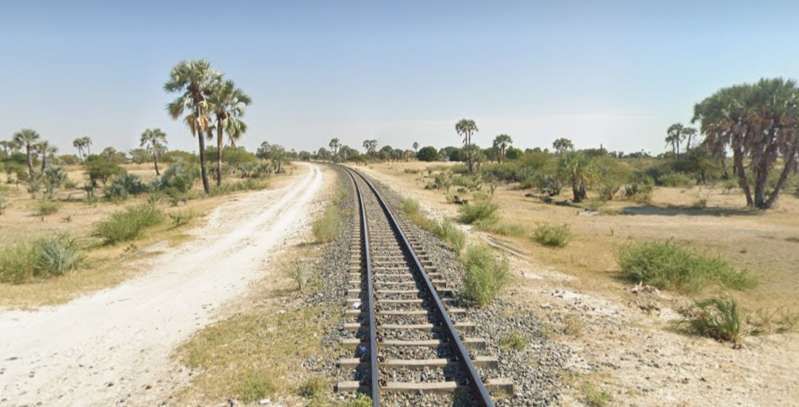
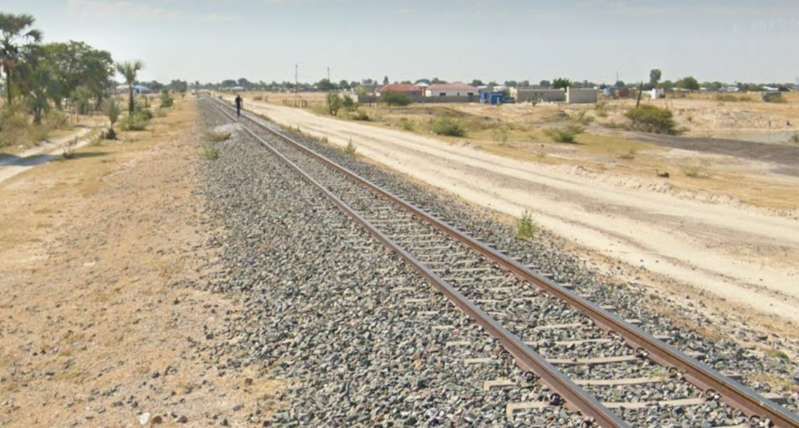
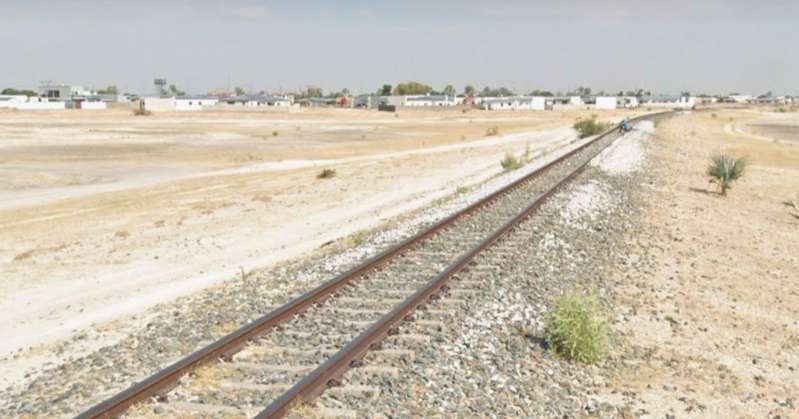
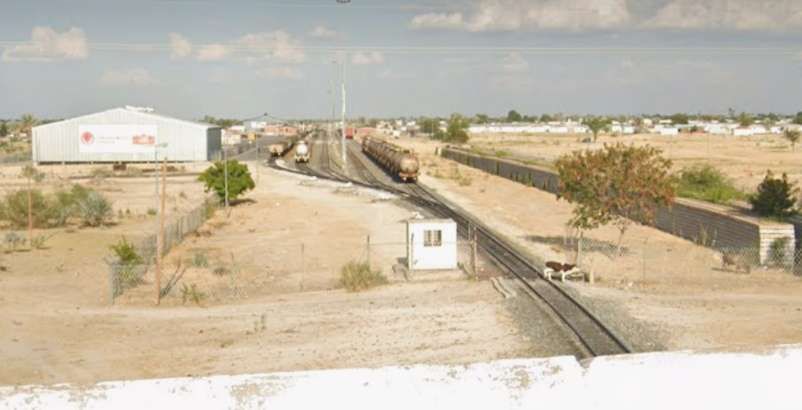
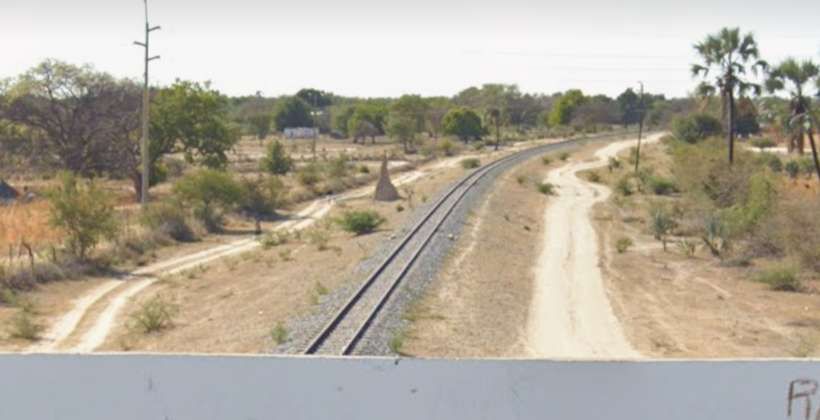





















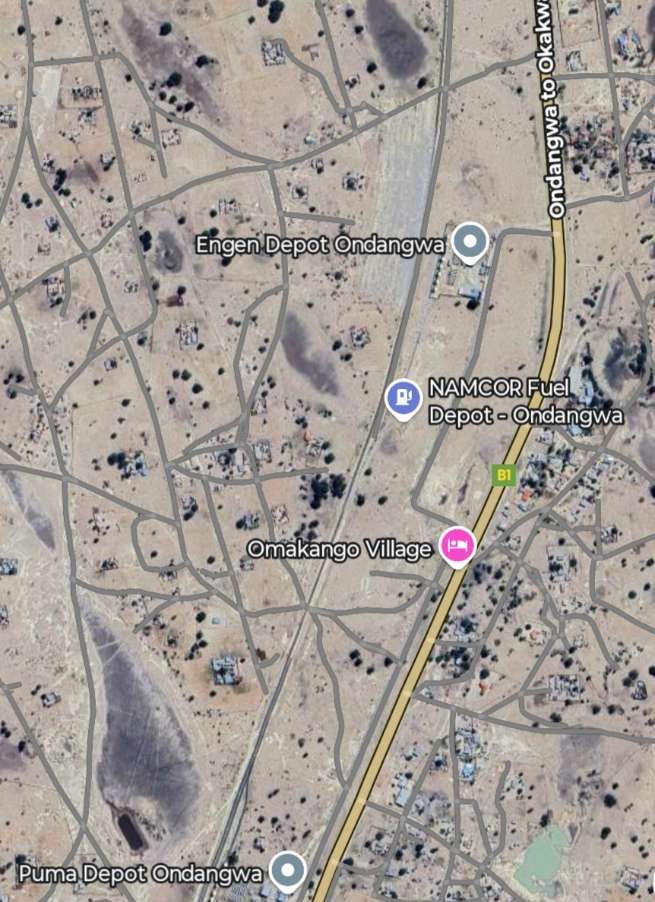

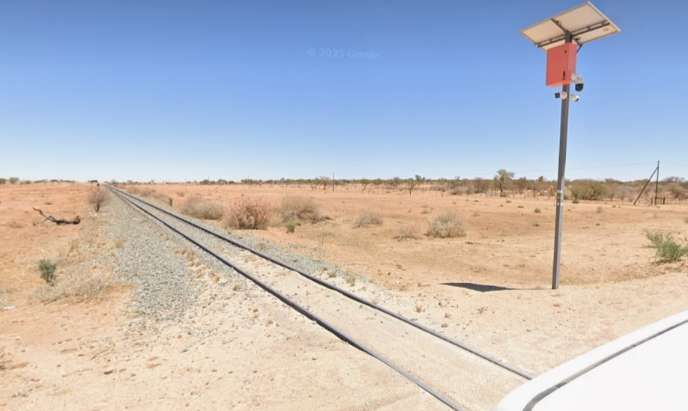
The next three images are a sequence of North-facing photogra



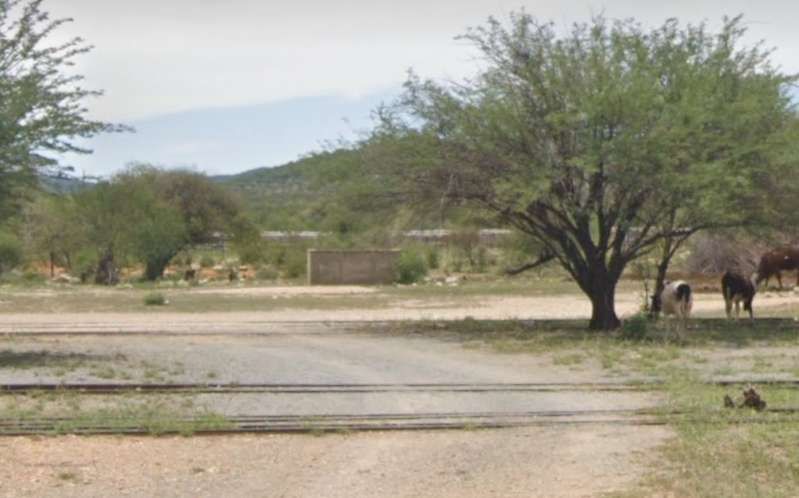
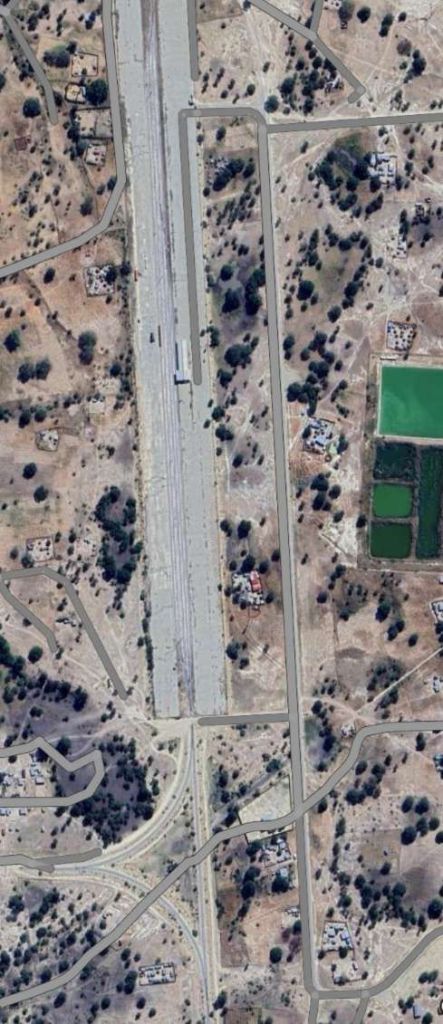
The last photograph on the northern line is a satellite image showing the railhead

References
- Charles E. Lee; The Longest Narrow-Gauge Railway; in The Railway Magazine, February 1952, Tothill Press, Westminster, London, p121-123.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_South_West_Africa, accessed on 7th June 2025.
- https://www.britannica.com/place/German-South-West-Africa, accessed on 7th June 2025.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/South_West_African_Jung, accessed on 7th June 2025.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_rail_transport_in_Namibia, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- Helmut Schroeter; Die Eisenbahnen der ehemaligen