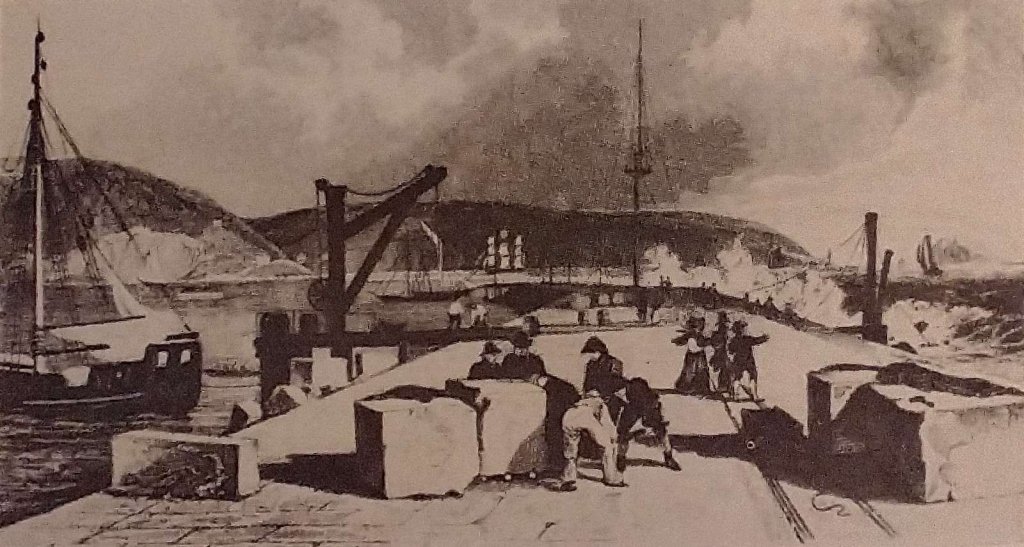
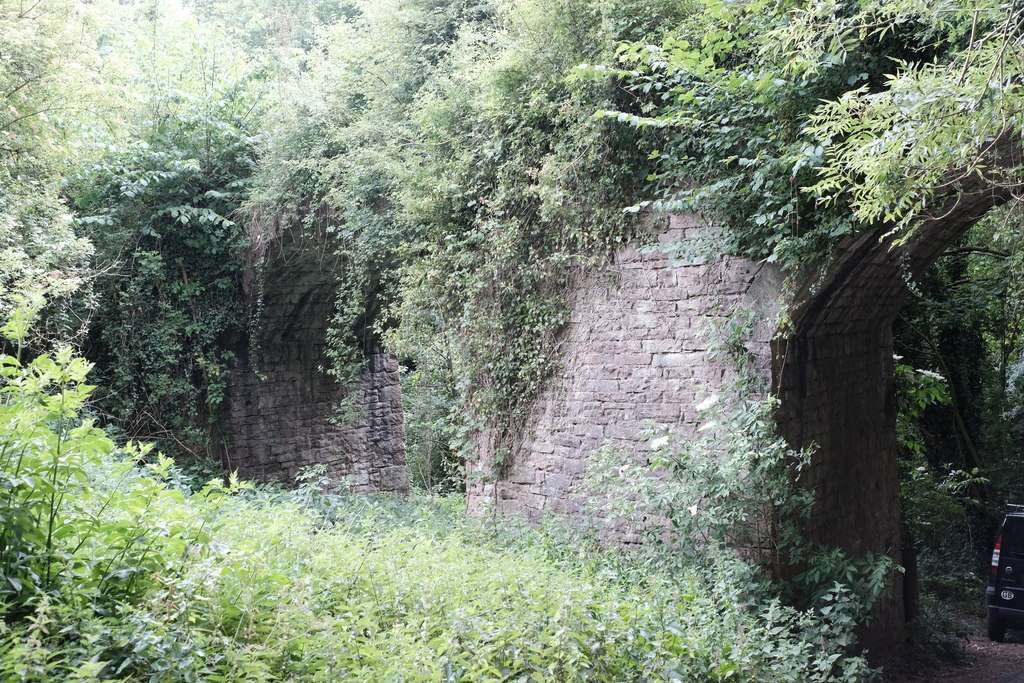
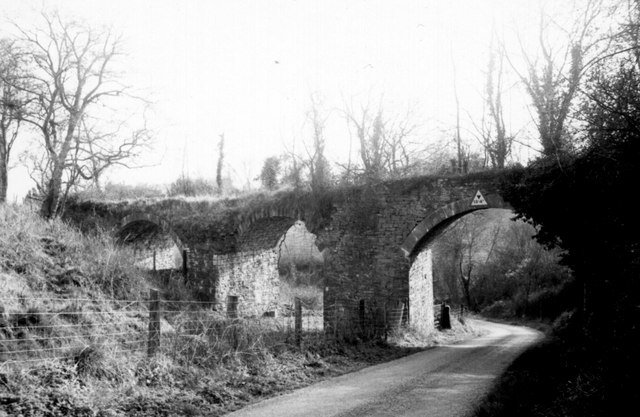
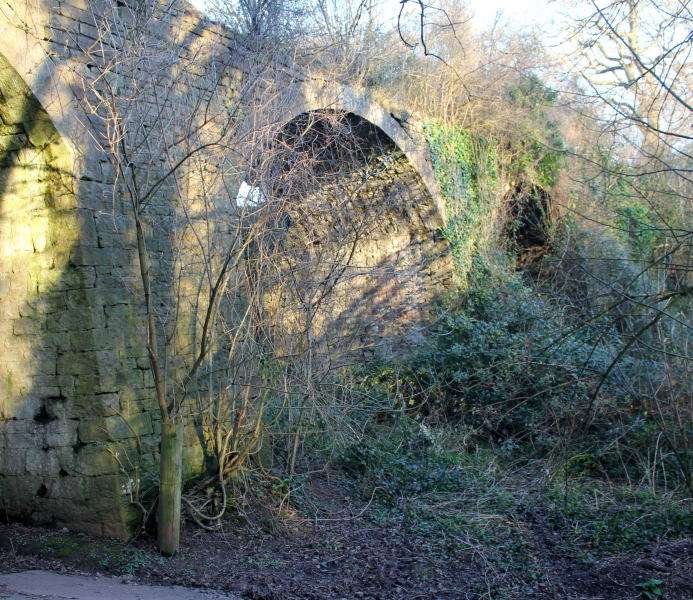
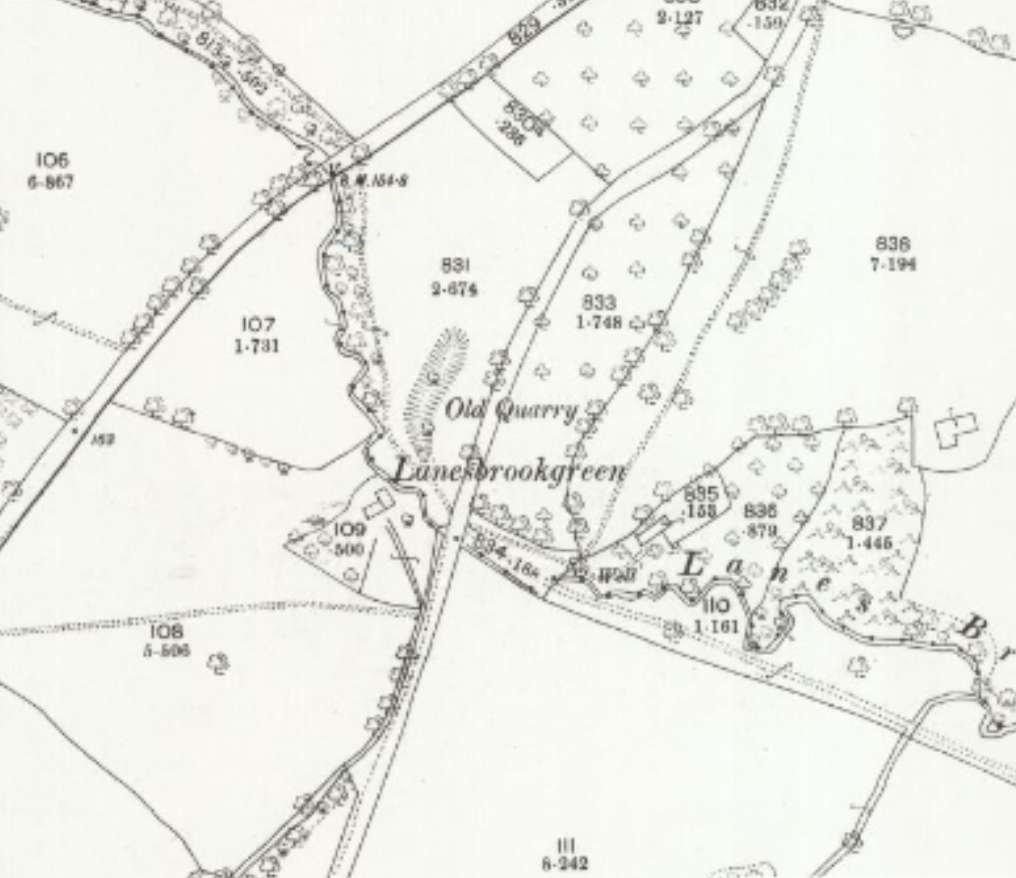
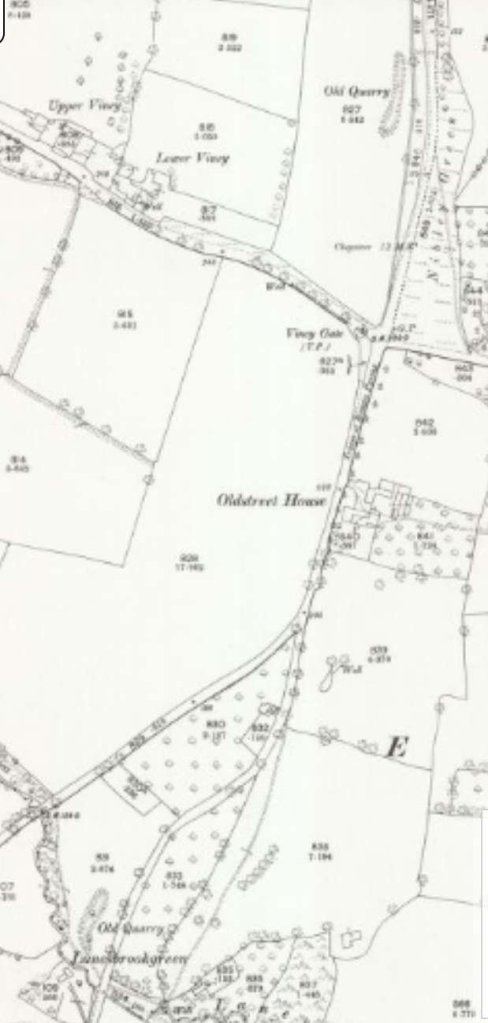
Reading the November 1899 edition of The Railway Magazine, I came across an article about railways and tramways in the Forest of Dean … ‘The Severn & Wye Joint Railway’ by E.A. Clark. [1]
The article from 1899 adds something to the series of posts already made about the Forest and it railways
Clark says that “it was in the year 1809 that the initiative of the Severn and Wye took place. It had long been felt that there was great commercial scope in the Forest of Dean, and in this year Parliament sanctioned the construction of a tram road through the district. The undertaking was incorporated by the name of the Lydney and Lydbrook Railway Company, ‘for the purpose of making a railway or tramway from the River Wye at Lydbrook to the River Severn