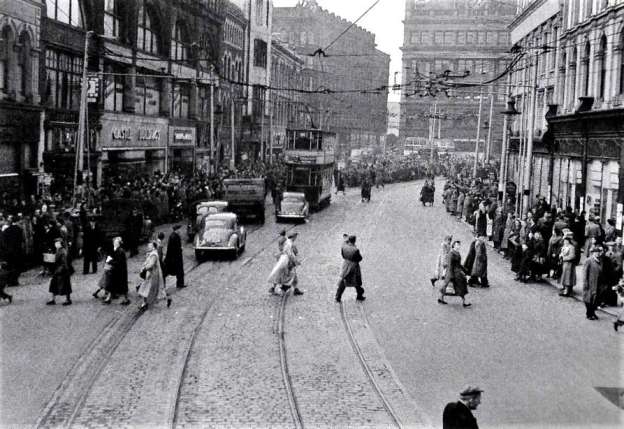
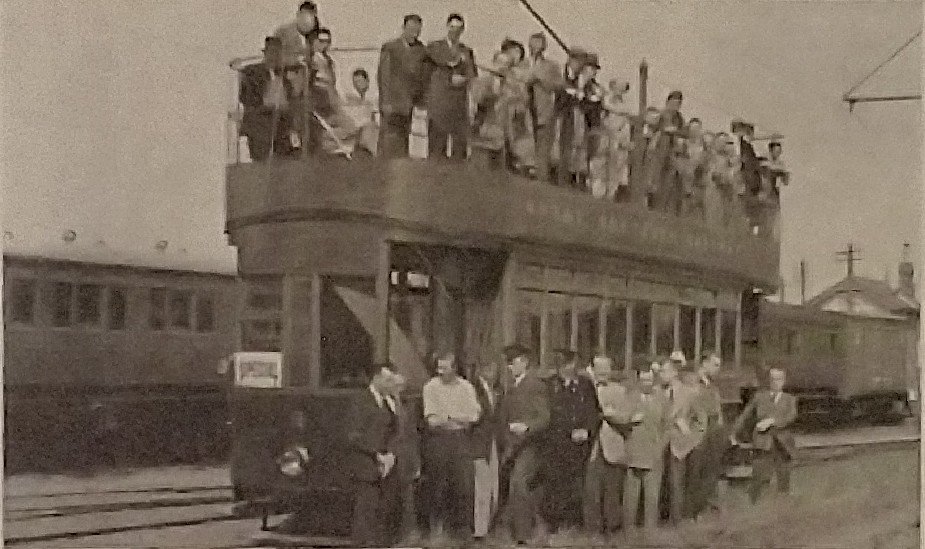
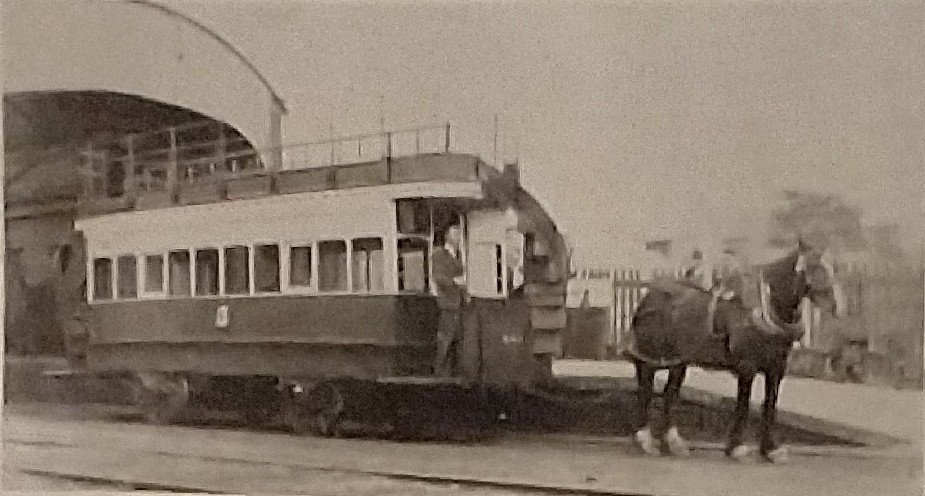
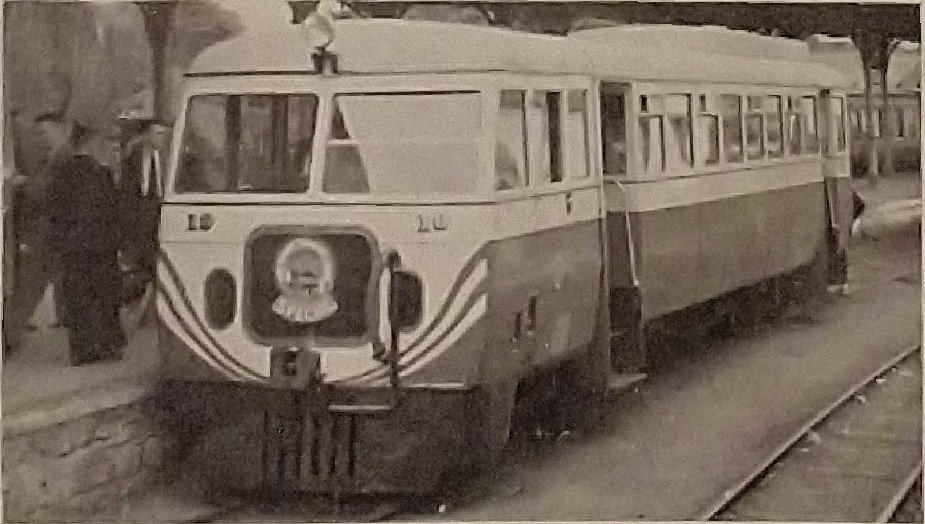
The November 1899 edition of The Railway Magazine carried a short article about the L&LSR which was not heavy on technical detail. It mostly reads as though it were a holiday brochure rather than an article in a railway journal. None-the-less, the article is still of interest, particularly for the fact that it was written during the period when the L&LSR was expanding.
Chisholm starts his article: the L&LSR “is one of those excellent little lines constructed on the narrow gange principle, which are to be found in all parts of Ireland. The country has the benefit of light rail ways It is with one of these lines that the present article is intended to deal. It is to be hoped that the following notes respecting the L&LSR will prove interesting to readers.” [1: p461-464]
Chisholm then spends a number of paragraphs explaining how best a traveller from the mainland to Derry.
I found his outline of the route from London interesting as it highlighted the number of railway companies whose rails the journey would cross. “Leaving London (Euston or St. Pancras) the passenger is taken to Carlisle, the ‘Clapham Junction of the North’. The journey is continued to Stranraer on the Portpatrick and Wigtownshire Joint Railway, owned by the London & North Western, Midland, Caledonian, Glasgow & South Western, Companies. The steamers run alongside the harbour station, Stran raer. The boats are well built, and are fitted with the latest improvements, The joint companies are financially interested in this steam boat service, as is also the Belfast and Northern Counties Railway. The time occupied in crossing is approximately two hours. Larne harbour station also adjoins the steamer pler, … A narrow gauge train awaits the arrival of the boat, and by this train the traveller is taken to Ballymena, It is necessary to change here into the broad gauge ‘Londonderry Express’, which speedily runs to the city on the banks of the Foyle.” [1: p464-465]
At that time, Derry “consist[ed] of two towns, one on each side of the River Foyle. The waterside station of the Belfast and Northern Counties Rail- way is on the eastern bank. The river is spanned by the stately Carlisle Bridge, a fine structure, which can truly be termed ‘[Derry’s landmark’. … The [L&LSR’s] station was on the western bank of the river. On entering it and viewing for the first time the rolling stock therein, the Londoner’s thoughts [would] immediately fly to the London and South Western Railway. The carriages before him [were] painted almost exactly after the style of that Company’s coaching stock. In addition to this, [the L&LSR] Company paint their engines a bright grass green – another prominent ‘South Western’ feature.”