deutschen Schutzgebiete Afrikas und ihre Fahrzeuge = Die Fahrzeuge der deutschen Eisenbahnen 7 [The Railways of the former German Protectorates in Africa and their Rolling Stock = the Rolling Stock of the German Railways 7]. (in German); Verkehrswissenschaftliche Lehrmittelgesellschaft, Frankfurt am Main, 1961.
- Helmut Schroeter and Roel Ramaer; Die Eisenbahnen in den einst deutschen Schutzgebieten: Ostafrika, Südwestafrika, Kamerun, Togo und die Schantung-Eisenbahn: damals und heute [German colonial railways: East Africa, Southwest Africa, Cameroon, Togo and the Shantung Railway: then and now] (in German and in English); Röhr-Verlag, Krefeld, 1993.
- Brenda Bravenboer and Walter Rusch; The First 100 Years of State Railways in Namibia; TransNamib Museum, Windhoek, 1997.
- According to Schroeter; Bravenboer does not mention this line.
- Klaus Dierks; The South African Period 1915–1989: The Development of the Namibia Railway Network!; via http://www.klausdierks.com/Namibia_Rail/2.htm, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_transport_in_Namibia, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- Not used.
- Ministry of Trade & Industry; Northern Railway Extension; via http://www.mti.gov.na/subpage.php?linkNo=72, this link is broken.
- Angola- Namibia Link; railwaysafrica.com; via https://web.archive.org/web/20141023100300/http://www.railwaysafrica.com/blog/2014/10/21/angola-namibia-link-3, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- Namibia: Community Vandalizes New Railway Line (9th July 2012); New Era; via http://allafrica.com/stories/201207090857.html, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- RailwaysAfrica No. 5, 2014, p11, via https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Railways_Africa, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- https://steam-locomotives-south-africa.blogspot.com/2008/07/walvis-bay-hope-steam-locomotive.html?m=1, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- The Industrial Railway Record Issue No. 37, June 1971, p78-85.
- https://www.expertafrica.com/namibia/windhoek/desert-express, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- https://www.rossing.com, accessed on 8th June 2025.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Usakos_railway_station, accessed on 9th June 2025.