at Lydney, with various branches to serve the collieries in the Forest of Dean’. The Company finding their undertaking not complete, owing to there not being proper accommodation at Lydney for the export of coal, etc., in the following year (1810) obtained power by an Act of Parliament for the construction of a canal (over one mile in length) and docks or basins at Lydney to communicate with the River Severn, and the name of the Com- pany was changed by the same Act to the Severn and Wye Railway and Canal Company.” [1: p434-435]

Clark goes on to tell us that “the cost of construction of the tramway was nearly £90,000. The tramway was laid with tram plates and worked by horse power until the year 1865, when the first locomotive engines were used. From 1810 to 1868, the concern worked very satisfactorily and good dividends were paid. The Great Western Railway Company had constructed a railway on the broad gauge principle to the Forest at one or two points, and this rendered it necessary for the Severn and Wye in 1868 to lay down a broad gauge railway upon that part of their undertaking which lies between the South Wales Railway (Great Western Railway) at Lydney and Wimberry Slade near to the station now known as Speech House Road. Parliamentary authority was obtained to confirm this and to extend the line from Wimberry Junction to Cinderford, also to construct a very important branch, known as the ‘loop Line’ which runs from a point known as ‘Tufts’ between Lydney and Whitecroft on the main line, passing round the eastern side of the forest with sidings to the various collieries, and meeting the main line again at a point known as Drybrook Road, where there is now a passenger station. The loop line is 6 miles 55 chains.” [1: p435]
Clark continues: “The following year, a further Act empowered the Company to convert the tramway on the Lydbrook section to a railroad, with connection with the Great Western Railway at Stowefield, now known as Lydbrook Junction. In 