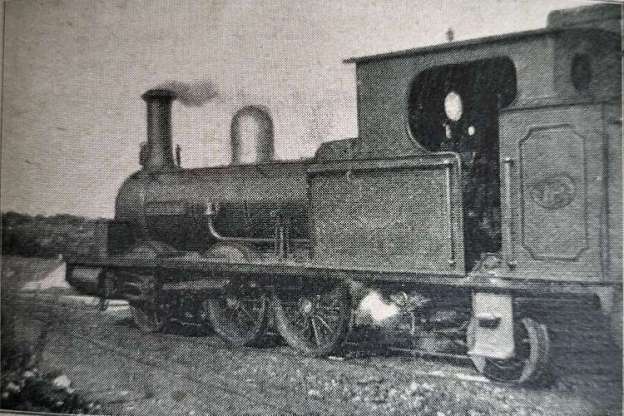
The featured image for this article shows L&LSR Locomotive No.1 J.T. Macky which was built by Black, Hawthorn & Co., of Gateshead in 1883. At the time of Chisholm’s article this locomotive was only around 6 years old. In a surprising digression from the more general nature of his article, Chisholm provides quite some detail about this locomotive. “It was named after the then Chairman of the Company. Mr. Fred. Dawson, the … General Manager of the Company, … supplied the [Chisholm] with the leading dimensions of ‘J.T. Macky’. It [was an 0-6-2T loco], a six-coupled engine with a two-wheeled pony truck at the rear. The diameter of the coupled wheels [was] 3 ft. 6 in., the diameter of the trailing wheels being 2 ft. 2 in. The gauge of the line [was] 3 ft 0 in. ‘J. T. Macky’ [had] cylinders 13 in. by 19 in.; a total heating surface of 592 square feet. …(112 tubes); a steam pressure of 140 lbs. per square inch, and a total length over the buffers of 27 ft. The total weight of the engine in working order [was] 23 tons 3 cwt.” [1: p462]
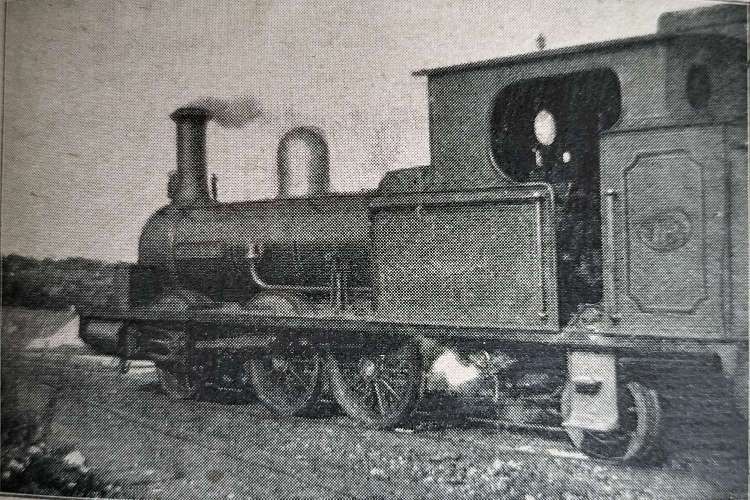
It is clear that Chisholm was quite taken by this locomotive: “The locomotive is extremely handsome, being painted … brought green picked out with black and white stripes. A bright brass dome is mounted on the top of the barrel.” [1: p462]
In 1899, Chisholm claimed that the L&LSR owned ten locomotives the first four named, respectively, J.T. Macky, Londonderry, Donegal and Inneshowen. The remaining engines bore numbers only. J.T. Macky, Londonderry, and Donegal were numbered ‘1’ to ‘3’ and were all 0-6-2T locomotives supplied by Black, Hawthorn & Co. Inneshowen was numbered ‘4’, supplied by the same company it was an 0-6-0T. I have only found evidence of a further four locomotives having been supplied to the L&LSR by 1899: No. 5(A) and No. 6(A), both supplied by Robert Stephenson & Co. in 1873, both 2-4-0T locomotives; and No. 5 and No. 6, both supplied by Hudswell Clarke in 1889, both 4-6-2T locomotives. [3]
Chisholm continues: The L&LSR consisted of “two branches. … The longer branch extend[ed] to Letterkenny, and the shorter to Buncrana. [At that time] the company work[ed] and own[ed] 14.5 miles of line.” [1: p462-463]
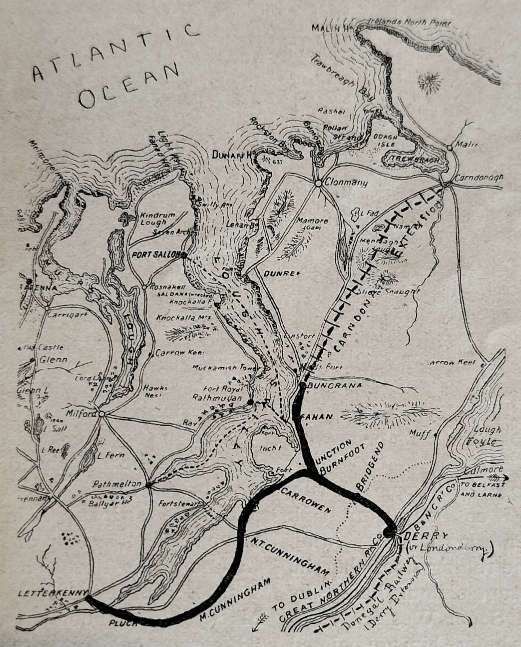
Chisholm goes on to write about the L&LSR’s expansion plans. Looking forward from the end of 1899, he says: “It aspires to greater things, … there are now being made extensions of great importance. The first of these is a line from Letterkenny to Burtonport, 49.5 miles. An extension from Buncrana northwards to Carndonagh (see map) is also now being undertaken. The latter will be 18.5 miles long. It will be seen that when these extensions are completed, the Lough Swilly Railway will be a comparatively big concern.” [1: p463]