- https://steam-locomotives-south-africa.blogspot.com/2007/11/plinthed-class-hd-at-usakos-in-namibia.html?m=1, accessed on 9th June 2025.
- Leith Paxton & David Bourne; Locomotives of the South African Railways (1st ed.); Struik, Cape Town, 1985, p117 & 121.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windhoek_railway_station, accessed on 9th June 2025.
- https://www.facebook.com/share/p/1De1p8q5Mj/l, accessed on 9th June 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:LocomZwillinge_Windhoek1.JPG, accessed on 9th June 2025.
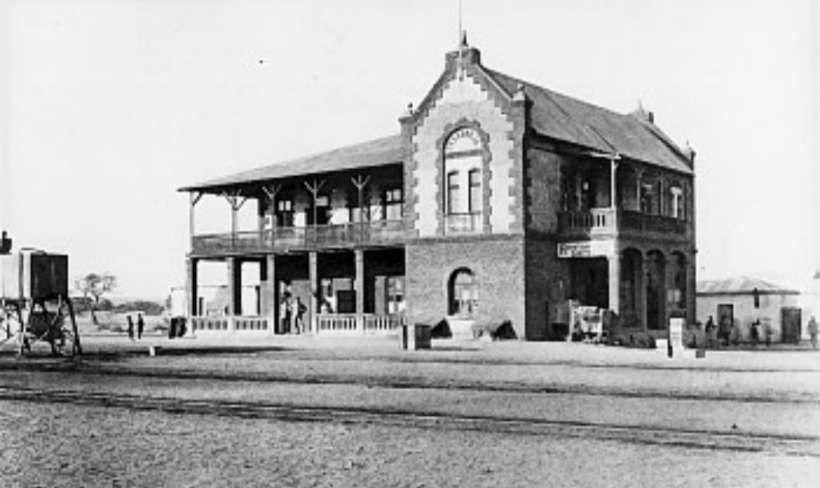
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Okahandja_railway_station, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Train_station_Windhoek_(2018).jpg, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://www.gettyimages.co.uk/detail/news-photo/trainload-of-armoured-cars-south-west-africa-world-war-i-news-photo/463970465, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://m.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7089896#/media/File%3AEisenbahnstation_Omaruru_1906.jpg, a cessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Karibib_aerial_view.jpg, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kranzberg_Station.jpg, accessed on 20th June 2025.
- https://www.facebook.com/groups/namib2footers/permalink/6730769210360985, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://www.facebook.com/groups/namib2footers/permalink/6730826530355253, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://www.namibian.com.na/historic-train-preserved-for-posterity, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://steam-locomotives-south-africa.blogspot.com/2007/?m=1, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://www.news24.com/life/travel/go/then-now-swakopmund-railway-station-20240927, accessed on 10th June 2025.
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/johan-stewart-laubscher-53342658_namibia-railinfrastructure-makinghistory-activity-6815601290438037504-swBC?utm_source=share&utm_medium=member_android&rcm=ACoAAFKPlCQBKyM6SVcRIYzuUN4W9XocTSJS0sY, accessed
- https://steam-locomotives-south-africa.blogspot.com/2007/11/narrow-gauge-locomotive-plinthed-at.html?m=1, accessed on 11th June 2025.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windhoek_railway_station, accessed on 11th June 2025.
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Otavi_Mining_and_Railway_Company, accessed on 12th June 2025.
- Frederic J. Shaw; Little Railways of the World; Howell-North, Berkeley, California, 1958.
- Dick Andrews; Extra Narrow Gauge Junction: Otavi Ry., State Northern Ry. in South Africa [sic]; in Narrow Gauge and Short Line Gazette, Volume 16 No. 1, 1991, p63–66.
- https://www.namport.com.na/news/428/grootfontein-train-station-new-logistics-hub-for-drc-zambia, accessed on 12th June 2025.
- http://atom.drisa.co.za/collections/N_Collection_lo-res/N70462.jpg, accessed on 12th June 2025.
- https://www.facebook.com/share/p/1CBLYcCydW, accessed on 12th June 2025.
- https://www.facebook.com/share/p/15abDSmZ7m, accessed on 12th June 2025.
- https://maps.app.goo.gl/Ta8Pcutiq8dYKQ1c8?g_st=ac, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tsumeb_Railway.JPG, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://www.britannica.com/place/Tsumeb, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://dundeeprecious.com/about-us/overview, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e6/Diagram_Tsumeb_railway_station_2007.jpg, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tsumeb_2.JPG, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://www.flickr.com/photos/jbdodane/13848969294, accessed on 13th June 2025.
- https://picryl.com/media/1908-bahnhof-tsumeb-b561a6, accessed on 13th June 2025.