1872, the tramway to Milkwall was substituted by a railway from the main line at Parkend with an ex-tension to Coleford. In 1875 the ‘Foresters’ (as the natives of the district are called) had their first experience of riding behind a locomotive engine. For it was in 1872 that an Act of Parliament was passed, which sanctioned the Severn and Wye Railway conveying passengers. … The year 1872 was a very important one to the Foresters, for in addition to the powers obtained as above described, the Severn Bridge Railway Company [was] incorporated for the purpose of making a railway from the Severn & Wye Railway and the Great Western Railway at Lydney across the River Severn to Sharpness Docks … and the Midland Railway.” [1: p435-437]
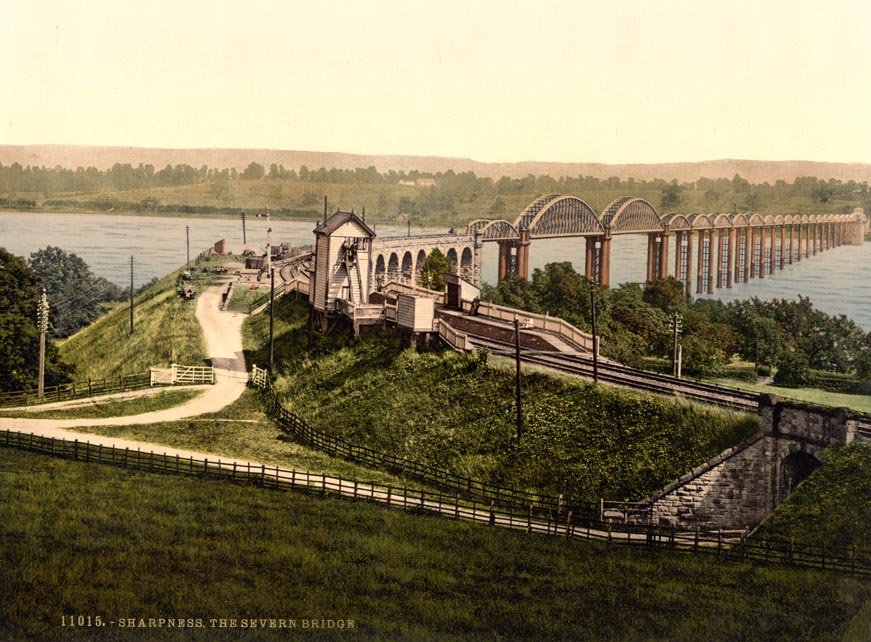
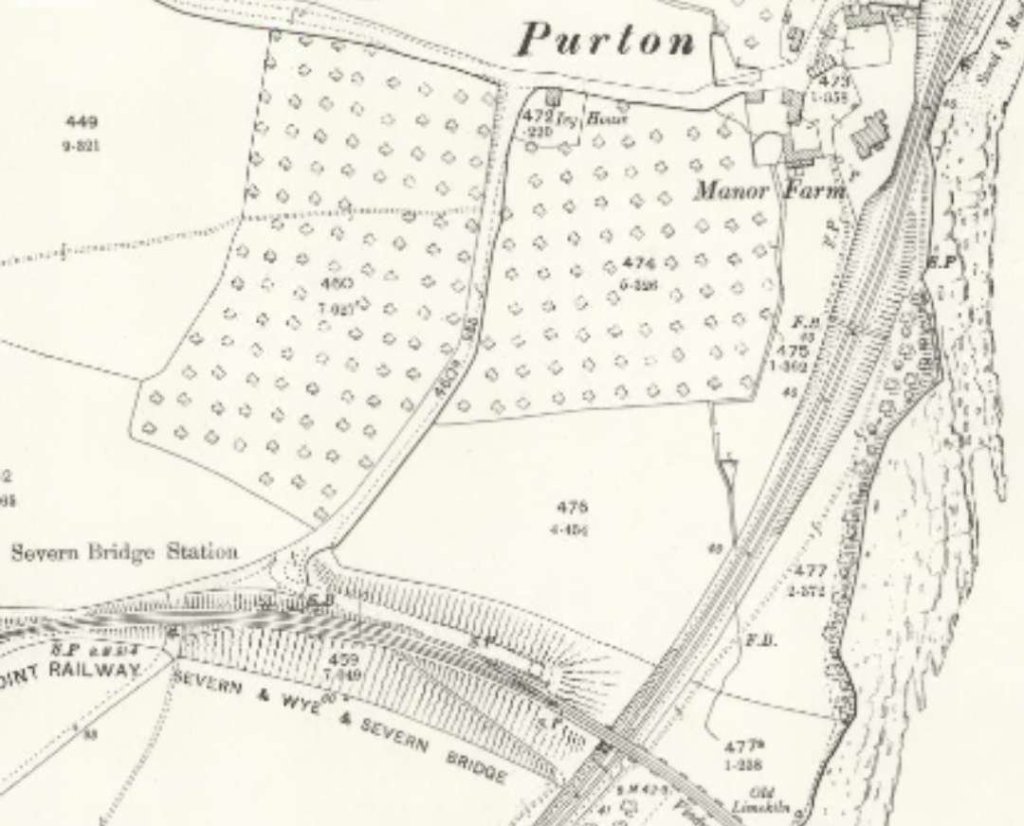
The Severn Bridge Railway