From this point in his article, Chisholm sells the area around the L&LSR as a holiday destination. “The scenery in and around … County Donegal is exceptionally fine. … Buncrana has truly been described as a lovely spot. It is an ideal holiday resort. A fine building – the Lough Swilly Hotel – has been erected, where tourists will find excellent accommodation. The Lough Swilly Railway is fully alive to the fact that the district served by its line is essentially a resort for the tourist. With this view, [the Company] has introduced a number of facilities for holiday makers. For example, cheap tickets are issued daily between Londonderry and Buncrana – the fare for the double journey being only one shilling. The tickets are available by all trains. The passenger has not to get up at an unearthly hour in the morning to catch a special train. … There has also been introduced, … passengers proceed by rail from Londonderry to Buncrana, thence to Fahan, by steamer from Fahan to Rathmullan, by coach from Rathmullan to Rosapenna, Dunfanaghy, Gweedore, Dungloe, Glenties, Ardara, Carrick, Killybegs, thence by rail to [Derry]. ” [1: p463]
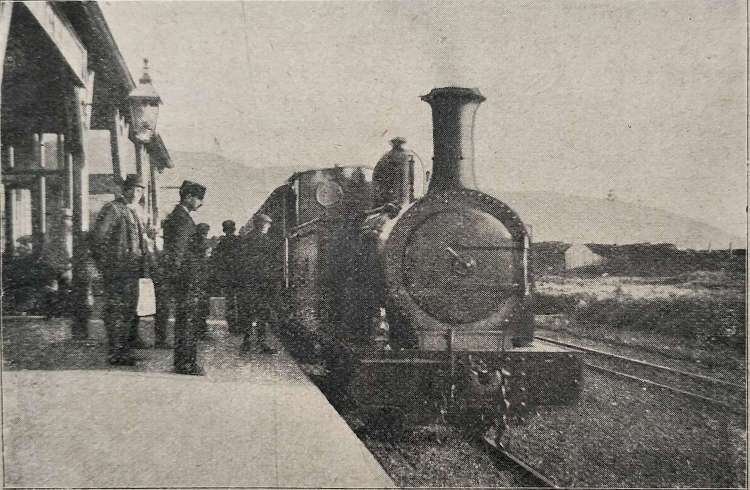

In Chisholm’s concluding remarks, he comments that “the railway is a thoroughly up-to-date concern. … The management is … thoroughly enterprising. The railway … is an interesting and well-managed line; the scenery in the district it serves can truly be described as amongst the grandest in the British Isles.” [1: p464]
References
- A J. Chisholm; The Londonderry & Lough Swilly Railway; in The Railway Magazine, London, November 1899, p461-464.
- My completed articles about the L&LSR can be found on this blog on the following links:
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2023/04/28/the-burtonport-extension-of-the-londonderry-lough-swilly-railway-part-1
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2023/05/05/the-burtonport-extension-of-the-londonderry-lough-swilly-railway-part-2
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2024/04/30/the-burtonport-extension-of-the-londonderry-amp-lough-swilly-railway-part-3
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2023/07/13/the-burtonport-extension-of-the-llsr-londonderry-and-lough-swilly-railway-part-4-barnes-gap-to-letterkenny
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/?p=54704
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2024/05/27/the-lough-swilly-railway-continued-letterkenny-to-derry-part-2
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Londonderry_and_Lough_Swilly_Railway, accessed on 14th September 2024.