“The Severn Bridge was opened for passenger traffic on 17th October 1879. That year, the Severn & Wye Railway & Canal Company amalgamated with the Severn Bridge Railway, and was incorporated under the name of the ‘Severn and Wye and Severn Bridge Railway Company’. This new departure was not a financial success, and the most important Act had yet to be passed, and that was in 1894, for vesting in the Great Western and Midland Railway Companies the whole undertaking of the Severn and Wye and Severn Bridge Railway Company (at a cost of over £447,000), and by the same Act the Midland Company were empowered to transfer to the joint Committee (fe. the Great Western and Midland Com-panies), their branch known as the ‘Gloucester and Berkeley New Docks Branch’ rom Sharp- ness to Berkeley Road, joining the Midland main line.” [1: p437]
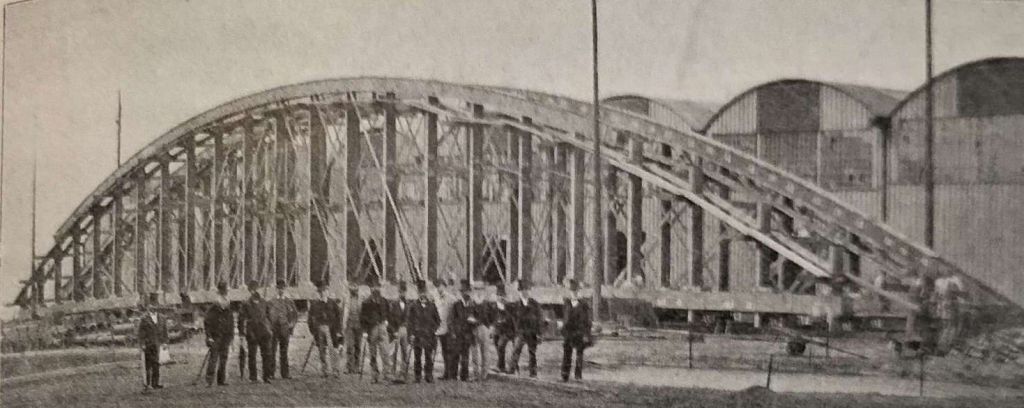
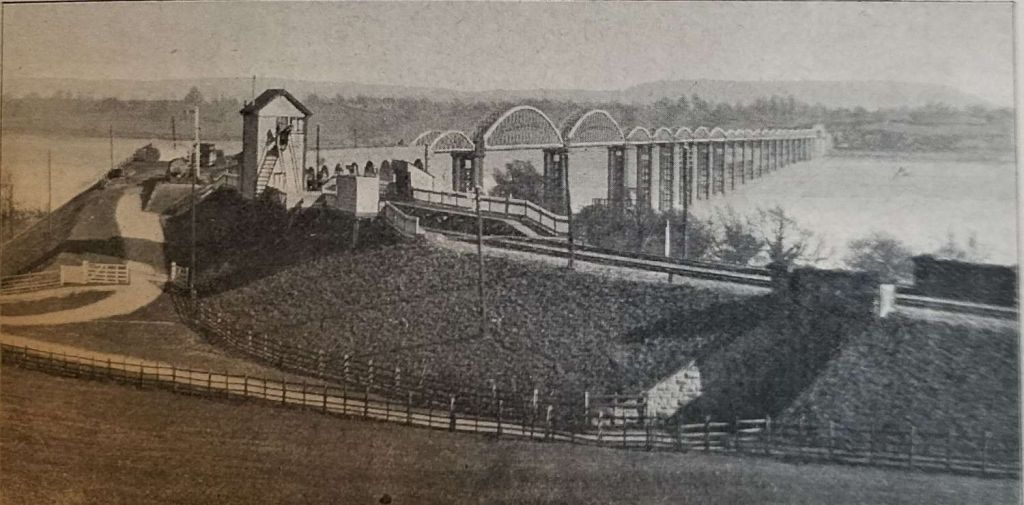


There was much local opposition which meant compromise was necessary. Several conditions were therefore enjoined in the Act, one was the extension of the railway into Cinderford Cinderford, should be extended into the town.
At the time of the writing of the article (November 1899) there were over 40 collieries; two large tin-plate works; several iron ore mines; and numerous quarries. “Total traffic carried by Severn and Wye Railway Company:- 1875, 492,931 tons; 1890, 674,545 tons; 1898, 1,149,631 tons. Of course the great increase in the 1898 figures, as compared with the 1890 figures, [was] due to some extent owing to the traffic from Sharpness not being accounted for in the 1890 figures – the Berkeley Branch then belonged to the Midland Railway. … Passenger traffic [had] doubled during the last two years as compared with ten years [before].” [1: p438-439]
‘Little John’, its Class Mates and Later Locos
Clark provides two pictures of what he says was the first broad gauge locomotive belonging to the Severn & Wye Railway (‘Little John’). The pictures below show it as an 0-4-0WT locomotive. It is possible that, a few years earlier, the Company purchased a single loco on a trial basis. “This locomotive was [possibly] ‘Little Nell’, an 0−4−0 saddle tank, the first locomotive built at the Boyne Engine Works, Leeds, by Manning, Wardle & Company, and delivered to Sheepbridge on 5th February 1859.” [4]
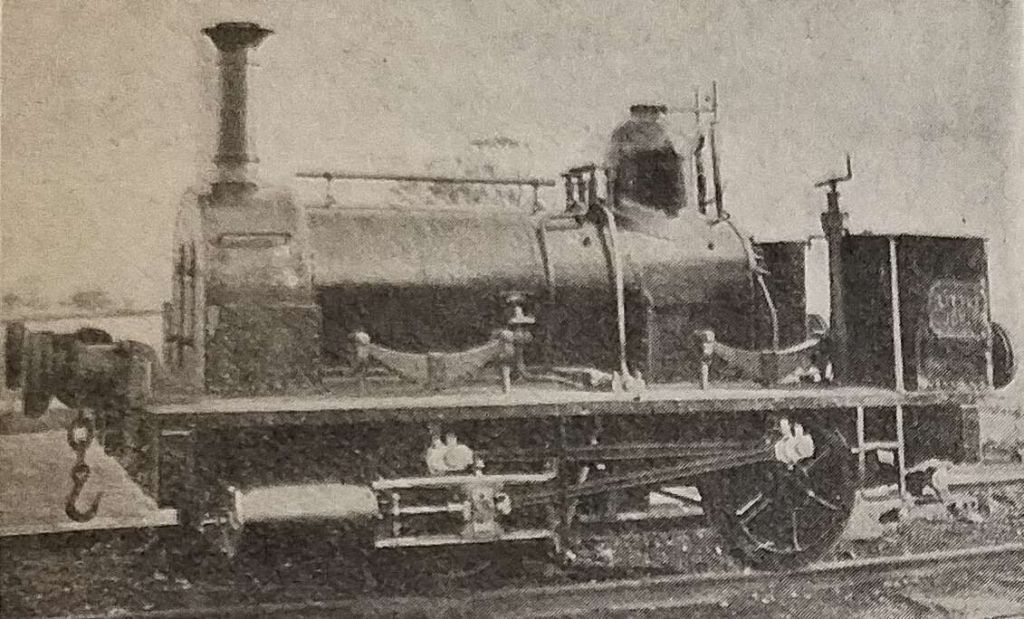
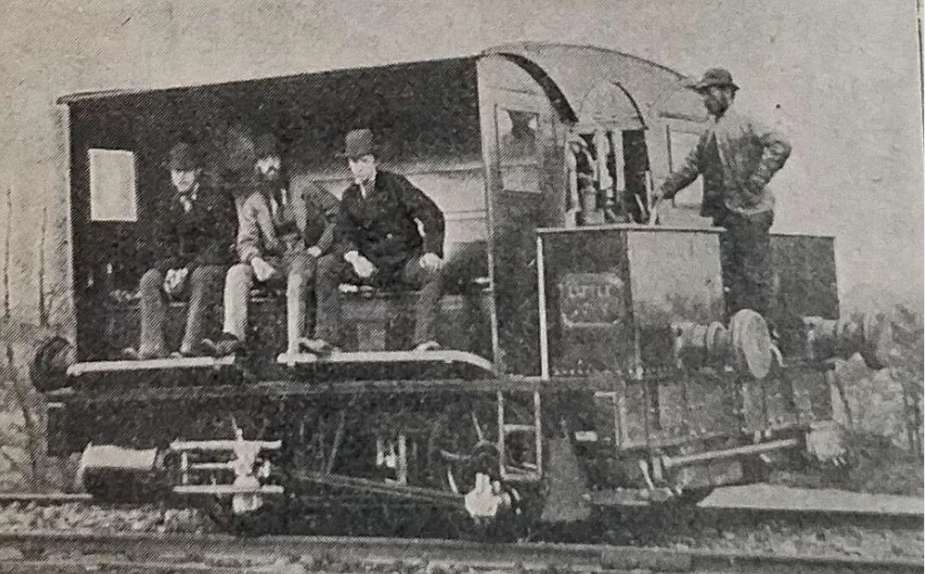
Some notes on the Western Thunder website suggest that ‘Little John’ was one of three locomotives of the same design which were supplied to the Severn & Wye Railway (S&WR). The three locos were ‘Will Scarlet’, ‘Little John’ and ‘Alan-a-Dale’. The writer of those notes assumed that ‘Little John’ and its class-mates were 0-6-0WTs and mentions that the three locos were divided between the GWR and MR when the S&WR was taken into joint ownership in July 1894, ‘Will Scarlet’ (FJ 122) became GWR 1356, ‘Little John’ (FJ 140) became Midland 1123A, and ‘Alan-a-Dale’ (FJ 157) became Great Western 1355. [3]
It seems from the discussion on that website that six 0-6-0T locos were purchased by the S&WR, these were of various designs from different suppliers. Fletcher Jennings supplied locos as shown below.
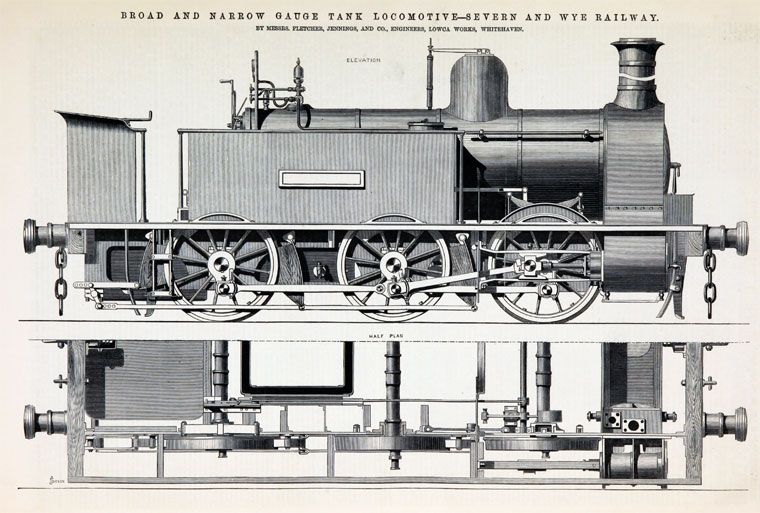
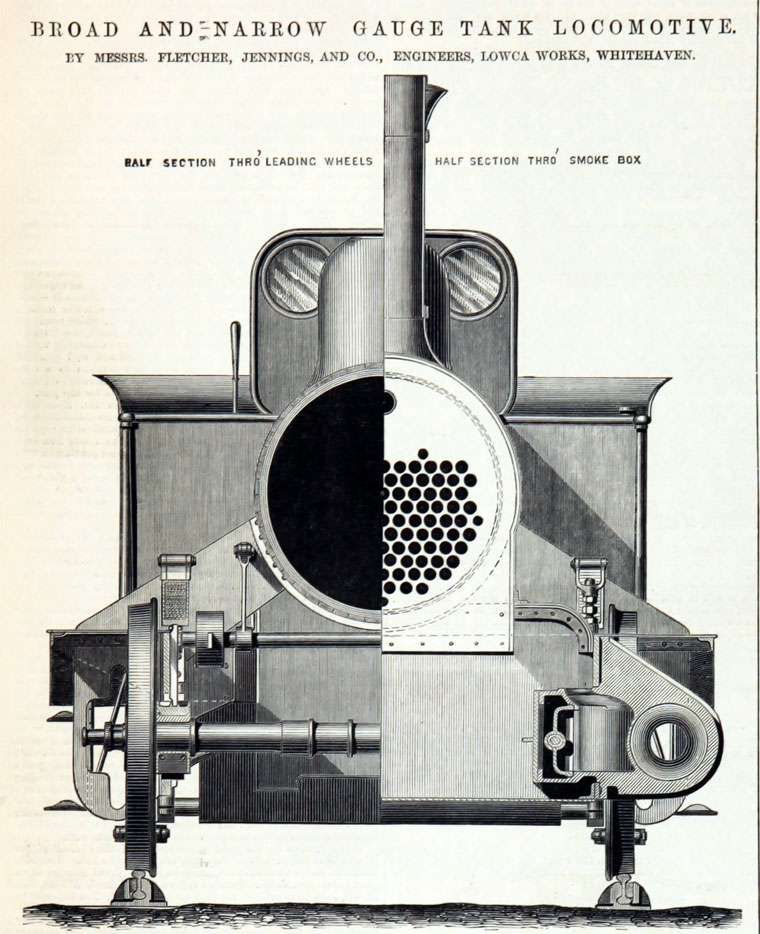
The notes associated with the two images above say: “This somewhat remarkable engine – illustrated above … which is of the broad, or 7ft. gauge, has been specially constructed with a view to its being readily altered if occasion should require to suit the ordinary narrow gauge, and with as little expense as possible. To this end the axles are made, as will be seen by reference to the plan and section, with a third journal and wheel seat in positions proper for 4ft. 8.5 in. gauge, the coal-box, water tanks – except the one under footplate – fire-box, smoke-box, side foot-plates, and other parts are all made to suit the narrow gauge, so that when the alteration, which is anticipated, is required, little more is needed than to shorten the frame stays and buffer beams, remove certain brackets which support the fire-box and smoke-box, place the frames nearer together, shorten the axles, and remove one of each pair of wheels to its inner wheel seat. The cylinders are 14in. diameter, and the stroke is 20in.; the wheels 4ft. diameter, and extreme wheel centres 11ft. 3in.; tires, piston-rods, motion bars, crank pins, &c., are of steel. The fire-box is 3ft. 3in, long, 3ft. 3in. broad, and 4ft. 10in. deep. The boiler barrel, which is telescopic, is 3ft. 6in. mean diameter, and 8ft. Shin. long; the tubes are of brass . long, 2in. outside diameter, and 105 in number. … The total weight with a full supply of water and fuel is 28 tons 6 cwt., and this is distributed as follows:- Leading wheels, 9 tons; driving wheels, 9 tons 1 cwt.; trailing wheels, 10 tons 5 cwt. With partially filled tank and coal-box, the weight is equally distributed on the wheels.” [5]
Another source on ‘rmweb’ provides the following notes which were sourced from the RCTS publication, ‘Locomotives of the GWR – Part 3’. “Severn and Wye loco history is not simple. … They started to get steam engines in 1865, when there was thirty miles of 3’8” tramway. By 1867 they had five locos, and decided to go broad gauge, converting three engines. Two broad gauge engines were obtained, but in 1872 they decided to go to standard gauge, so the five broad gauge engines were converted to standard. The S&WR amalgamated with the Severn Bridge Railway in 1879. A receiver was appointed in 1883, and the railway was taken over jointly by the MR and GWR in 1894. … The first five engines were Fletcher Jennings 1864, with flangeless wheels for the tramroad. 1-4 were 0-4-0WT, 2-3 being the ones that were converted, 1 becoming a canal dredger. 5 was an 0-6-0ST which also went through two gauge conversions. All these had gone by the time of the receivership.
The RCTS publication, ‘The Locomotives of the Great Western Railway Part 3 Absorbed Engines 1854-1921‘, details the following locomotives as well:
- Robin Hood, Fletcher Jennings 1868, MR 1121A – was broad gauge originally.
- Will Scarlet, Fletcher Jennings 1873, GWR 1356.
- Little John, Fletcher Jennings 1874, MR. 1123A.
- Alan-a-Dale, Fletcher Jennings1876 GWR 1355.
- Friar Tuck, Avonside, 0-6-0T 1870 MR 1122A – was broad gauge.
- Maid Marian, Avonside, 0-6-0T 1872 GWR 1357.
- Ranger 0-6-0 (rebuilt ST), GWR 1358 – very complicated history.
- Raven 0-6-0ST, Boulton, 1876 – sold on.
- Wye 0-4-0T, Fletcher Jennings, 1876 GWR 1359.
- Sharpness, Vulcan, 1880 MR. 1124A.
- Severn Bridge, Vulcan, 1880 GWR 1354.
- Sabrina, Vulcan, 1882 MR 1125A.
- Forester, Vulcan, 1886 MR 1126A.
- Gaveller, Vulcan, 1891 GWR 1353.
- Four locos were hired from Boulton’s siding at different times.
The net result of these different notes is that the 0-4-0WT loco shown in Clark’s article in the Railway Magazine is unlikely to be ‘Little John’. ‘Little John’ was probably one of the later 0-6-0T locos and may well not have been a broad gauge engine at any time during its working life.
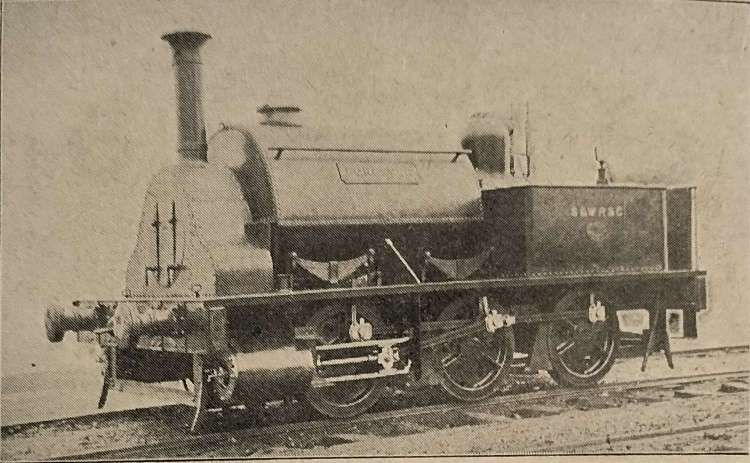
References
- E.A. Clark; The Severn & Wye Joint Railway; in The Railway Magazine, London November 1899, p434-441.
- https://www.gracesguide.co.uk/File:Im1869EnV27-p305.jpg, accessed on 10th September 2024.
- https://www.westernthunder.co.uk/threads/seeking-info-on-severn-wye-rly-fletcher-jennings-engines.5132, accessed on 10th September 2024.
- https://rogerfarnworth.com/2019/02/08/a-first-steam-locomotive-for-the-severn-and-wye-tramway
- https://www.rmweb.co.uk/forums/topic/131654-annies-virtual-pre-grouping-grouping-and-br-layouts-workbench/?do=findComment&com, accessed on 10th September 2024.
- The Locomotives of the Great Western Railway Part 3 Absorbed Engines 1854-1921;
Railway Correspondence and Travel Society, 1976.